![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
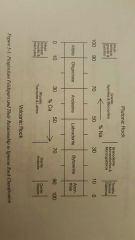
Bowen's Reaction Series |

|
|
|
Mineral |
A naturally occurring, inorganic, solid, with an internal crystal structure. |
|
|
Mineral Assemblage |
The minerals that compose a rock, including the different kinds and their relative abundance. |
|
|
Cation |
A positively charged ion |
|
|
Anion |
A negatively charged ion. |
|
|
Polymorphism |
Characteristic of a mineral to exist in more than one crystal form. |
|
|
Silicates |
Compounds whose crystal structure contain SiO4 tetrahedra, either isolated or joined to form groups, rings, single or double chains, sheets, or 3D frameworks. |
|
|
Twinning |
The intergrowth of two or more crystals in a symmetrical way. |
|
|
Zeolite |
Group of hydroaluminosilicate minerals that are analogous in composition to Feldspars. Chief metals are Na, Ca, and K. Occur in basalt cavities, saline lake and deep sea sediments, and volcanic tuff. Use: Water softeners, desiccants. |
|
|
Solid-Solution Series |
A series of minerals of identical crystal structure that contain a mixture of 2 or more elements over a range of proportions. |
|
|
Feldspars |
The most widespread mineral group in Earth's crust, comprising 60% of crust.
Rock-forming mineral.
Orthoclase, Microcline, Sanidine KAlSi3O8
Plagioclase (Na, Ca, Ba, Rb, Sr, Fe)Al (Alx, Si(1-x))2O8 |
|
|
Zoning |
Variation of composition of a crystal, characteristic of Feldspars, Zircon, Monazite, etc. Interior or center is formed by high temperature phase, whereas exterior or margin is formed by low temperature phase. |
|
|
Cleavage |
The breaking of minerals along planes of weakness that are parallel to the crystal faces. |
|
|
Luster |
Property of light reflection from the mineral surface. |
|
|
Specific Gravity |
The ratio of the mineral density to the density of the same volume of water. |
|
|
Nesosilicates |
SiO4 Silicate crystal characterized by isolated tetrahedra.
Includes: -Olivine Group minerals -Garnet Group minerals -Phenacite Group minerals -Zircon -Al2SiO5 Group minerals -Topaz -Staurolite -Chondrodite Group minerals -Datolite -Sphene |
|
|
Sorosilicates |
Si2O7 Silicate crystal characterized by isolated double or linked tetrahedra. Includes: -Epidote Group minerals -Hemimorphite -Lawsonite |
|
|
Cyclosilicate |
SiO3 Silicate crystal characterized by rings of tetrahedra. Includes: -Beryl Group minerals -Tourmaline -Chrysocolla -Axinite |
|
|
Inosilicates |
SiO3 Silicate crystal characterized by single and double chains of tetrahedra. Single-chains include: -Pyroxene Group minerals -Pyroxenoid Group minerals Double-chains include: -Amphibole Group minerals |
|
|
Phyllosilicates |
Si2O5 Silicate crystal characterized by sheets of tetrahedra. Includes: -Micas -Clays -Serpentines |
|
|
Tectosilicates |
SiO2. and Si3O8. Silicate crystal characterized by frameworks of tetrahedra. Includes: -Zeolite Group minerals -SiO2 Group minerals -Feldspar Group minerals -Feldspathoid Group minerals -Scapolite Group minerals |
|
|
Gypsum |
CaSO4•2H2O |
|
|
Quartz |
SiO2 |
|
|
Calcite, Aragonite |
CaCO3 |
|
|
Dolomite |
CaMg(CO3)2 |
|
|
Apatite |
Ca3 (PO4)2 |
|
|
Mohs Hardness Scale |
10 - Diamond 9 - Corundum 8 - Topaz 7 - Quartz 6.5 - Steel knife 6 - Orthoclase Feldspar 5.5 - Pocket knife 5 - Apatite 4 - Fluorite 3.5 - Copper penny 3 - Calcite 2.5 - Fingernail 2 - Gypsum 1 - Talc |
|
|
Plagioclase Feldspar |
Group of Feldspar minerals that form a solid solution series between Albite (Na-pure end member) and Anorthite (Ca-pure end member).
Degree of substitution varies with pressure and temperature. |
|
|
Feldspathoid minerals |
Group of relatively rare rock-forming minerals consisting of aluminosilicates or Na-, K-, Ca- silicates, with too little silica to form feldspar. Never found in the same rock with quartz. Includes: -Leucine -Nepheline -Sodalite -Lazurite -Melilite |
|
|
Albite |
Feldspar mineral composed of 90-100% Na. Crystallizes from igneous melt at lower temperatures (~1120°C - ~1260°C). |
|
|
Anorthite |
Feldspar mineral composed of 90-100% Ca. High crystallization temperature (~1550°C - ~1570°C). |
|
|
Phase Diagram |
Diagram describing the fractional crystallization of minerals that exhibit solid solution series (e.g., Plagioclase feldspar).
Y-axis = Temperature Upper curve = Liquidus Upper X-axis = Composition of the liquid by weight % of one end member ---In Plagioclase, typically use wt% Ca Lower X-axis = Composition of the solid Lower curve = Solidus
|
|
|
Asbestos |

Naturally occuring fibrous silicate minerals found in serpentines and amphiboles. Common forms: Found in serpentines: -Chrysotile Found in amphiboles: -Amosite -Crocidolite -Tremolite -Actinolite -Anthophyllite |

