![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
145 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most commonly isolated bacteria?
|
Enterobactericeae
|
|
|
Enterobactericeae are predominant aerobes found in the __; hence, they are natural flora.
|
bowel
|
|
|
Enterobactericeae that are covered in this section include what 5 organisms?
|
1. Salmonella 2. Shigella 3. E. coli 4. Yersinia enterocolitica 5. Yersinia pestis
|
|
|
Enterobactericeae are gram negative __.
|
rods
|
|
|
Enterobactericeae are __ __ (environment).
|
facultative anaerobes
|
|
|
Enterobactericeae are the predominant __ found in the human bowel.
|
aerobes
|
|
|
Can Enterobactericeae ferment glucose?
|
Yes - they all do
|
|
|
Are Enterobactericeae oxidase negative or positive?
|
oxidase negative
|
|
|
Enterobactericeae are facultative anaerobes that can survie in an environment with __% or less oxygen.
|
20%
|
|
|
Most Enterobactericeae are nitrate positive or negative?
|
Nitrate Positive
|
|
|
How many Enterobactericeae can ferment lactose?
|
Most, but not all of them.
|
|
|
Enterobactericeae are known as coliforms. What are coliforms?
|
Coliforms are a broad class of bacteria found in our environment, including the feces of man and other warm-blooded animals. They are natural flora found in the colon.
|
|
|
Enterobactericeae are nitrate positive, so they break down nitrates into __.
|
nitrites
|
|
|
Can enterobactericeae be found in sputum or urine samples?
|
yes
|
|
|
In real labs, what kind of tests are generally used to ID enterobactericeae?
|
strip tests, because they can perform many tests at once.
|
|
|
The gut is an __ environment.
|
anaerobic
|
|
|
Can E. coli, Klebsiella, and Enterobacter ferment lactose?
|
yes - they can be tested in a TSI acid slant
|
|
|
Proteus, Morganella, and Providencia are Enterobactericeae that do or do not ferment lactose?
|
Do not / they are nonlactose fermenting
|
|
|
Proteus, Morganella, and Providencia are tested using which kind of TSI slant?
|
alkaline
|
|
|
Will Proteus, Morganella, and Providencia turn pink on MAC agar?
|
No, because they are nonlactose fermentors
|
|
|
Which 3 Enterobactericeae are filled with coliforms that ferment lactose?
|
E. coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter
|
|
|
Which 3 coliforms ferment lactose and are tested using a TSI acid slant?
|
E. coli, Klebsiella, and Enterobacter
|
|
|
Salmonella and Citrobacter turn what color on XLD?
|
black / they are H2S POS
|
|
|
Coliforms such as E. coli, Klebsiella, and Enterobacter are all lactose fermentation positive and ONPG (POS or NEG?)?
|
ONPG Positive
|
|
|
Will E. coli, Klebsiella, and Enterobacter turn pink on MAC agar?
|
Yes / they ferment lactose
|
|
|
What type of hemolysis can be seen from Escherichia coli on BAP?
|
sometimes beta-hemolytic
|
|
|
What color is E. coli on BAP?
|
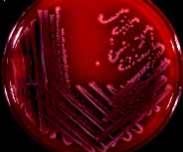
grey
|
|
|
What color does E. coli turn on MAC?
|
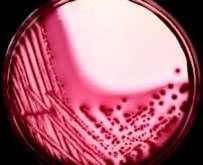
Purple, show bile precipitation too.
|
|
|
E. coli appear what color on EMB?
|
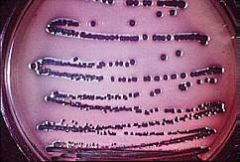
Metallic, deep purple - black
|
|
|
XLD and HEA are slightly __ of E. coli.
|
inhibitory
|
|
|
*The IMVC for got E. coli is ?
|
++--
|
|
|
E. coli are urease __.
|
negative
|
|
|
Urease positive organisms turn what color?
|
Bright pink or fuschia
|
|
|
What is the most frequently isolated Enterobactericieae?
|
E. coli
|
|
|
E. coli is a common cause of __ (because it's so nearby).
|
UTI
|
|
|
E. coli can sometimes cause what CNS infection?
|
meningitis
|
|
|
Serotyping of E. coli looks for what antigens?
|
K (capsule), O (endotoxin), H (flagellum)
|
|
|
*What is the ID number for E. coli?
|
O157:H7
|
|
|
*E. coli O157:H7 is negative for fermentation of __.
|
sorbitol
|
|
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a coliform bacteria that is usually __.
|
encapsulated
|
|
|
Klebsiella has what kind of sheen on EMB?
|
metallic
|
|
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae has what appearance on MAC?
|
Purple, stringy (can use string test it's so stringy)
|
|
|
Klebsiella does what to TSI?
|
turns it yellow, lifts or breaks the TSI due to gas
|
|
|
The IMVC for Klebsiella is ?
|
--++ (opposite of E. coli, same as Enterobacter)
|
|
|
Klebsiella is urease POS or NEG?
|
Slightly positive (barely turns pink)
|
|
|
Decarbolyation reactions for Klebsiella pneumoniae are ?
|
ornithine - and lysine +
|
|
|
*One difference between Klebsiella and Enterobacter is that Enterobacter is never __.
|
stringy (remember this since they are the same IMVC)
|
|
|
Is Klebsiella pneumoniae normal flora?
|
Yes - it's opportunistic
|
|
|
Klebsiella is a frequent cause of what 5 things?
|
1. UTI 2. peritonitis 3. septicemia 4. enteritis in children 5. pneumoniae in lungs (can cause pneumoniae quickly if it overgrows other flora)
|
|
|
Despite their similarities, Klebsiella is __, while Enterobacter is not.
|
stringy
|
|
|
*Enterobacter is motility POS or NEG?
|
POS (Klebsiella is motility NEG)
|
|
|
What are the decarboxylation test results for Enterobacter spp.?
|
Ornithine + and lysine - (opposite of Klebsiella)
|
|
|
Enterobacter is or is not encapsulated?
|
It is not encapsulated
|
|
|
Proteus spp. (P. vulgaris and P. mirabilis) are known to do what on BAP?
|
swarm
|
|
|
What color is Proteus (P. vulgaris and P. mirabilis) on BAP?
|
grey
|
|
|
How does Proteus look on EMB and MAC?
|
It is nonlactose fermenting, so they are basically colorless. If they were lactose fermenters, they would turn pink.
|
|
|
Proteus turns what color on TSI?
|
Black (POS for H2S)
|
|
|
Proteus turns what color on urease testing?
|
bright pink/fuschia (it's POS for urease)
|
|
|
What color does Proteus turn on PDase?
|
Green (Positive for PDase)
|
|
|
Proteus' reaction to citrate testing is ?
|
variable
|
|
|
Is Proteus spp. motile?
|
Yes - it swarms BAP
|
|
|
How can you tell P. vulgaris from P. mirabilis?
|
P. vulgaris is POS on Indole but NEG on ornithine. P. mirabilis is the reverse - NEG on Indole and POS on ornithine.
|
|
|
A positive for Indole turns the organism what color?
|
red
|
|
|
A positive for ornithine turns the organism what color?
|
yellow
|
|
|
Proteus spp. is normal flora of what area?
|
the GI tract
|
|
|
If Proteus overwhelms the GI tract, it can cause what 2 thing?
|
Peritonitis and abscesses
|
|
|
What infections are Proteus spp. known to cause if gets outside the GI tract?
|
1. UTI 2. Septicemia (secondary to UTI) 3. Eye and ear infections (rare)
|
|
|
Morganella morganii colonies resemble what organism?
|
Proteus spp.
|
|
|
How can you tell Morganella morganii from a Proteus?
|
1. H2S negative (so it doesn't turn black on TSI) 2. doesn't swarm quite as much as Proteus, but still swarms
|
|
|
What is the best media for grown Providencia spp. (including P. stuartii, P. rettgeri, and P. alcalifaciens)?
|
XLD - but HE can also be used
|
|
|
Can Providencia spp. turn black on TSI?
|
No - doesn't use make H2S. No gas either.
|
|
|
Is Providencia motile?
|
yes
|
|
|
Providencia is POS or NEG for citrate?
|
POS - few of these organisms are citrate POS!
|
|
|
Providencia can turn a lysine slant what color?
|
red - lysine will be deaminated by not decarboxylated
|
|
|
How does Salmonella look on XLD?
|
Red colonies with black centers
|
|
|
Which Salmonella looks black on bismuth sulfite agar?
|
S. typhi (we are most concerned about this strain of Salmonella)
|
|
|
Salmonella spp. is POS or NEG for H2S production?
|
POS
|
|
|
Salmonella is lysine POS, so it turns __ on a lysine slant.
|
yellow
|
|
|
Salmonella spp. has somatic antigens ?
|
A through I
|
|
|
Salmonella has a capsular antigen called ?
|
Vi
|
|
|
Aside from somatic and capsular antigens, what other antigen does Salmonella spp. have?
|
flagellar antigens
|
|
|
Salmonella is always __.
|
pathogenic
|
|
|
Is Salmonella POS or NEG for lysine?
|
POS (turns yellow)
|
|
|
Salmonella can be found in the GI tract of ?
|
animals (so it's fecal/oral)
|
|
|
Salmonella spp. is the most common cause of diarrhea due to ingestion of foods contaminated by ?
|
animals or their products
|
|
|
What kind of foods are known to carry Salmonella that infects humans?
|
Poultry, eggs, dairy products, shellfish, pork
|
|
|
Typhoid fever (by S. typhi) is often seen during natural __.
|
disasters
|
|
|
Salmonella typhi settles into the __ __ of the GI tract.
|
Peyer's patches
|
|
|
From the GI tract, Salmonella typhi can enter the bloodstream and the __ system, causing septicemia.
|
lymphatic system
|
|
|
S. typhi can actually hide in __ cells and evade your immune system!
|
nonphagocytic cells
|
|
|
What can S. typhi do inside of a macrophage?
|
multiply
|
|
|
What are the 4 main symptoms of S. typhi?
|
1. fever (Typhoid or enteric fever) 2. pain 3. hemorrhage 4. constipation followed by bloody diarrhea
|
|
|
What is the incubation period for S. typhi?
|
10-14 days
|
|
|
Patients can become __ of S. typhi after they recover.
|
carriers
|
|
|
Salmonella paratyphi can cause a milder form of Typhoid fever called ?
|
Paratyphoid fever
|
|
|
Can S. paratyphi go septic as easily as S. typhi?
|
no - it usually doesn't have a septic stage
|
|
|
Salmonella choleraesuis usually has no __ manifestation.
|
intestinal
|
|
|
What percentage of patients can become carriers of Salmonella typhimurium?
|
3%
|
|
|
One way to tell Citrobacter freundii from Salmonella is ?
|
C. freundii is urease POS while Salmonella is NEG
|
|
|
Shigella spp. is known to be "__" because it is negative on most biochem test.
|
lazy
|
|
|
The best media inoculation of Shigella spp. is ?
|
XLD (HE can also be used)
|
|
|
Shigella is POS for __.
|
ONPG
|
|
|
Most Shigella are NEG for ornithine. What is the one exception?
|
Shigella sonnei is POS for ornithine
|
|
|
What are the 4 serotypes for Shigella?
|
1. Serotype A = S. dysenteriae 2. B= S. flexneri 3. C= S. boydii 4. D= S. sonnei (which is ornithine POS)
|
|
|
How is Shigella transmitted?
|
The 4 F's: Food, fingers, feces, flies
|
|
|
How long can Shigella spp. remain in water supplies?
|
6 months
|
|
|
Which organism is the most virulent from this group?
|
Shigella spp. - one organism is enough to cause infection!
|
|
|
What kind of toxin does Shigella spp. have?
|
Shiga-toxin
|
|
|
Yersinia spp. grows on which kind of agar?
|
CIN (Sin growns on cin)
|
|
|
The CIN agar can be used to separate Yersinia spp. from other ?
|
non-lactose fermenters
|
|
|
How does Yersinia spp. look on CIN agar?
|
Colonies are red bulls eyes surrounded by a colorless halo
|
|
|
Is Yersinia motile?
|
no
|
|
|
What caused the bubonic plague?
|
Yersinia pestis (it was spread more so by humans than by rats or rat fleas)
|
|
|
Yersinia pestis causes a swelling of the lymph nodes, which turn blue or black, called __.
|
buboes
|
|
|
The mortality rate of Yersinia pestis is ?
|
50%
|
|
|
Yersinia enterocolitica mimics __.
|
appendicitis
|
|
|
All gram negative curved rods are __ pathogens, meaning they are always bad.
|
primary
|
|
|
Vibria spp. (a gram neg curved rod) is a natural inhabitant of ?
|
sea water
|
|
|
Vibrio spp. prefers a more __ pH.
|
alkaline
|
|
|
What is the etiologic agent of cholera?
|
Vibrio cholerae
|
|
|
Is V. cholerae motile?
|
Yes! You might even be able to see the flagella microscopically.
|
|
|
V. cholerae ferments sucrose and forms __ colonies on TCBS agar.
|
yellow (very yellow)
|
|
|
Non sucrose fermenters form __ colonies on TCBS agar.
|
blue or blue-green
|
|
|
Vibrio cholerae is positve on ?
|
all biochemical tests
|
|
|
Which serotypes of Vibrio cholerae are most virulent?
|
O1-O139
|
|
|
What test is used to detect V. cholerae toxins?
|
ELISA
|
|
|
V. cholerae produces an enterotoxin that causes ?
|
"rice water" stools and watery diarrhea that can rapidly dehydrate the patient and lead to death.
|
|
|
Vibrio parahemolyticus looks like V. cholerae, but is non-sucrose fermenter, meaning it looks __ on TCBS.
|
blue to blue-green
|
|
|
V. cholerae is acquire by ?
|
drinking contaminated water
|
|
|
What kind of Vibrio is endemic to the Chesapeake Bay?
|
Vibrio parahemolyticus
|
|
|
Watermen and fisherman can catch V. parahemolyticus through cuts. You can also get it by eating ?
|
blue crabs or any shell fish
|
|
|
What kind of Vibrio can be caught from fishing hooks as well as seafood?
|
V. vulnificus
|
|
|
If it lives in salt water or can be caught by seafood, think __.
|
Vibrio
|
|
|
What organism shows darting motility on darkfield wet prep?
|
Campylobacter jejuni
|
|
|
What is the optimum temp for growing Campylobacter jejuni?
|
42C (for 72 hours)
|
|
|
What is the preferred media for growing Campylobacter jejuni?
|
Campy BAP
|
|
|
Campylobacter jejuni is __ to naladixic acid and __ to cephalothin.
|
Susceptible to naladixic acid and resistant to cephalothin.
|
|
|
Campylobacter jejuni is normal flora in __.
|
puppies (found in their GI tract and feces)
|
|
|
Campylobacter jejuni can cause ?
|
severe systemic disease, fever, gastroenteritis
|
|
|
How do you treat Campylobacter jejuni?
|
Erythromycin (naladixic acid also works, but costs more)
|
|
|
What organism has lots of flagella?
|
Helicobacter pylori
|
|
|
What kind of media is used to isolate Helicobacter pylori?
|
BAP or CHOC
|
|
|
Helicobacter pylori turns __ rapidly on the urease test.
|
pink (POS)
|
|
|
Helicobacter pylori is the only bacteria known to cause __.
|
cancer
|
|
|
Helicobacter pylori is a source of stomach __.
|
ulcers
|

