![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Economics is |
the science or study of decision making |
|
|
Thomas Malthus |
-Studied the principle of population -Technology prevents our trade off of population to resources |
|
|
What is 2 ways in which society responds to stuff? |
1. Positive Feedback Loops -self reinforcing loop 2. Negative Feedback Loops -self correcting loop |
|
|
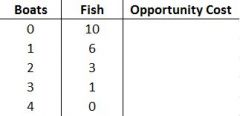
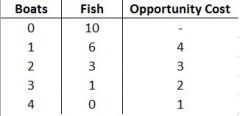
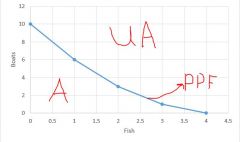
Production Probabilities Model |
All of the combinations of two goods/services a country (or organization) can produce |
|
|
|
|
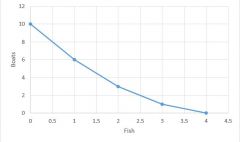
Label: Unattainables Attainables PPF |
|
|
|
Opportunity Cost is... |
what you give up in order to get something |
|
|
General Trend for Production Prob Model |
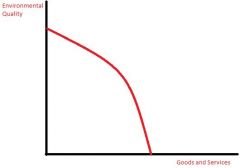
|
|
|
Fig 2.1: Economic System & the Environment |
|
|
|
A closed system is... |
no inputs or out puts (there are not true examples) |
|
|
An open system is... |
inputs and outputs present (Figure 2.1 is a great example!) |
|
|
Positive Economics is... |
"What is" |
|
|
Normative Economics is... |
"What should be" |
|
|
Cost Benefit Analysis |
-If costs are greater than benefit --> don't do it -If costs are less than benefit --> DO IT |
|
|
Anthropocentric |
In terms of the human experience |
|
|
Deep Ecology |
Every part of nature has intrinsic value (Think of the blue people in Avatar) |
|
|
Present Value (PV) |
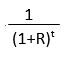
r= discount/interest rate t= time (in years) |
|
|
Net Present Value (NPV) |
All of the PVs added up |
|
|
Future Value (FV) |
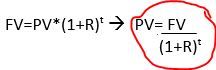
|
|
|
NPV is the same equation as FV, but what does NPV mean... |
How much we are willing to pay today for a future payment (money given to us or gained in the future) OR How much we value a future outcome today |
|
|
What wording should you use to answer... r=10% t=1 PV= 95.45 |
"We would (should) pay $95.45 for $105 one year from now at a discount (interest) rate of 10%" |
|
|
If rate increases, NPV... |
Decreases |
|
|
If rate decreases, NPV... |
Increases |
|
|
If time increases, NPV... |
Decreases |
|
|
If time decreases, NPV... |
Increases |
|
|
Demand is... |
a line or schedule of number of goods/services consumers are willing to purchase at each given price |
|
|
Typical Demand Curve |
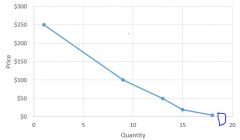
|
|

|
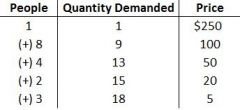
|
|
|
A General Supply Curve looks like... |
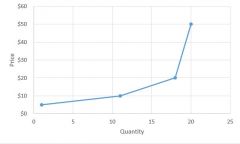
|
|
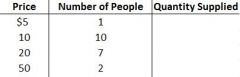
|
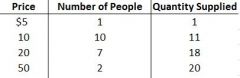
|
|
|
Supply is... |
A line or schedule of the number of goods or services produces are willing and able to sell at each given price |
|
|
Supply and Demand Model |
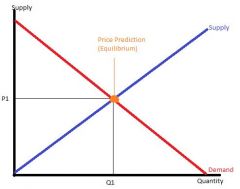
|
|
|
What direction does Demand line move if there is a DECREASE? Price change? Quantity Change? |
left Decrease Decrease |
|
|
What direction does Demand line move if there is an INCREASE Price change? Quantity Change? |
Right Increase Increase |
|
|
What direction does Supply move if there is an INCREASE Price change? Quantity Change? |
Right Decrease Increase |
|
|
What direction does Supply move if there is a DECREASE Price change? Quantity Change? |
Left Increase Decrease |
|
|
Perfectly Inelastic means... |
Quantity will not change if price changes Steeper slope (forms the I) |
|
|
Perfectly Elastic means... |
If price changes a small amount, Quantity changes a large amount No slope (forms the E) |
|
|
The Equimarginal Principle |
-how to minimize cost of production given a set level of output -how to maximize the benefit of buying goods and services with a set level of $ (remember homework technique) |
|
|
Ex ante |
before it occurs |
|
|
Ex post |
after if occurs |
|
|
Anthropogenic (Anthropocentric) |
how it relates to humans |
|
|
Environmental amenity |
the use of the part of the env that has a (anthropogenic) market value |
|
|
Stock |
the current value of an env amentity |
|
|
Flow |
the value of a stream of env amenities (Forest is a stock and flow) |
|
|
Risk Assessment |
identify the magnitude of the env risk -evaluates substance to determine if it is harmful to a population (What concentration of CO2 will cause harm?) |
|
|
Risk Management |
evaluates the desirability of various options to control env risks |
|
|
4 Steps of Risk Assessment |
1. Hazard Identification- exposure causes harm? 2. Dose-response assessment- how much/long? 3. Exposure Assessment-pathways, intensity? 4. Risk Characterization-estimation of effect |
|
|
Total Willingness to Pay (TWP) |
how much would one pay for an env amenity |
|
|
3 Parts of TWP |
1. Use Value- current value of use 2. Option Value- possibility of use in future 3. Nonuse Value- value placed, but will never be used |

