![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell Division |
The reproduction and division of cell DNA and the cytoplasm. |
|
|
Mitosis |
The division of the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell. |
|
|
Cytokinesis |
The division of a cell's cytoplasm. |
|
|
Genome |
The cell's genetic information, stored in the DNA. |
|
|
Chromosome |
A molecule of DNA. |
|
|
Chromatin |
The uncondensed mix of DNA and proteins. |
|
|
Centromere |
The area of the chromosomes that holds both sister chromatids together. |
|
|
Kinetochore |
A protein that binds to the centromere of certain chromosomes at the centromere. |
|
|
G1 Phase |
Copies of organelles are made. |
|
|
S phase |
DNA synthesis and replication. |
|
|
G2 Phase |
Proteins and RNA synthesize |
|
|
M phase |
Mitosis: The division of the nucleus and separation of sister chromatids. |
|
|
What stages of the cell cycle occur during interphase? |
G1, S, G2 |
|
|
Is the DNA during interphase condensed or uncondensed? |
Uncondensed. |
|
|
Is the DNA during Mitosis condensed or uncondensed? |
Condensed. |
|
|
Chromatid |
Individual copies of chromosomes. |
|
|
During what parts of the cell cycle does a chromosome have 2 sister chromatids? |
S phase, G2 phase, Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase. |
|
|
Prophase |
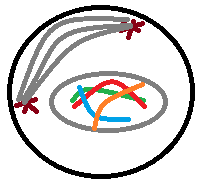
DNA Condenses into visible chromosomes. Centrosomes begin to move apart. |
|
|
Prometaphase |
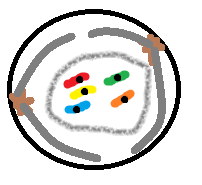
DNA is fully condensed. Nuclear membrane breaks down. Centrosomes move to opposite sides. MT's attach to kinetochores. |
|
|
Metaphase |
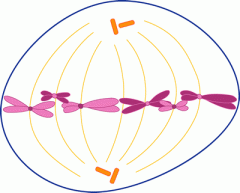
Chromosomes align at metaphase plate. MTs attach to kinetochores. |
|
|
Anaphase |
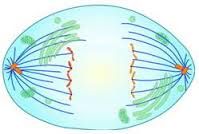
Centrosomes move farther apart. MTs shorten. Chromosomes move apart from each other. |
|
|
Telophase |
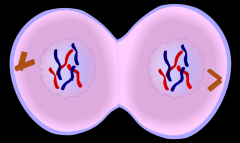
DNA begins to decondense. 2 Nuclear membranes begin to form. Each cell keeps 1 centrosome. MTs dissassemble |
|
|
What is the purpose of mitotic cell division? |
It allows damaged cells to be replaced and it allows the organism to grow. |
|
|
What is the function of the mitotic spindle during mitosis? |
It helps pull the chromosomes apart, and holds cellular structure during mitosis. |
|
|
Why are centrosomes important for the mitotic spindle |
The centrosome organizes the microtubules. |
|
|
What is the mitotic spindle made of? |
Microtubules. |
|
|
how are kinetochore microtubules different from non-kinetochore microtubules? |
Kinetochore microtubules attach to the kinetochores on chromosomes. Non-kinetochore microtubules do not attach to chromosomes and give the cell its shape. |
|
|
How are non-kinetochore microtubules important for separation of sister chromatids? |
They attach to the chromosomes so when the centrosomes move away the chromosomes move apart. |
|
|
how are the non-kinetochore microtubules important for separation of sister chromatids? |
The non-kinetochore microtubules overlap each other and push each other apart, pulling the kinetochore microtubules with them. |
|
|
How does cytokinesis differ in animals and plants? |
In animals, a cleavage furrow forms, and in plant cells, a cell plate forms between both nuclei. |
|
|
What is a cleavage furrow? |
A ring of actin filaments. |
|
|
How are actin filaments involved in cytokinesis in animal cells? |
The active filaments contract, pinching off the cells form each other. |
|
|
What is binary fission? |
Division in half. |
|
|
What types of cells use binary fission? |
Bacteria, archea, and single-celled organisms. |
|
|
What is cancer? |
An uncontrollable growth of cells. |
|
|
What is a carcinogen? |
Something that causes cancer (physical, chemical, or biological). |
|
|
What is the difference between a benign and a malignant tumor? |
A benign tumor stays where it began and can be removed by surgery. A malignant tumor spreads to other tissues. |
|
|
What treatments do doctors use to treat cancer Why? |
Chemotherapy and radiation. To inhibit cell growth. |

