![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the common characteristics of Systemic Mycoses? |
- All can cause pneumonia and disseminate |
|
|
How do Systemic Mycoses compare to TB? |
- Both have granuloma formation |
|
|
What are the systemic mycoses? |
- Histoplasmosis |
|
|
Which mycoses is endemic to the Mississippi and Ohio River valleys? What does it cause? Pathologic features? |
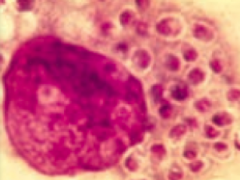
Histoplasmosis |
|
|
Which mycoses is endemic to the states east of the Mississippi River and Central America? What does it cause? Pathologic features? |
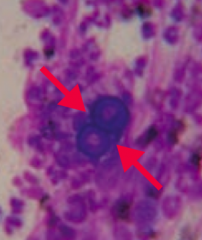
Blastomycosis |
|
|
Which mycoses is endemic to the SW US and California? What does it cause? Pathologic features? |
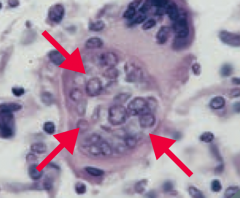
Coccidioidomycosis |
|
|
Which mycoses is endemic to Latin America? What does it cause? Pathologic features? |

Paracoccidioidomycosis |
|
|
What is the relative size of the systemic mycoses to RBCs? |
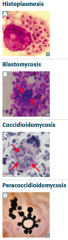
- Histoplasmosis: smaller than RBC |
|
|
What is the location in which the systemic mycoses are endemic? |
- Histoplasmosis: Mississippi and Ohio River valleys |
|
|
What are the cutaneous mycoses? |
- Tinea versicolor |
|
|
What is the cause of Tinea Versicolor? When is it more common? |
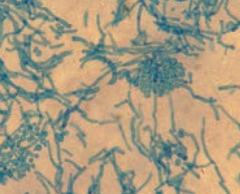
Malassezia Furfur - "spaghetti and meatball" appearance |
|
|
What does Malassezia Furfur cause? |
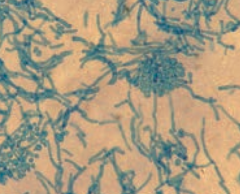
- Degradation of lipids produces acids that damage melanocytes |
|
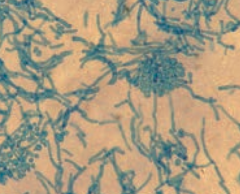
How do you treat Tinea Versicolor (Malassezia Furfur)? |
Topical miconazole, selenium sulfide (Selsun) |
|
|
What causes the other Tineae (eg, pedis, cruris, corporis, capitis, unguium)? Types of lesions? |
- Caused by Dermatophytes (Microsporum, Trichophyton, and Epidermophyton) |
|
|
What are the Dermatophytes that cause Tineae? Appearance? |
- Microsporum |
|
|
What are the opportunistic fungal infections? |
- Candida albicans |
|
|
Which fungus causes oral and esophageal thrush in immunocompromised (neonates, steroids, diabetes, AIDS), vulvovaginitis (diabetes, use of antibiotics), diaper rash, endocarditis in IV drug users, disseminated infection (to any organ), and chronic mucocutaneous infection? |
Candida albicans (alba = white) |
|
|
What forms does Candida albicans have? |
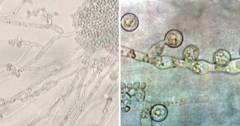
Dimorphic yeast |
|
|
What kind of Candida albicans infection occurs in patients who are immunocompromised (neonates, steroids, diabetes, AIDS)? Treatment? |
Oral and esophageal thrush - treat with fluconazole or caspofungin |
|
|
What kind of Candida albicans infection occurs in patients who have diabetes or are using antibiotics? Treatment? |
Vulvovaginitis - treat with topical azole |
|
|
What kind of Candida albicans infection occurs in infants? |
Diaper rash |
|
|
What kind of Candida albicans infection occurs in patients who are IV drug users? |
Endocarditis |
|
|
How do you treat systemic Candida albicans infections? |
Fluconazole, Amphotericin B, OR Caspofungin |
|
|
Which fungus can cause invasive infection, allergic bronchopulmonary infection, and masses of fungus in lung cavities? |
Aspergillus fumigatus |
|
|
Characteristics of Aspergillus fumigatus? Appearance? |
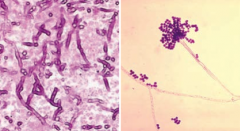
- Septate hyphae branch at 45° angle ("think A for Acute Angles in Aspergillus") |
|
|
Who is most likely to get invasive Aspergillus fumigatus infection? |
Immunocompromised and those with chronic granulomatous disease |
|
|
Which form of Aspergillus fumigatus infection is associated with asthma and cystic fibrosis? What can it cause? |
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) |
|
|
What form of Aspergillus fumigatus infection is more common after TB infection? |
Aspergillomas in lung cavities |
|
|
What can some species of Aspergillus fumigatus produce? Implications? |
Some species produce AFLATOXINS which are associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
|
|
Which fungus is found in soil and pigeon droppings and can cause meningitis? |
Cryptococcus neoformans |
|
|
Characteristics of Cryptococcus neoformans? |
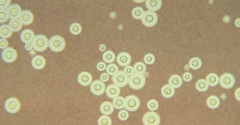
- Heavily encapsulated yeast with unequal budding |
|
|
What disease is caused by Cryptococcus neoformans infection? How is it acquired? |
- Cryptococcal meningitis |
|
|
Which fungus causes "soap bubble" lesions in the brain? |
Cryptococcus neoformans |
|
|
Which fungus causes disease mainly in ketoacidotic diabetic and leukemic patients? |
Mucor and Rhizopus species → Mucormycosis |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of Mucor and Rhizopus species? |
- Fungi proliferate in blood vessel walls when there is excess ketone and glucose |
|
|
What are the symptoms of infection by Mucor and Rhizopus species? |
- Headache |
|
|
How do you treat Mucor and Rhizopus species infections? |
Amphotericin B |
|
|
What is the appearance of Mucor species? |
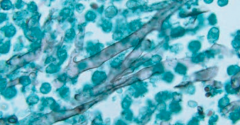
Irregular, broad, non-septate hyphae branching at wide angles |
|
|
Which fungus is usually asymptomatic but in immunosuppressed (eg, AIDS) causes a diffuse interstitial pneumonia? |
Pneumocystis jirovecii |
|
|
Who is affected by Pneumocystis jirovecii infection? How? |
- Inhaled |
|
|
What are the characteristics of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)? Diagnosis? |
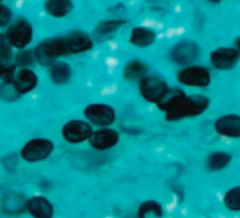
- Diffuse interstitial pneumonia |
|
|
What is the appearance of Pneumocystis jirovecii? |
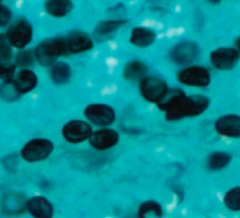
Yeast: |
|
|
How do you treat a Pneumocystis jirovecii infection? |
- TMP-SMX |
|
|
When should you do prophylactic treatment for Pneumocystis jirovecii? Regimen? |
- Start prophylaxis when CD4 counts drop <200 cells/mm3 in HIV patients |
|
|
Which fungus typically presents in gardeners and causes a local pustule or ulcer with nodules along draining lymphatic (ascending lymphangitis) |
Sporothrix schenckii |
|
|
What is the appearance and location of Sporothrix schenckii? |
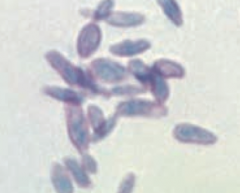
Dimorphic, cigar-shaped budding yeast that lives on vegetation |
|
|
How do you get infected with Sporothrix schenckii? Disease? |
- Spores are usually traumatically introduced into the skin, typically by a thorn ("rose gardener's disease") |
|
|
How do you treat Sporothrix schenckii? |
Itraconazole or POTassium iodide |

