![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Prokaryote
|
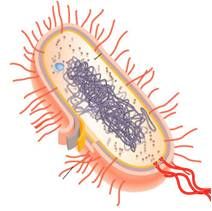
pre nucleus;
One circular piece DNA not in a membrane no histones no organelles peptidoglycan cell walls binary fission |
|
|
|
Eukaryote
|
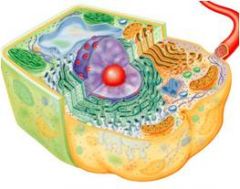
true nucleus;
Paired (homologous) chromosomes within nuclear membrane histones organelles polysaccharide (plants) or chitin (fungi) or no cell wall (animal) mitosis |
|
|
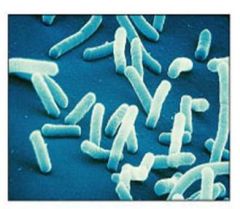
|
bacillus
|
|
|
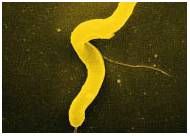
|
spirillum
|
|
|
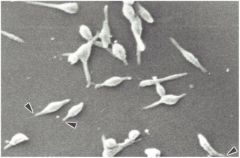
|
Mycoplasma
|
|
|
|
diplococci and diplobacilli
|
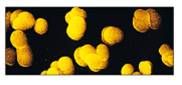
pairs
|
|
|
|
clusters
|
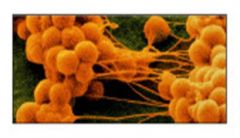
staphylococci
|
|
|
|
Glycocalyx
|
"capsule"
outside cell wall extracellular polysaccharide allows cell to attach to surfaces and one another Virulence Factor: capsules prevent phagocytosis by neutrophiles and macrophages |
|
|
|
virulence factor
|
any property of a bacterium that allows it to avoid host defenses and cause disease
|
|
|
|
Flagella
|
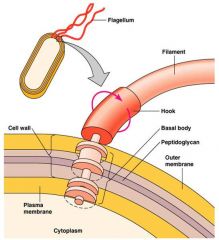
|
filament
protein flagellin attached to a protein hook anchored within the wall and membrane by the basal body (rotates like propeller) virulence factor: penetrate mucous secretions move away from toxins |
|
|
Axial Filaments
|
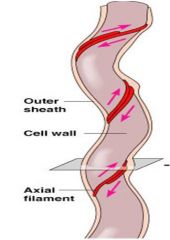
Endoflagella
In spirochetes Ex. syphilis Rotation causes cell to move A specialized spirillum shape “corkscrew” |
|
|
|
G+ (not easily decolorized)
(Type of cell wall) |
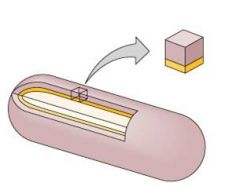
thick cell wall (peptidoglycan)
cell membrane (yellow) (Alcohol dehydrates thick peptidoglycan CV-I crystals do not leave Cells filled with blue stain and cannot be counterstained) |
|
|
|
G- (rapidly decolorized)
|
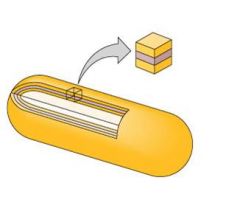
outer membrane (yellow)
thin peptidoglycan cell membrane (yellow) (Alcohol dissolves outer membrane and leaves holes in thin peptidoglycan CV-I washes out) Cells are colorless and able to pick up the red counterstain |
|
|
|
Lysozyme
|
Enzyme in tears saliva, tissue secretions
digests peptidoglycan Cell are killed as a result of osmotic lysis cell does not have to be growing to be affected by lysozyme |
|
|
|
Penicillin
|
inhibits formation of peptidoglycan
actively growing cells lack a cell wall cells are killed as a result of osmotic lysis Cell must be actively growing to be affected by penicillin |
|
|
|
Plasma Membrane
|
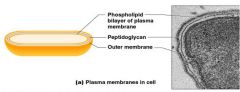
Phospholipid bilayer (viscous as olive oil)
Proteins move laterally and rotate peripheral proteins Trans membrane proteins |
|
|
|
Phospholipid bilayer
|
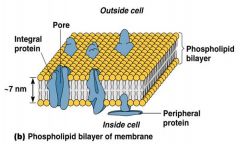
(viscous as olive oil)
selective permeability |
|
|
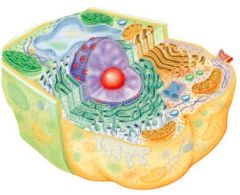
eucaryotic cells (mitochodria)
|
mitochondria arose from symbiotic relationship between primative eucaryotic cell and bacteria.
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasm
|
Cytoplasm is the sum total of all the dissolved substance within the plasma membrane
sugars, amino acids, phospholipids, minerals |
|
|
|
Ribosomes
|
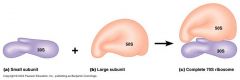
small ‘sand-like’ particles ~20nm diameter
30S and 50S subunit function in protein synthesis (translation of mRNA) Bacterial ribosomes are similar to ribosomes (70S) found inside mitochondria of eucaryotic cells but differ slightly from ribosomes associated with endoplasmic reticulum in the cytoplasm (80S) |
|
|
|
Inclusions
|
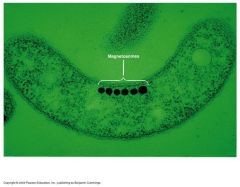
Examples:
Metachromatic granules (volutin) Polysaccharide granules Lipid inclusions Sulfur granules Magnetosomes (Iron Oxide) Phosphate Reserves Energy Reserves |
|
|
|
Endospores
|
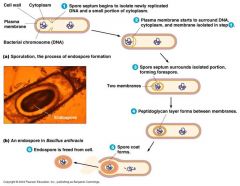
dormant structure
resistant to desiccation, heat, chemicals sporulation: Endospore formation germination: return to vegetative state pathogenic spore-formers ex: Clostridium tetani Clostridium perfringenes Clostridium botulinium |
|
|
|
Pleomorphic
|
all different shapes
|
|
|
|
Plant versus Animal cell
|
plants have a cell wall, animal cells do not
|
|

