![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the primary metric units used to measure microbes?
|
Micrometer and Nanometer
|
|
|
Meter symbol?
|
m
|
|
|
Decimeter symbol?
|
dm (1/10 of a meter)
|
|
|
Centimeter Symbol?
|
cm(1/100 of a meter)
|
|
|
Millimeter Symbol?
|
mm(1/1000 of a meter)
|
|
|
Micrometer Symbol?
And use? |
um(1/1000 of a mm)
Use to measure cells |
|
|
Nanometer Symbol?
And use? |
nm(1/1000 of a um)
Use to measure organelles and viruses |
|
|
Definition of Microscopy?
|
Use of light or electrons to magnify objects
|
|
|
The Microscopy principles
|
wavelength of radiation
contrast of the specimen resolving power of the scope magnification of an image |
|
|
What is red's nm?
What is violet's? |
650 red
400 violet |
|
|
Which side of the color spectrum is longer?
Which is shorter? |
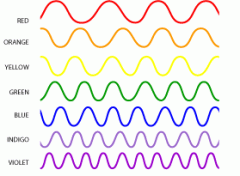
Longer->ROYGBIV<-Shorter
|
|
|
Do smaller or longer wavelengths enhance Microscopy?
|
Shorter
|
|
|
Modern microscopes use what kind of wavelengths? (include color)
|
Short
Blue light or electron beams |
|
|
What is magnification?
|
The apparent increase in size of an object
|
|
|
When does magnification occur?
|
When radiation refracts (alters/bends) as it passes through a lens
|
|
|
Why do curved glass lenses work?
|
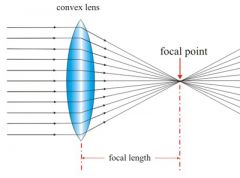
They bend light because they are optically dense as compared to the air.
|
|
|
As light enters a lens what does it do?
|
It slows down and bends.
|
|
|
When does a lens refract light rays the most?
|
When it passes through the periphery as compared to the center
|
|
|
Where does the lens focus light rays?
|
The focal point
|
|
|
What do light rays do as they pass through the focal point?
|
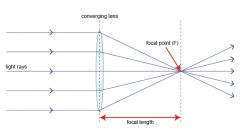
The light rays spread apart to form an enlarged image
|
|
|
What effects the degree to which an image is enlarged?
|
The lens thickness,
lens curvature, and the speed of light as it passes through the substance |
|
|
What does the clarity of a magnified object depend on?
|
Resolution and contrast
|
|
|
Definition of resolution.
|
Resolution is the ability to distinguish between objects that are close together
|
|
|
What is the resolution of a modern microscope?
|
0.2 um
|
|
|
What does resolution distance depend on?
|
wavelength of the electromagnetic rays
and numerical aperture of the lens |
|
|
Definition of aperture.
|
Aperture refers to the ability to gather light.
|
|
|
What is the Resolution distance formula?
|
0.61 x wavelength
resolution distance = --------------------------- numerical aperture |
|
|
Definition of contrast.
|
Differences in intensity between 2 objects, or between object and background
|
|
|
When does light increase contrast?
|
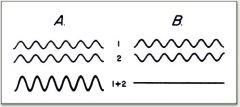
When all the light waves' crests and troughs are aligned.
Called phase. |
|
|
What is a bright-field?
|
When the background/field is illuminated
|
|
|
What is a dark-field?
|
The background is dark, therefore, the specimen appears light
|
|
|
Definition of phase.
|
uses of alignment of light waves to achieve contrast between specimen and background
|
|
|
Definition of fluorescent.
|
uses ultraviolet light to cause specimens to radiate visible light or fluorescence
|
|
|
Definition of confocal.
|
uses lasers to illuminate fluorescent chemicals in a thin plane of a specimen
|
|
|
What is a simple bright-field microscope like?
|
A magnifying glass
|
|
|
How do you calculate the magnification in a compound microscope?
|
in series (ocular + objective)
10x ocular X 4x scanning = 40x magnification |
|
|
What are the compound objectives called?
|
scanning lens 4x
low-power lens 10x high/dry lens 40x oil immersion lens 100x |
|
|
What does the oil immersion lens increase?
|
magnification
and resolution |
|
|
The oil between the slide and objective allows the lens to do what?
|
Increases the ability to capture light, does not refract, oil increases the numerical aperture
|
|
|
Why are the objective lenses important?
|
They bend light rays
|
|
|
How is total magnification of a compound microscope calculated?
|
By multiplying the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the ocular lens.
Ex. 10x ocular lens X 100x oil immersion objective = 1000x magnification |
|
|
What is the limit of useful magnification for light microscopes?
|
2000x
resolution is restricted by wavelength of visible light |
|
|
What is phase used for?
|
Examining living specimens that would be altered by staining or attachment to a slide.
|
|
|
What's differential interference contrast?
|
use prisms to split light and create more contrast
|
|
|
What's the range of wavelengths in electrons?
|
0.01nm and 0.001nm
HIGHER RESOLVING POWER |
|
|
When resolving power is high so is....
|
magnification
|
|
|
With electron microscopy, what is the range of magnification?
|
10,000x to 100,000x
|
|
|
Electron microscopes are good to use when you need to see what?
|
Details of viruses, bacteria, organelles, molecules, and large atoms
|
|
|
What are the two types of electron microscopes?
|
Transmission electron
and Scanning electron |
|
|
What does an SEM microscope use?
|
Magnetic fields within a vacuum tube to manipulate a beam of electrons.
|
|
|
What can be seen with a SEM?
|
whole specimens, sectioning not required
ONLY DEAD ORGANISMS only magnifies external surface |
|
|
How does a TEM work?
|
Generates a beam of electrons that produces an image on a fluorescent screen
|
|
|
What must the column be?
|
It must be a vacuum and the specimen must be very thin
|
|
|
With a TEM you can see what?
|
Only DEAD ORGANISMS
must be dehydrated and sectioned |

