![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Five parts of compound light microscope |
Ocular- eye piece- 10x Revolving nose piece w objectives Stage control levers Fine and course adjustment knobs Iris diaphragm lever |
|
|
Objectives |
Scanning 5x Low power 10x High power 45 x Oil immersion 100x |
|
|
Total magnification of objectives |
Scanning 50x Low power 100x High power 450x Oil immersion 1000 x |
|
|
Par focal definition |
If the microscope is in focus one 1 objective it should stay in focus for all objectives |
|
|
Three bacterial morphologies |
Cocci, bacilli, spiral |
|
|
Bacterial arrangements |
Strepto- chains Staphylo- grape like clusters Diplo -2 Tetras-4 Sarcinae-cube like pack of 8 |
|
|
Study the genus and species names of a given bacteria and be able to define them |
Staphylococcus aureus means cluster of cocci that are gold in color |
|
|
Study the genus and species names of a given bacteria and be able to define them |
Staphylococcus aureus means cluster of cocci that are gold in color |
|
|
Why do we use pure culture in the lab |
If you're studying one specific bacteria you don't want other types of bacteria invading your culture. If you're looking at a disease you need a pure culture to determine what best antibiotic could fight that organism. |
|
|
Why do we use a septic techniques in the lab |
Done to protect ourselves. To protect the environment. To not contaminate the bacteria with other bacteria. To maintain a pure culture |
|
|
Aseptic definition |
Absence of organisms that may cause contamination or disease. Sterile means completely devoid of life |
|
|
What would we use for a septic a transfer from a salad? |
And inoculating needle |
|
|
What would we use for a septic a transfer from a liquid |
An. Inoculating loop |
|
|
Know the difference between a graduated pipettes and a pipette pump |
graduated pipettes is marked for measurements. The pump is the blue thing used to suck the liquid up |
|
|
TSB |
Trypticase soy broth |
|
|
Turbid |
Means it's cloudy with bacteria Estimate 10 million bacterial cells per ml |
|
|
Alcohol a flaming a tech nique |
Apply alcohol on the forceps, run it through the flame horizontally, keep alcohol away from the burner, let it burn off and repeat three times |
|
|
Algae, kingdom Protista |
Genera, spirogyra, ulothrix, oedogonium, chlamydomonas, volvox |
|
|
Spirigrya |

Filamentous green algae commonly found in water. Chloroplasts are spirally arranged. |
|
|
Ulothrix |

Filamentous algae found in fresh and marine water. Thrive in low temps and spring and winter |
|
|
Oedegonium |

Filamentous green algae found in freshwater |
|
|
Chlamydomonas |
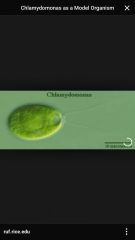
Fresh and marine water algae, unicellular, two flagella |
|
|
Volvox |
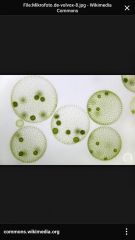
Freshwater Algae found and ponds and ditches. Adult colonies and daughter colonies |
|
|
Algae, kingdom Protista |
Genus to know Spirigrya, ulothrix, oedogonium, chlamydomonas, volvox |
|
|
Algae |
Kingdom Protista Single or multicellular organisms w cell wall. Live in water, undergo photosynthesis |
|
|
Brownian movement |
Just moving randomly |
|
|
True motility |
Moves towards something or in one direction |
|
|
Phototaxis |
Positive or negative, moving towards or away from light |
|
|
Chemotaxis |
Moving towards or away from chemicals |
|
|
Aerotaxis |
Moving towards or away from oxygen |
|
|
Cyanobacteria, monera |
Prokaryotic photosynthetic Know oscillatoria Anabaena Nostoc Gleocapsa |
|
|
Oscillatoria |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Oscillatoria |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Anabaena |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Nostoc |
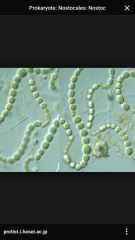
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Nostoc |
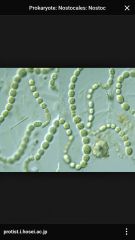
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Gleocapsa |
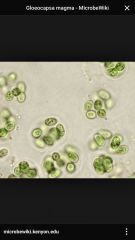
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Hetercysts |
Nitrogen fixation |
|
|
Gas vacuole |
Natural flotation |
|
|
Pathogenic Bacteria to know |
Treponema Pallidum-syphilis Neisseria Gonnorheae- gonorrhea Clostridium sp- tetani, botulinum, perfingens, difficle (Tetanus, botulism, gangrene, pseudomembranous colitis |
|
|
syphilis |
Treponema Pallidum Primary, secondary, tertiary, and neurosyphilis |
|
|
Botulism |
Clostridium Botulinum food poisoning. muscle paralysis Toxin |
|
|
Tetanus |
Clostridium tetani tetanospasm is neurotoxin lockjaw muscle spasms from rusty nail |
|
|
gas gangrene |
clostridium perfringens damages tissues, blood cells, and blood vessels need for amputation
|
|
|
c diff (pseudomembranous colitis) Antibiotic associated diarrhea |
clostridium diffcile |
|
|
spore locations to know |
central terminal terminal with an enlarged sporangium |
|
|
heterocysts |
are within chain for nitrogen fixation |
|
|
gas vacuoles |
are at end of chain, for flotation |
|
|
Protozoans -protista |
single celled eukaryotic organisms no cell wall most are motile
|
|
|
Chemoheterotropjs |
obtain energy and carbon from organic matter |
|
|
phagocytosis |
cell eating |
|
|
pinocytosis |
cell drinking |
|
|
trophozoit |
free living, feeding, motile form of protozoan |
|
|
cyst |
dormant resistant form of protozoan found during periods of environmental stress |
|
|
4 taxonomic groups based on motility |
sarcodina- amoeboid motion. sends out psuedopods (false foot) Mastogophora- travel by flagella (long slender fillamentous strands) Ciliata-move by cilia (short and numerous strands) Sporozoa-non motile |
|
|
protozoans to know |
Stentor-tornado shaped, whirl of cilia around the top, king of the ciliates. Chaos chaos- ameoba- sarcodina Euglena- long slender-each have flagella-only green one paramecium- long, oblong, ciliated, move fast blepharisma- similar to paramecium but with a bie taken out, its mouth actinosepharium- sun animal. spikes are pseudopods. used to catch prey. Sarcodina |
|
|
pathogenic protozoans to know and disease they cause Giardia Lamblia |
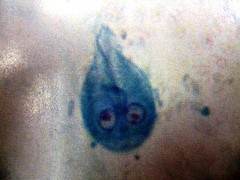
giardiasis, water born diarrhea, cell shaped like light bulb w 2 nuclei 4 pairs of flagella |
|
|
Entameoba histolytica |
amoebic dysentary, lysis of tissues, bloody diarrhea, |
|
|
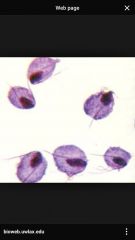
trichamonas vaginalis |
vaginitis turnip shaped cell w large nucleus and 2 flagella |
|
|
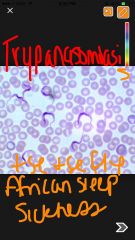
trypansoma gambiensa |
long protozoans with flagella vector is the tse tse fly causes trypansomiasis african sleeping sickness |
|
|
plasmodium vivox |
malaria lives inside rbcs looks like a diamond ring vector-mosquito |
|
|
bacterial are ________ charged |
negatively |
|
|
principle of staining |
unlike charges attract and like charges repel. would use a basic stain for bacteria since it is positively charged |
|
|
simple stain |
crystal violet or methylane blue rinse with water can identify morphology and arrangement |
|
|
gram stain |
hans christian gram most important in bacteriology gram + has thick peptidoglycan cell wall gram - has thin peptidoglycan cell wall |
|
|
process of gram staining |
crystal violet grams iodine is mordant alcohol for 1 sec and then 3 secs safranin gram postive is purple gram negative is red |
|
|
acid fast stain |
used for genus mycobacterium bc they have wax and lipid in cell wall (mycolic acid) |
|
|
chromophore |
the ionic component of a dye that imparts color to the cell can be positive or negative bacterial stains are positively charged to attract to negatively charged bacteria |
|
|
two basic smple dyes we use |
crystal violet and methylane blue |
|
|
simple stains identify? |
morphology and arrangement |
|
|
differential stains? |
gram stain acid fast stain |
|
|
mycobacterium and nocardia genera are |
acid fast |
|
|
acid fast can help diagnose? |
tb and leprosy |
|
|
acid fast cell walls contain |
lipoidal mycolic acid |
|
|
spore forming bacteria? |
clostridium and bacillus |
|
|
reagents used in acid fast staining |
carbolfuchsin, acid alcohol, methylane blue |
|
|
study stuudy study |
gotta get an A |
|
|
Stentor |
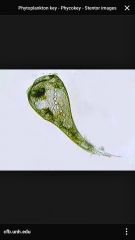
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Chaos chaos |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Euglena |
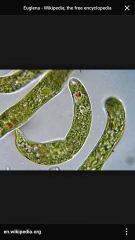
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Paramecium |
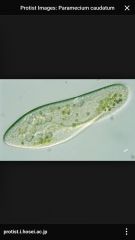
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Blepharisma |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Actinosepharium |
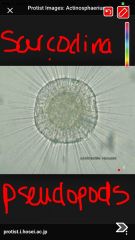
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Giardia lamlia-giardiasis |
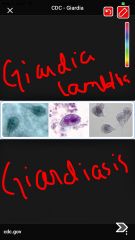
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Entamoeba histolytica- amoebic dystentary |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Trypanosoma gambiensa |
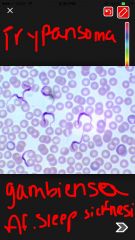
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Trypanosomiasis African sleeping sickness tsetse fly |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Trichamonas vaginalis |
Back (Definition) |

