![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How do yeast reproduce? What is a pseudohyphae?
|
Budding. Pseudohyphae: when buds do not separate they form long chains of yeast cells.
|
|
|
What is mycelia?
|
Mycelia is another term for mold. Fungi that live as multicellular colonies composed as branching hyphae are known as mold.
|
|
|
What is unique about dimorphic fungi?
|
Fungi that can grow as either a yeast or mold, depending on environmental conditions and temperatures. They usually grow as a yeast at body temperatures.
|
|
|
What is a dermatophyte? Name the three common dermatophytes?
|
Microsporum, trichophyton, and epidermophyton. They are fungi confined to the stratum corneum and its adnexal structures. Dermatophyte = superficial mycoses = ring worm.
|
|
|
What are the two diagnostic test used to identify cutaneous fungi?
|
Wood's lamp: UVA (365) light detects fluorescent metabolites. Microsporum will fluoresce a brilliant green.
KOH preparations: KOH digests keratin, dissolved skin scrappings will reveal branched hyphae. |
|
|
What is the most common cutaneous fungi found in young children (before puberty)?
|
Children most often are infected by microsporum. The family normally has a cat or dog.
|
|
|
What fungi infects the outer hair shaft, causes alopecia, and has a positive Wood's lamp?
|
Microsporum canis.
|
|
|
Which fungi infects the inner hair shaft causing tinea capitis and is negative under a Wood's lamp?
|
Trichophyton tonsurans.
|
|
|
What superficial fungi will cause hypopigmentation? What would a Wood's lamp show?
|
Tinea versicolor is caused by Malassezia furfur which is positive under a Wood's lamp. This fungi inhibits melanosome transfer to keratinocytes.
|
|

What fungi is this?
|
Spaghetti and meatball appearance. Malassezia furfur.
|
|

How do you treat this fungi which is infecting the hair shaft?
|
White piedra: Trichosporon beigelii. Treat with topical imidazole.
|
|

What cutaneous fungi is this?
|
Trichophyte is idetified by macroconidia and microconidia.
|
|
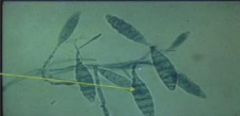
How do you treat this cutaneous fungi?
|
Microsporum: large boat shaped macroconidia. Treat with griseofulvin or imadazole.
|
|
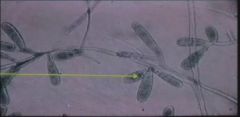
What cutaneous fungi is shown?
|
Epidermophyton: punching bag shape occurring in three.
|
|
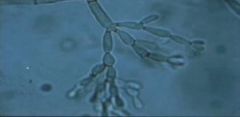
Skin scrappings from a cauliflower like skin lesion reveal this subcutaneous fungus.
|
Cladosporium carrionii causes eumycotic mycetoma or chromoblastomycosis.
|
|
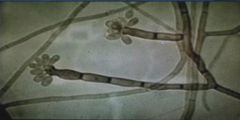
Like cladosporium, this fungus causes chromoblastomycosis. Tx?
|
Fonsecaea pedrosi. Tx: itraconazole or imidazole.
|
|
|
Skin scrappings with KOH of a chromoblastomycosis have what characteristic?
|
Copper-colored sclerotic bodies (Medlar bodies).
|
|
|
How does the fungus that causes rose gardener disease spread throughout the body?
|
Sporothrix schenkii infects gardeners after they are pricked by a thorn. A nodule will appear, become necrotic, and then ulcerate. New nodules will appears along lymphatics.
|
|
|
How do you treat sporothrix schnekii?
|
Oral potassium iodide or itraconazole.
|
|

Cigar shaped yeast.
|
Sporothrix schenckii (in vivo form).
|
|
|
Patient presents with sores on his mouth and physical weakness. X-rays show calcification in his lungs and spleen. History reveals that the patient was cave exploring in Ohio. What histological finding would help you diagnose this fungal infection?
|
Biopsy of a lesion will show Histoplasma capsulatum yeast within macrophages.
|
|
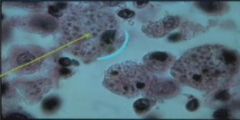
What fungus is this?
|
Histoplasma capsulatum. Note the yeast within macrophages.
|
|
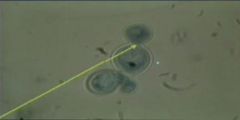
Name this dimorphic systemic fungus.
|
Blastomyces dermatitidis. Note the broad-based bud.
|
|
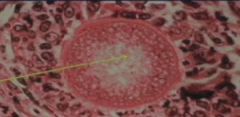
Spherules with endospores are characteristic of _________.
|
Coccidioides immitis.
|
|
|
A man presents with lesions on his mouth, erythema nodosum, and has flu-like symptoms. He says that he recently visited San Joaquin Valley. What does this man have?
|
San Joaquin Valley fever caused by Coccidioides immitis.
|
|
|
Name the fungi that cause systemic disease.
|
Coccidioides immitis, Histoplasma capsulatum, Blastomyces dermatitidis. Also Paracoccidioides brasiliensis which causes South American blastomycosis.
|
|

Patient from Michigan presents with weakness, night sweats, lung involvement. What fungus?
|
Blastomycosis dermatitidis.
|
|
|
What fungus causes oral thrush? How do you treat this?
|
Candida albicans. Patches of white exudate with a reddish base cover mucous membranes of the mouth. Difficult to scrape off. Swish and spit with nystatin or sucking on imidazole candies.
|
|
|
How is candida diagnosed?
|
KOH prep. Blood test for beta-D-glucan. Germ tube test.
|
|
|
What does candida albicans cause in normal hosts and in immunocompromised patients?
|
Normal: oral thrush, vaginitis, diaper rash.
Immunocompromised: esophagitis and systemic infection. |
|
|
Patient on chemotherapy for leukemia develops hemoptysis. Biopsy of pulmonary tissue reveals branched hyphae. Diagnosis?
|
Aspergillus fumigatus.
|
|
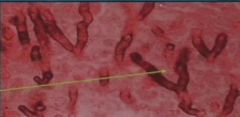
This fungus dines on dead/decaying vegetations.
|
Septate hyphae branching at 45 degree angle. Aspergillus fumigatus.
|
|
|
What three major types of diseases does aspergillus fumigatus cause?
|
Fungus ball (aspergilloma): develops in preexisting cavity in the lung. Causes hemoptysis.
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: type I and III hypersensitivity. Invasive aspergillosis: hemorrhagic infarctions and a necrotizing bronchopenumonia. |
|
|
What fungus secretes a certain toxin on peanuts and rice and may be associated with liver carcinomas?
|
Aspergillus flavus secretes aflatoxin.
|
|
AIDS patient with a silver stain of a lung biospy.
|
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia stains black on a silver stain.
|
|
|
Name the saprophytic molds that have broad (90 degrees), non-septated, branching hyphae.
|
Rhizopus, mucor.
|
|
|
Diabetic patient presents with a frontal lobe mass. What fungus caused this?
|
Mucor species that causes rhinocerebral mucormycosis in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis.
|
|

India Ink stain. What does this fungus cause?
|
Cryptococcus neoformans, contracted via pigeon droppings, causes meningitis and pneumonia.
|
|
|
What organisms are urease positive?
|
Pink color forms on urea agar.
Bacteria: Helicobacter and Proteus. Fungi: Cryptococcus neoformans. |
|
|
How does amphotericin B work?
|
Amphotericin B complexes with ergosterol disrupting fungal plasma membrane leading to cell death. It is used for serious systemic fungal infections.
|
|
|
What are some side effects of amphotericin B?
|
Renal toxicity: dose-dependent azotemia (reversible).
Acute febrile reaction with rigors. Anemia. Phlebitis at IV site. |
|
|
How does flucytosine work? What are its drawbacks?
|
Flucytosine is an anti-metabolite which inhibits DNA/RNA synthesis. Most fungi are resistant.
|
|
|
Name the imidazoles. How do they work? Which two are used for topical fungal infections.
|
Imidazoles are broad spectrum antifungals which inhibit cytochrome p-450 which is involved in ergosterol synthesis.
Ketoconazole, miconazole (topical), clotrimazole (topical). |
|
|
What are side effects of ketoconazole?
|
Hepatotoxicity, GI distrubances, and symptoms due to a decrease in testosterone: gynecomastia, impotence, decreased libido, and decreased sperm production.
|
|
|
What is Fluconazole used to treat?
|
Candida albicans and cryptococcal meningitis (adjunct to IV amphotericin).
|
|
|
Voriconazole is a broad spectrum antifungal. -azoles inhibit CYP450, which inhibits ergosterol production. What are the toxic effects of voriconazole?
|
Voriconazole is a triazole (as a pose to a imidazole) and toxics effects inclue visual changes, hepatotoxicity and rash.
|
|
|
Ravuconazole is used to treat ______.
|
Ravuconazole (a triazole) is used to treat Rhizopus species.
|
|
|
If amphotericin B is not useful in treating aspergillosis what drug is used?
|
Caspofungin which inhibits fungal cell wall by inhibiting glucan synthesis.
|
|
|
What antifungal is used for esophageal fungal infections?
|
Nystatin.
|
|
|
What is the mode of action of griseofulvin?
|
Prevent mitosis by inhibiting spindle formation in fungi.
|
|
|
Itraconazole inhibits cytochrome p450 which converts _____ to _____. Is this a fungicidal or fungistatic mechanism?
|
Lanosterol to ergosterol. Fungistatic.
|
|
|
What is the key component of fungal spores, which provides the fungus with resistance to dehydration, heat, and chemicals?
|
Dipicolinic acid.
|
|
|
Actinomyces and Nocardia are both gram _____. How does ones differentiate the two in the laboratory?
|
Actinomyces forms sulfur granules. Nocardia is acid-fast.
|
|
|
A women presents with an abscess in her mouth which is draining pus and yellowish granules. The doc says the bug is part of her normal flora, and the abscess could have formed during her recent dental surgery. What gram positive rod is this?
|
Actinomyces israeli.
|
|
|
Amphotercin B can cause what electrolyte imbalances?
|
Hypokalemia, hypomagnesium. It also causes neuphrotoxicity, acute febrile reaction, anemia, phlebitis.
|

