![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Sterilization and Give an example?
|
Is the destruction of all microbes (vegetative cells and endospores) and viruses
Ex. Boiling=kills vegetative cells and most endospores Autoclave=kills all vegetative cells and endospores (for autoclave=the sterilizing agent is the moist heat not the pressure) Dry Heat Filtration Radiation |
|
|
Define disinfection and Give an example?
|
refers to the reduction of pathogens in an inanimate object/surface
3 Catergories: High level=kills everything intermediate level=kills everything but endospores Low level=kills veg bact., fungi/protozoa and some viruses |
|
|
What are high-level disinfectants used for?
|
-used for critical objects that cannot be autoclaved (endoscopes/plastics)
method involves treatment with moist heat and liquids such as gluteraldehyde/hydrogen peroxide/PAA etc... |
|
|
What are intermediate-level disinfectants used for?
|
-used on surfaces/objects not expected to be contaminated with endospores (semicritcal objects=endoscopes, laryngoscopes, vaginal specula)
ex. of agents= alcohol, iodophors, phenolics |
|
|
What are the low-level disinfectants used for?
|
Used to treat non-critical instruments and devices (BP cuffs, stethtoscopes, EEG electrodes)
Agents= Quatenary ammonium compounds |
|
|
Define Antisepsis and give an example?
|
refers to the reduction of pathogen content in an animate object/surface
Ex. Alcohol=active against everything except endospore (degerming) Iodophors=slight toxic to skin than -OH Chlorhexidine=broad spectrum against bact/mycobact Parachlorometaxylenol |
|
|
Define an Aseptic environment?
|
Is an environment free of pathogens
|
|
|
Define Degerming?
|
Is the removal of microbes from a surface
(Alcohol is a degerming agent) |
|
|
Define sanitization?
|
Is the reduction of pathogen is public places or objects used by the public
|
|
|
Define pasteurization?
|
Its not a sterilization but the ability to eliminate pathogens and reduce the amount of spoilage organism
Kills pathogens such as: Mycobacteria bovis and Coxiella burnetii |
|
|
Define stasis/static?
|
Inhibition of metabolism or growth
|
|
|
Define cide/cidal?
|
the ability to kill or prevent metabolism or multiplication
|
|
|
Describe the process of autoclaving moist heat method and its importance. Explain why materials to be autoclaved should not be wrapped in aluminum foil or other impervious material.
|
Involves pressure being applied to a boiling water and preventing the steam from escaping
As temperature increase=pressure increases Do not wrap object in foil paper or impervious material because it prevent access of STEAM |
|
|
Describe two methods for determining the efficacy of sterilization using the autoclave. Explain how
one method is more reliable than the other. State the microbial species used for the more reliable determination. |
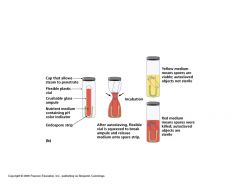
Two methods:
1. Heat sensitive chemical indicator that changes color when the sterile temperature has been reached 2. Endospore test ampule The heat indicator is less reliable b/c it only tells you when the ideal temperature has been reached and not an indicator that all objects are sterile. The ampule is more effective b/c a test for growth is usually assessed after the procedure. (Microbe used here= Geobacillus stearothermophilus) |
|
|
Describe the use of dry heat for sterilization and a method for determining the efficacy of sterilization using dry heat. State the microbial species used for this determination. What precautions should be taken when using this method?
|
Used for products (powder, oils) that cannot be treated with moist heat
1hr at 171Cel 2hr at 160Cel 3hr at 121Cel Effectiveness is tested using Bacillus subtilis (relatively resistant to killing by dry air compared to Geobacillus St.) Precaution: At the end of the heating period, turn off oven but do not open oven until it cools to room temperature...!!! |
|
|
List the microbial order of resistance to disinfectants and explain the basis for their rankings?
|
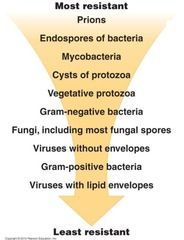
Nature of site to be treated (cannot use steam on skin)
and natural relative sterility of that site (e.g., mucous membrane or skin vs. a body cavity or injection through the skin) • Degree of susceptibility of microbes involved (more on this -- it's very important, see the next slide) • Environmental conditions that pertain (pH, temperature, presence of organic materials) ▫ it's easier to sterilize a clean object than a physically dirty one |
|
|
Define the three levels of disinfection and give examples of each.
|
3 Catergories:
High level=kills everything intermediate level=kills everything but endospores Low level=kills veg bact., fungi/protozoa and some viruses |
|
|
List the factors that affect disinfectant/antiseptic activity.
|
-treatments are most effective when it object/surface is cleaned off (dirt alters its effectiveness)
|
|
|
Use of Aldehydes and drawbacks?
(Formaldehyde, Gluteraldehyde) |
-Used both as a sterilant or high-level disinfectant
low conc= bacteriostatic high conc= kills everything (enhanced killing effect by mixing with -OH) Drawbacks Formalin=too much of an irritant for general use, carcinogenic (gas form) Gluteraldehyde= inactivated by organic matter and expensive |
|
|
Use of Hydrogen Peroxide and drawbacks?
|
-kills most bact. @ conc of 3-6% in water
-kills everything @ conc of 10-25% -can be used as a gas vapor to sterilize rooms -Used on plastic implants, surgical lenses, prosthesis Drawbacks: Cannot be used on body cells b/c they have catalase which inactivates it |
|
|
Use of Iodine compounds (Iodophors) and drawbacks?
|
-Used as skin disinfectants and are sporocidal at high concentration
-in concentrations used as an antisepsis, they are usually not sporocidal Drawbacks: they tend to discolor the skin |
|
|
Use of Chlorine compounds and drawbacks?
|
-used as disinfectants in water
-its the active agent in bleach (NaOCl) Drawbacks: inactivated by organic material |
|
|
Use of Phenolic compounds and drawbacks?
|
-are used as intermediate-low disinfectants (lysol)
-effective in the presence of organic matter -active against organisms including mycobact but are not sporocidal Drawbacks: Have a disagreeable odor |
|
|
Use of Alcohol compounds and drawbacks?
|
-used as an intermediate-level disinfectant
-denatures ptns and disrupts cell memb Drawbacks: dissipates rapidly (can also be advantageous) |
|
|
Use of Quatenary ammonium compounds and drawbacks?
|
-Used as low-level disinfectants
-colorless, tasteless and harmless to humans Drawbacks: Pseudomonas a. can grow and metabolize in them |
|
|
Use of Paracetic acid (PAA) and drawbacks?
|
-is a gas vapor that is used as a sterilant
-used in decontaminating animal rooms as a dry fog |
|
|
Use of Ethylene Oxide and drawbacks?
|
-used as a gas vapor sterilant (heart valves)
-kills by alkylation of essential chemical groups Drawbacks: -extremely toxic and explosive |
|
|
Define Phenol coefficent?
|
its used to determine the effectiveness of a disinfectant by comparison to that of a phenol (carbolic acid)
If Phe. coeff. >1 = more effective than a Phenol |
|
|
Describe the Use-Dilution test?
|
-dry test used to test organisms in a metal cylinder
-cylinder is placed in diff dilutions of disinfectants -removed from the disinfectants, rinsed and placed in a broth to see if growth occurs (most effective agent prevents growth at greater dilutions) - |
|
|
Describe the In-Use test?
|
-takes swabs from equipment and test for growth before and after disinfectants
|
|
|
Describe the Kirby-Bauer method (Disk-Diffusion Method) of comparing disinfectants and antiseptics.
|
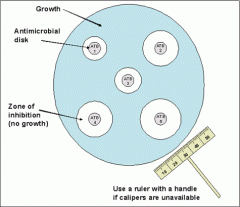
A paper disk is moistened with agent to test and placed
on the surface of a freshly inoculated lawn of test bacteria on a Mueller-Hinton agar plate. After overnight growth, measure the diameter of the zone of growth inhibition and compare it to defined standards. |

