![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Inoculate
|
Add small amount of microbe to media (food) to obtain microbial growth
|
|
|
Incubate
|
Place in an incubator at a set temperature in order to get microbe to grow
|
|
|
Autoclave
|
method used to kill microbes using moist heat and parameters of 121C at 15 psi for 15 min
|
|
|
body temp
|
37C
|
|
|
room temp
|
25C
|
|
|
refrigerator temp
|
4C
|
|
|
Aseptic technique
|
measures we use to prevent contamination and preserve a pure culture
|
|
|
What are the 4 types of organic molecules?
|
proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, lipids
|
|
|
Example of Disaccharides
|
maltose (glucose-glucose)
sucrose (glucose-fructose) lactose (glucose-galactose) |
|
|
Example of Polysaccharides
|
glycogen
starch cellulose |
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus
|
G+ Bacteria, coccal, facultative anaerobe
Halophile (salt loving) Grape like clusters |
|
|
Micrococcus luteus
|
G+ Bacteria, Spherical, obligate aerobe.
Found in human mouth, mucosae, oropharynx and upper respiratory tract. |
|
|
Bacillus subtilis
|
G+ Bacteria, bacillus, obligate aerobe
endospore |
|
|
How are agar plates positioned when incubated? Why?
|
upside down. Prevents condensation form dripping onto plate.
|
|
|
How are agar plates positioned when disposed of?
|
right-side up
|
|
|
What is the proper labeling of agar plates?
|
Organism Name
Media, Temp Date, Lab # Your Name |
|
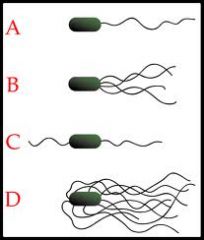
Name the types of flagella.
|
A. Monotrichous
B. Lophotrichous C. Amphitricous D. Peritrichous |
|
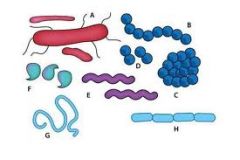
Name the bacterial shapes.
|
A. Bacilli
B. Stretococci C. Staphylococci D. Diplococci E. Spirochete F. Club Rod G. Filamentous H. Streptobacilli |
|
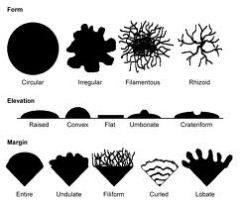
Study these morphological terms.
|
Name and describe the Shapes, Margins, and Elevations terms.
|
|
|
Amino acids are held together by what kind of bond?
|
peptide bond
|
|
|
A long chain of amino acids is called?
|
polypeptide
|
|
|
Describe DNA and RNA base pairing.
|
DNA: Adenine:Thymine, Cytosine:Guanine
RNA: Adenine:Uracil, Cytosine:Guanine |
|
|
What are the three types of RNA?
|
mRNA (provides genetic message)
tRNA (transfers amino acids to ribosome) rRNA (makes up ribosome) |
|
|
How many hydrogen bonds does A:T have? C:G?
|
A:T has 2 and C:G has 3
|
|
|
DNA has a 3' hydroxyl end and 5' phosphate end. Which end are nucleotides added to during replication.
|
3' end.
|
|
|
Describe replication, transcription, translation,
|
DNA replicated during replication, DNA is converted to mRNA in transcription, mRNA codons are used as instruction for which amino acid to use in protein synthesis.
|
|
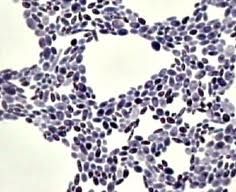
Identify the microorganism. What type of microorganism is it?
What type of stain was used? |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast/fungi)
Crystal violet simple stain. |
|
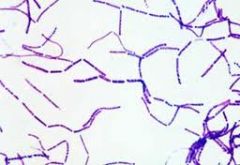
Identify the microorganism.
G+ or G-? |
Bacillus subtilis
G+ |

