![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Normal bone is called?
|
Lamellar
|
|
|
Immature and pathologic bone is called?
|
Woven
|
|
|
Lamellar bone can be these 2 types
|
Cortical and Cancellous
|
|
|
Describe Woven bone compared to Lamellar
|
Immature and pathologic, more random with more osteocytes than lamellar bone, increased turnover, weaker, and more flexible than lamellar bone.
Lamellar bone is stress oriented; voven is not |
|
|
This type of bone makes up 80% of the skeleton
|
Cortical
|
|
|
Cortical bone is composed of tightly packed __1__ or __2__ connected by __3__ containing arterioles, venules, capillaries, nerves, and possibly lymphatic channels. __4__ lie b/w Osteons. __5__ frequently connect lamellae but do not cross __6__
|
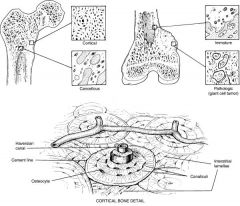
1. osteons
2. Haversion systems 3. Haversion or Volkmann's canals 4. Interstitial lamellae 5. Fibrils 6. Cement lines |
|
|
This is where bone resorption has stopped and new bone formation has begun; also define the outer border of an osteon
|
Cement line
|
|
|
This provides nutrition to cortical bone
|
Intraosseous circulation (canals and canaliculi = cell processes of osteocytes)
|
|
|
Compare Cortical bone to Cancellous bone
-turnover rate -Young modulus -resistance to torsion and bending |
-slower
-higher -higher |
|
|
Osteoblasts form bone by generating this type of matrix
|
organic, nonmineralized
|
|
|
Osteoblasts are derived from these cells
|
undifferentiated mesenchymal cells
|
|
|
More differentiated, metabolically active osteoblasts line this part of bone
|
bone surfaces
|
|
|
Where do less active osteoblasts lie?
|
"resting regions" or are entrapped cells and maintain the ionic milieu of bone
|
|
|
What activates entrapped osteoblasts?
|
Disruption of the active-lining cell layer of osteoblasts
|

