![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
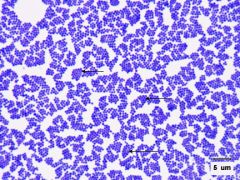
Identify the microorganism. (Don't forget to underline) |
Staphylococcus aureus
|
|
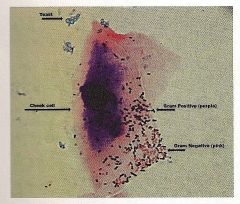
Identify the type of stain used and the procedure.
|
Gram Stain
1. crystal violet for 1 min and rinse 2. gram's iodine 1 min and rinse 3. 3 drops of alcohol and immediate rinse 4. safranin for 1.5 to 2 min and rinse |
|
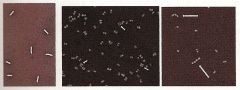
Identify the stain technique and the microorganisms. Don't forget to underline the genus and species.
|
From left to right:
1. Bacillus cereus 2. Micrococcus luteus 3. Streptococcus faecalis |
|
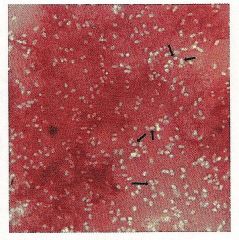
Identify the type of stain and the microorganism.
|
Capsule Stain
Klebsiella pneumoniae Don't forget to underline! |
|
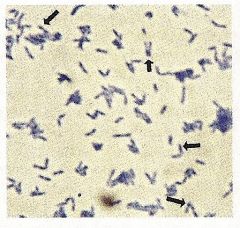
Identify the type of stain and the microorganism. What are the dark spots?
|
1. Methylene Blue Stain
2. Corynebacterium diphtheriae 3. Metachromatic Granules |
|
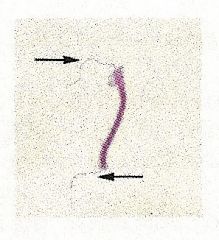
Identify the type of stain and the microorganism. What are the arrows pointing to and what is this arrangement called?
|
1. Flagellar Stain
2. Spirillum volutans 3. Flagella 4. Amphitrichous |
|
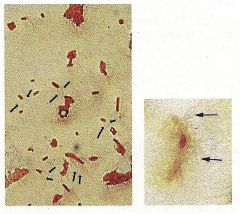
Identify the type of stain and the microorganism. What do the areas indicate and what type of arrangement is this?
|
1. Flagellar Stain
2. Proteus vulgaris 3. Flagella 4. Peritrichous |
|
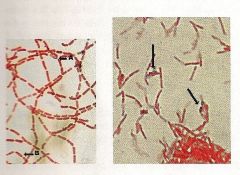
Identify the type of stain and the microorganism. What are the arrows pointing to?
|
1. Endospore Stain
From left to right: 2. Bacillus subtilus 3. Clostridium botulinum 4. endospores |
|
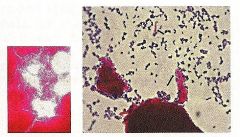
Identify the type of stain and the microorganism. Why is this stain used?
|
1. Acid Fast Stain
2. Mycobacterium tuberculosis 3. Some bacteria contain a waxy lipid, mycolic acid, in there cell wall. This layer is durable and commonly associated with pathogens. Once stained the acid fast cell walls will not decolorize with alcohol and will remain pink from the carbol fuschin stain. |
|
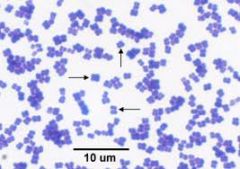
Identify the microorganism, the stain used, and the morphological features.
|
1. Micrococcus luteus
2. Crystal Violet 3. Tetrad coccus |
|
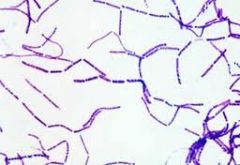
Identify the microorganism and the stain used.
|
1. Bacillus subtilus
2. Crystal Violet |
|
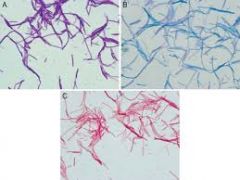
Identify the microorganism and the types of stains used.
|
1.Bacillus subtilis
2. Simple Stains: A. Crystal Violet B. Methylene Blue C. Carbol Fuschin |
|
|
What is negative stain used for and give examples of microorganisms.
|
Allows visualization of shape, size, and arrangement by providing a dark background so organisms appear white/clear.
1. Micrococcus luteus 2. Streptococcus pneumoniae |
|
|
What is capsule stain used for and give examples of microorganisms.
|
Capsules will appear clear around the organism which appears like a pink dot. Do not heat fix.
1. Enterobacter aerogenes 2. Klebsiella pneumoniae |
|
|
What is methylene blue stain used for and give an example of microorganism.
|
Methylene blue will stain phosphate granules (metachromatic granules).
1. Corynebacterium diphtheriae |
|
|
What is acid fast stain used for and give examples of microorganisms.
|
Organisms containing mycolic acid surrounding their peptidoglycan layer will stain pink with the carbol fuschin. Non -acid fast organisms will be blue from the methylene blue counterstain.
1. Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) 2. Mycobacterium leprae (Leprosy) 3. Nocardia asteroides (lung & skin infections) 4. Cryptosporidium parvum (diarrhea) |
|
|
Describe what happens when flagella move clockwise. Counterclockwise.
|
1. tumble (change directions)
2. run (forward movement) |
|
|
What are the three parts of flagellum?
|
1. filament (the long part)
2. hook (attaches to bassel body) 3. basal body (attaches flagellum to cell) |
|
|
How many rings do Gram negative flagella have? Gram positive?
|
1. Gram negative have 2
2. Gram positive have 1 |
|
|
List 5 microbes that are not motile.
|
1. Staphylococcus aureus
2. Streptococcus pneumoniae 3. Micrococcus luteus 4. Klebsiella pneumoniae 5. Shigella dysenteriae |
|
|
List 5 microbes that are motile.
|
1. Citrobacter freundii
2. Enterobacter aerogenes 3. Escherichia coli 4. Proteus vulgaris 5. Salmonella typhimurium |
|
|
What does axial filament describe? Give an example of a microorganism.
|
Spirochetes move by flexing and spinning movements via an axial filament.
1. Treponema pallidum (syphilis) |
|
|
Describe gliding motility and give an example of a microorganism.
|
Movement across a solid structure with no visible structures seen.
1. Synechococcus elongatus (cyanobacteria) 2. Beggiatoa alba (Myxomycetes) |
|
|
Where can spores be located in bacterial cells and how are they classified by this location? Give examples of microorganisms.
|
1. central (Bacillus cereus)
2. Subterminal (Bacillus subtilis) 3. Terminal (Clostridium tetani) |
|
|
What is a simple stain?
|
Technique were only one stain is used. Can determine size, shape, and arrangement. Common dyes include crystal violet, methylene blue, safranin, and carbol fuschin.
|
|
|
Give an example of a gram variable organism.
|
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
|
|
|
What color is gram positive? Gram Negative?
|
Positive is purple and negative is pink
|
|
|
Are yeast gram positive or negative. Give examples.
|
Gram positive.
1. Saccharomyces cerevisiae 2. Candida albicans |
|
|
Name the 11 gram positive organisms listed in the lab book.
|
1. Staphylococcus aureus
2. Streptococcus pneumoniae 3. Lactobacillus acidophilus 4. Lactococcus lactis 5. Micrococcus luteus 6. Bacillus subtilis 7. Clostridium botulinum 8. Mycobacterium tuberculosis 9. Enterococcus faecalis 10. Sporosarcina ureae 11. Sarcina aurantiaca |
|
|
Shape/arrangement of:
1. Micrococcus 2. Sarcina 3. Streptococcus |
1. tetrads (4 square shape)
2. sarcina (cube shape) 3. chains |
|
|
Shape/arrangement of:
1. Neisseria 2. Staphylococcus 3. Mycobacterium |
1. diplococci
2. grape like cluster 3. cords |
|
|
How do you find the number of cells after x amount of time?
|
You take the initial number of cells and multiply by 2 to the power of the number of generations.
|

