![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sexuality of fungal spores
|
Asexual (mostly)
|
|
|
Which fungal infections are transmitted by inhalation of asexual spores?
|
1. Coccidioidomycosis 2. Histoplasmosis
|
|
|
What are conidia?
|
Asexual fungal spores
|
|
|
What disease states does Candida albicans cause?
|
1. Thrush esophagitis in immunocompromised patients (neonates, steroids, diabetes, AIDS) 2. endocarditis in IV drug users 3. vaginitis post-antibiotic use 4. diaper rash 5. Disseminated candidiasis to any organ 6. Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis
|
|
|
Treatment for Candida Albicans infection
|
Superficial: Nystatin - Serious systemic: Amphotericin B
|
|
|
Histologic appearance of Candida Albicans
|
Budding yeast with pseudohyphae in culture at 20 degrees celsius - Germ tube formation at 37 degrees celsius
|
|
|
Candida albicans: Germ tube formation at 37 degrees celsius
|
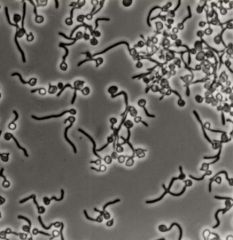
What is this?
|
|
|
Candida albicans: Budding yeast with pseudohyphae in culture at 20 degrees celsius
|
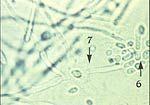
What is this?
|
|
|
Which fungus causes thrush in immunocompromised
|
Candida albicans
|
|
|
Which fungus causes vulvovaginitis?
|
Candida albicans (high pH, diabetes, use of antibiotics)
|
|
|
Which fungus is endemic to Southwestern US?
|
Coccidioidomycosis
|
|
|
Which fungus is endemic to Mississippi and Ohio river valleys
|
Histoplasmosis
|
|
|
What fungus is this area known for: Southern Ohio
|
Histoplasmosis
|
|
|
What fungus is this area known for: Southern Illinois
|
Histoplasmosis
|
|
|
What fungus is this area known for: Missouri
|
Histoplasmosis
|
|
|
What fungus is this area known for: Kentucky
|
Histoplasmosis
|
|
|
What fungus is this area known for: Tennessee
|
Histoplasmosis
|
|
|
What fungus is this area known for: Arkansas
|
Histoplasmosis
|
|
|
What fungus is this area known for: Southern California
|
Coccidiomycosis
|
|
|
What fungus is this area known for: Southern Arizona
|
Coccidiomycosis
|
|
|
What fungus is this area known for: Mississippi river valley
|
Histoplasmosis (also Blastomycosis)
|
|
|
What fungus is this area known for: Ohio river valley
|
Histoplasmosis (also Blastomycosis)
|
|
|
What fungus is this area known for: Southwestern US
|
Coccidiomycosis
|
|
|
What fungus is this area known for: Rural Latin America
|
Paracoccidioidomycosis
|
|
|
What fungus is this area known for: Wisconsin
|
Blastomycosis
|
|
|
What fungus is this area known for: Minnesota
|
Blastomycosis
|
|
|
Spherule filled with endospores in coccidioidomycosis
|
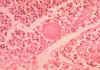
What is this?
|
|
|
Characterize histoplasmosis histologically
|
Tiny yeast inside macrophages. Thin cell wall with no true capsule.
|
|
|
What is the vector for histoplasmosis?
|
Bird or bat droppings
|
|
|
What do bird and bat droppings carry?
|
Histoplasmosis
|
|
|
histoplasmosis showing intracellular organisms in bone marrow macrophages
|
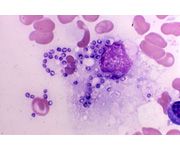
What is this?
|
|
|
Paracoccidioidomycosis (captain's wheel appearance)
|

What is this?
|
|
|
Blastomycosis (Big, Broad-Based Budding)
|
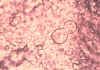
What is this?
|
|
|
What characterizes dimorphic fungi?
|
Mold in soil (lower temperature) and yeast in tissue (body temperature) - Mnemonic: Cold is mold, heat is yeast
|
|
|
List the dimorphic systemic fungi
|
Histoplasmosis, Blastomycosis, and Paracoccidioidomycosis (but not coccidioidomycosis which is a spherule in tissue)
|
|
|
Treatment for coccidiomycosis
|
Local: Fluconazole or ketoconazole - Systemic: Amphotericin B
|
|
|
Treatment for paracoccidiomycosis
|
Local: Fluconazole or ketoconazole - Systemic: Amphotericin B
|
|
|
Treatment for Histoplasmosis
|
Local: Fluconazole or ketoconazole - Systemic: Amphotericin B
|
|
|
Treatment for Blastomycosis
|
Local: Fluconazole or ketoconazole - Systemic: Amphotericin B
|
|
|
What is cultured on Sabouraud's agar?
|
Fungi (specifically dimorphic fungi)
|
|
|
What disease state does Malassezia furfur cause?
|
Tinea versicolor: Hypopigmented skin lesions which occur in hot humid weather.
|
|
|
Treatment for Tinea versicolor
|
Topical miconazole or selenium sulfide (Selsun)
|
|
|
What resembles spaghetti and meatballs histologically?
|
combination of mycelium strands and numerous spores of Malassezia furfur in KOH prep
|
|
|
What disease state does Cladosporium werneckii cause?
|

Tinea nigra: Infection of keratinized layer of skin. Appears as brownish spot.
|
|
|
What causes Tinea versicolor?
|
Malassezia furfur
|
|
|
What causes Tinea nigra?
|
Cladosporium werneckii
|
|
|
Treatment for Tinea nigra
|
topical salicylic acid
|
|
|
What are the common dermatophytes and what do they cause?
|
Microsporum, Trichophyton, and Epidermophyton cause all the tineas except for versicolor and nigra
|
|
|
What causes Tinea corporis?
|
Dermatophytes (such as Microsporum, Trichophyton, and Epidermophyton)
|
|
|
What causes Tinea cruris?
|
Dermatophytes (such as Microsporum, Trichophyton, and Epidermophyton)
|
|
|
What causes Tinea pedis?
|
Dermatophytes (such as Microsporum, Trichophyton, and Epidermophyton)
|
|
|
What causes Tinea capitis?
|
Dermatophytes (such as Microsporum, Trichophyton, and Epidermophyton)
|
|
|
What causes Tinea unguium?
|
AKA Tinea onychomycosis. Dermatophytes (such as Microsporum, Trichophyton, and Epidermophyton)
|
|
|
What causes Tinea onychomycosis?
|
AKA Tinea unguium. Dermatophytes (such as Microsporum, Trichophyton, and Epidermophyton)
|
|
|
How does Tinea corporis present?
|
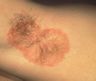
Ring shape with a red raised border on the body.
|
|
|
How does Tinea cruris present?
|
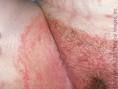
AKA jock itch - Itchy red patches on groin and scrotum
|
|
|
How does Tinea pedis present?
|
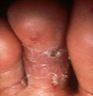
AKA athlete's foot - Begins between toes and causes cracking and peeling of the skin.
|
|
|
How does Tinea unguium/onychomycosis present?
|
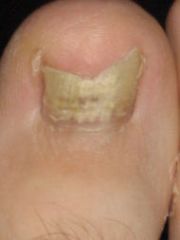
Nails are thickened discolored and brittle
|
|
|
Lab diagnosis of dermatophyte infection
|
1. Dissolve skin scrapings in KOH, which digests the keratin. Microscopic examination reveals branched hyphae. 2. Direct examination of skin with Wood's light (UV light at 365 nm wavelength) will fuoresce green if Microsporum.
|
|
|
Treatment for dermatophyte infection
|
1. Topical imidazoles 2. Oral griseofulvin (Tinea capitus and tinea unguium)
|
|
|
What causes a fungus ball?
|
Aspergillus
|
|
|
What disease states does Aspergillus cause?
|
1. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis 2. Lung cavity aspergilloma 3. Invasive aspergillosis
|
|
|
Histologic appearance of aspergillus
|

Mold (not dimorphic) with septate hyphae that branch at a V-shaped (45 degree) angle). Rare fruiting bodies.
|
|
|
Aspergillus (septate hyphae branching at 45 degrees with fruiting bodies)
|

What is this?
|
|
|
What disease states does cryptococcus neoformans cause?
|
1. Cryptococcal meningitis 2. Cryptococcosis
|
|
|
Histologic appearance of cryptococcus neoformans
|
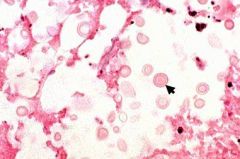
5-10 micrometer yeasts with wide capsular halo. Narrow based unequal budding.
|
|
|
How is cryptococcus neoformans stained?
|
1. India ink 2. Latex agglutination test for polysaccharide capsular antigen
|
|
|
Where is cryptococcus neoformans found?
|
Soil and pigeon droppings.
|
|
|
What is the histologic appearance of Mucor?
|
Just like Rhizopus - Mold with irregular, broad, empty looking, nonseptate hyphae branching at wide angles (over 90 degrees)
|
|
|
What is the histologic appearance of Rhizopus?
|
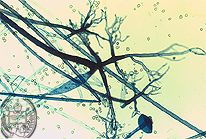
Just like Mucor - Mold with irregular, broad, empty looking, nonseptate hyphae branching at wide angles (over 90 degrees)
|
|
|
Which patients are likely to have Mucor/Rhizopus?
|
1. Ketoacidotic diabetics 2. Leukemics
|
|
|
Where in the body does Mucor/Rhizopus proliferate?
|
1. Walls of blood vessels, causing infarction of distal tissue 2. Rhinocerebral frontal lobe abscesses
|
|
|
What is pneumocystis jirovecii?
|
Formerly pneumocystis carinii. Yeast (originally classified as a protozoan)
|
|
|
What disease states does Pneumocystis cause?
|
Diffuse interstital pneumonia - Immunosuppresion predisposes to disease.
Most infections are asymptomatic. |
|
|
How is pneumocystis diagnosed?
|
Lung biopsy or lavage. Methenamine silver stain of lung tissue.
|
|
|
Treatment for pneumocystis
|
Combination of TMP-SMX, Pentamidine, and Dapsone.
|
|
|
Characterization of sporotrix schenckii
|
Dimorphic fungus that lives on vegetation.
|
|
|
Presentation of sporotrichosis
|
1. Traumatically introduced into the skin by a thorn 2. Local pustule/ulcer with nodules along draining lymphatics (ascending lymphangitis) 3. Little systemic illness
|
|
|
What is rose gardener's disease?
|
Sporotrichosis
|
|
|
Histologic appearance of sporotrix schenckii
|
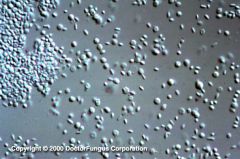
Cigar-shaped yeast visible in pus with unequal budding
|
|
|
Treatment for sporotrichosis
|
Itraconazole or potassium iodide
|
|
|
Type of bug: Candida albicans
|
Dimorphic fungus, cutaneous OR systemic infection
|
|
|
Type of bug: Coccidioides immitis
|
Monomorphic fungus, systemic infection
|
|
|
Type of bug: Histoplasma capsulatum
|
Dimorphic fungus, systemic infection
|
|
|
Type of bug: Blastomyces dermatidis
|
Dimorphic fungus, systemic infection
|
|
|
Type of bug: Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
|
Dimorphic fungus, systemic infection
|
|
|
Type of bug: Malassezia furfur
|
Monomorphic fungus, superficial infection
|
|
|
Type of bug: Cladosporium werneckii
|
Monomorphic fungus, superficial infection
|
|
|
Type of bug: Microsporum
|
Monomorphic fungus, cutaneous infection
|
|
|
Type of bug: Trichophyton
|
Monomorphic fungus, cutaneous infection
|
|
|
Type of bug: Epidermophyton
|
Monomorphic fungus, cutaneous infection
|
|
|
Type of bug: Aspergillus fumigatus
|
Monomorphic fungus, opportunistic systemic infection
|
|
|
Type of bug: Cryptococcus neoformans
|
Monomorphic fungus, opportunistic systemic infection
|
|
|
Type of bug: Mucor
|
Monomorphic fungus, opportunistic systemic infection
|
|
|
Type of bug: Rhizopus
|
Monomorphic fungus, opportunistic systemic infection
|
|
|
Type of bug: Pneumocystis jirovecii
|
Monomorphic fungus, opportunistic systemic infection
|
|
|
Type of bug: Sporothrix schenckii
|
Dimorphic fungus, subcutaneous infection with some lymphatic spread
|

