![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List the macrominerals (measured in % of diet) |
Ca, P, Mg, K, Na, Cl, S |
|
|
List the microminerals (measured in g) |
B, Co, Cu, F, Fe, I, Mn, Mo, Se, Zn |
|
|
What are the functions of Ca |
In bones for structure, muscle contraction, nerve transmission, blood coagulation, milk production, etc. |
|
|
How is Ca maintained in the body in correct amounts? |
- Reabsorption (kidneys to blood) - Resorption (release from bones) - Absorption (from intestine to blood) |
|
|
What hormones regulate Ca and what do they do? |
PHT: reabsorption from parathyroid Calcitonin: lay down more in bone, calcification, from thyroid |
|
|
What happens when Ca is low in the blood? |
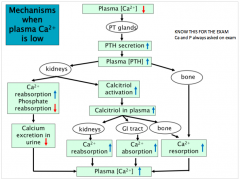
|
|
|
What is the difference between primary and secondary deficiencies? |
Primary: not ingesting enough Secondary: reduced digestion or absorbtion |
|
|
What are symptoms of Ca deficiency in young and old animals? |
Young animals: - Rickets (secondary to Ca:P) big head in horses - Poor bone development Adults - stiffness, difficulty calving, reduced condition - Osteomalacia (soft bones) - Milk fever (excitable, down, coma) |
|
|
What causes eclampsia in bitches? |
High Ca during gestation (tremors, aggression, etc.) |
|
|
How is P absorbed, available, and excreted? |
Absorbed normally (too much stops Ca absorption) Available in phytic acid in plants (birds and pigs cannot use, require phytase enzyme) Excreted in urine |
|
|
What does P do? |
- ATP - Skeleton - DNA - Membranes |
|
|
What are the signs of P deficiency? |
- Pica (eat dirt) - Rickets |
|
|
What are signs of P toxicity? |
- diarrhea - pigs suffocate because soft ribs - low Ca issues |
|
|
What are signs of Mg deficiency? |
Puppies: depression, lethargy Pigs: crooked legs, twitching, tetany, death General calcification necrosis Cattle: Grass tetany (bad ratios) |
|
|
What are the roles of Sodium? |
- pH - Fluid volume - Water reabsorption in kidney |
|
|
What are the roles of potassium? |
- Intracellular cation - Insulin release - Nerves - Muscle function |
|
|
What are the roles of Cl? |
- primary anion - pH - HCl in stomach |
|
|
What are the signs of salt toxicity? |
Pigs: stilted walk into walls, convulsions Chickens: Ascites |
|
|
what are the roles of S? |
- Cartilegde - Acid base - in feathers and wool |
|
|
What are the signs of S toxicity and deficiency? |
Both RARE Toxicity: H2S can be bad Deficiency: poor wool growth and weight gain |

