![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Bryophytes |
Non-vascular plants |
|
|
Mosses |
Gametophyte: solely consist of stems and leaves Sporophytes: consist of a seta (stalk) and the capsule |
|
|
Acrocarpous Mosses |
The Sporophytes develop from the branch tips. This taxa typically have an erect growth form. |
|

|
Acrocarpous Moss- Sporphyte tissue |
|
|
Pleurocarpous mosses |
The sporophytes develop from the side brances, typically have prostrate growth (growing closely along ground) |
|

|
Pleurocarpous moss: sporophyte tissue |
|
|
Liverworts |
Sporophytes are very small, FOCUS on the gametophytes |
|
|
Thallose liverworts |
have wide body growth form |
|
|
Leafy liverworts |
Typically have narrow growth form with overlapping scales or leaves. Frullania is the most common taxon here in NW Missouri. |
|
|
Rotifers |
Small zooplankton |
|
|
Microlejunea |
Possibly one of the smallest plants in the world. Minute lobules with rotifers in this taxon as well. |
|
|
Monilophytes |
Ferns: vascular plants |
|
|
Monilophytes (3 clades) |
Equisetopsida- Horsetails Ophioglassales- Botrychium Polypodiales- most diverse |
|
|
Equisetopsida |
Equisetum: green, cylindrical stems with silica and sporangia that look like cones |
|
|
Ophioglassales |
Botrychium: two-parted leaf. One part is sterile (cholorophyllous) and the other part is fertile (achlorophyllous) and covered in sporangia. |
|
|
Polypodiales |
Most diverse clade of monilophytes. |
|
|
Sori |
Sori (singular is sorus) are made of sporangia. They may be circular, linear or other shaped structures. Usually located on underside of leaves. |
|
|
Indusia |
An indusium is a flap of tissue that covers each sorus. |
|
|
Annulus |
Main function is spore dispersal (looks like little brown worms) |
|
|
Three major groups of angiosperms |
Basal Angiosperms- Nymphaceae Monocots- Poaceae (grasses) Eudicots-Carya ovata |
|
|
Monoecious |
Flowers imperfect, the staminate and pistillate flowers borne on same plant. |
|
|
Dioecious |
Flowers imperfect, the staminate and pistillate flowers are borne on different plants. |
|
|
Basal |
Flowering plants which diverged from the lineage leading to most flowering plants. |
|
|
Monocots |
Flowering plants whose seeds typically contain only one embryonic leave or cotyledon. No woody monocots, arborescent, flower parts in 3's, parallel leaf venation. Includes Poaceae and Cyperaceae |
|
|
Eudicots |
2 cotyledons in the seed, flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5. |
|
|
Gymnosperms |
A plant that has seeds unprotected by an ovary or fruit. Gymnosperms include the Coniferophyta.
A pollen grain is a gametophyte (3 cells generally) |
|
|
Vascular plants |
homeohydric: Roots, Xylem (H2O), Phloem (photosynthates) |
|
|
Pokilohydric |
Cannot maintain their own water balance |
|
|
Gymnosperm: Coniferophyta (Conifers) 2 families native to Missouri |
Pinaceae (Pinus) Cupressaceae ( Juniperus virginiana) |
|
|
Adnate |
Different parts fused together |
|
|
Peduncle |
holds the inflorescence, each flower is attached to a short stem called a Pedicel |
|
|
Inflorescence |
The flowering part of a plant, a flower cluster, the arrangement of the flowers on the flowering axis. |
|
|
Infructescense |
(fruiting head) is defined as the ensemble of fruits derived from the ovaries of an inflorescence. It usually retains the size and structure of the inflorescence. |
|
|
Perfect flower |
When it contains both stamens and pistils |
|
|
Imperfect (uni-sexual) |
Contains either stamens or pistils but never both. |
|
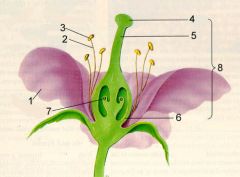
|

|
|
|
Corolla |
all of the petals of a flower |
|
|
Calyx |
All of the sepals |
|
|
Perianth |
All of the sepals and petals |
|
|
Gynoecium |
All of the Pistils |
|
|
Androecium |
All of the stamens |
|
|
Connate |
Fusion of like parts, as the fusion of staminal filaments into a tube |
|
|
Adnate |
Fusion of unlike parts, as the stamens to the corolla |
|
|
Anemophilous |
Wind pollinated; producing wind borne pollen Puts energy towards pollen not towards pistils and stamens |
|
|
Resource Allocation |
dependent on type of pollination |
|
|
Entomophilus |
Insect pollinated Plants tend to have strong fragrance, bright colors, or nectar. Nectar guides, distinctive color patterns |
|
|
Catkin= Ament |
an inflorescence consisting of a dense spike or raceme of apetalous, unisexual flowers. |
|
|
Bract |
A leaflike structure at the base of a flower or inflorescence |
|
|
Asteraceae |
Sunflower: Most abundant family in the world Consist of ray flowers and disk flowers |
|
|
Peduncle |
stalk of the inflorescence |
|
|
What is the most abundant and diverse group of non-vascular plants that occur in Missouri |
Mosses |

