![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Utility |
satisfaction, or pleasure, that people receive from consuming a good or service |
|
|
Total utility |
amount of satisfaction received from all the units of a good and service consumed |
|
|
Marginal utility |
change in total utility from one additional unit of a good or service |
|
|
Law of diminishing marginal utility |
extra satisfaction of a good or service declines as people consume more in a given period |
|
|
Consumer equilibrium |
total utility cannot increase by spending more of a given budget on one good or spending less on another |
|
|
Income effect |
change in quantity demanded of a good or service caused by a change in real income |
|
|
Substitution effect |
change in quantity demanded of a good or service caused by the change in its price relative to its substitutes |
|
|
Indifference curve |
different combinations of two goods that provide the same satisfaction or total utility to a consumer |
|
|
Marginal rate of substitution |
consumer is willing to substitute one good for another good without a change in total utility |
|
|
Indifference map |
selection of indifference curves with each curve representing a different level of satisfaction or total utility |
|
|
Budget line |
line that represents all combinations of two goods that a consumer can purchase with a fixed amount of money given the price of each good |
|
|
Indifference curve |
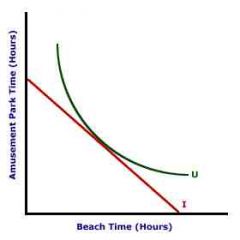
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Budget line |
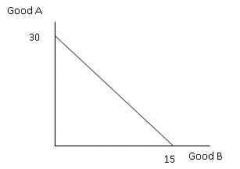
Back (Definition) |

