![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
humans have _____________ _____________ to certain pathogens as well as three overlapping lines of defense.
|
species resistance |
|
|
|
the first two lines of defense compose __________ _____________, which is generally nospecific and protects the body against a wide variety of potential pathogens. A third line of defese is ___________ ______________, which is a specific response to a particular pathogen. |
adaptive immunity |
|
|
|
The first line of defense includes the skin, composed of an outer _______________ and a deeper _________. ___________ _________ of the epidermis devour pathogens. Sweat glands of the skin produce salty sweat containing the enxyme called ___________ and _____________ ____________ (defensis), which are small peptide chains that act against a broad range of pathogens. _________ is an oily substance of the skin that lower pH, deterring the growth of many pathogens. |
epidermis dermis dendritic cells lysozyme antimicrobial peptides sebum |
|
|
|
the mucous membranes, another part of the body's first line of defense, are composed of tightly packed cells that are replaced frequently by _________ ________ division and often coated with sticky mucus secreted by goblet cells.
|
stem cell |
|
|
|
_____________ ________________, the competition between ________ ______________ and potential pathogens, also contributes to the body's first line of defense.
|
normal microbiota |
|
|
|
tears contain antibacterial lysozyme and also flush invaders from the eyes. Saliva similarly protects the teeth. The low pH of the stomach inhibits most microbes that are swallowed. |
|
|
|
|
the second line of defense includes cells (especially ____________), antimicrobial chemicals (toll-like receptors, NOD proteins, interferons, complement, lysozyme, and antimicrobial peptides), and processes (phagocytosis, inflammation, and FV).
|
phagocytes
|
|
|
|
The epidermis also contains phagocytic cells called __________ _______/ The Slender, fingerlike processes of _________ _________ extend among the surrounding cells, forming an almost continuous network to intercept invaders.
|
dendritic cells dendritic cells |
|
|
|
A pathogen can cause diease only if it can do what three things?
|
. attach itself to the host cells . evade the body's defense mechanisms |
|
|
|
______ line of defense: external physical barriers to pathogens eg. Skin, mucous membranes. |
First |
|
|
|
________ line of defense: Internal- protective cells, bloodborne chemicals, processes that inactivate or kill invaders.
|
Second |
|
|
|
First and Second- ________ _______- present at birth and work on wide variety of pathogens- Protozoa, parasitic worms, fungi, bacteria, viruses
|
Innate immunity |
|
|
|
Third line of defense: ______ ________- responds against unique species and strains of pathogens and alters the body defenses. |
adaptive immunity |
|
|
|
responds against unique species and strains of pathogens and alters the body defenses.
|
third line of defense adaptive immunity |
|
|
|
present at birth and work on wide variety of pathogens- Protozoa, parasitic worms, fungi, bacteria, viruses
|
2nd and 3rd line of defense innate immunity |
|
|
|
external physical barriers to pathogens eg. Skin, mucous membranes.
|
1st line of defense innate immunity |
|
|
|
Internal- protective cells, bloodborne chemicals, processes that inactivate or kill invaders non specifically
|
innate immunity |
|
|
|
epidermal __________ _______ phagocytize pathogens
|
Dendritic cells |
|
|
|
Chemicals secreted in perspiration that defend against pathogens? -______- inhibits growth of pathogens -______________ ___________ (defensins)- Dermicidins - broad spectrum -__________- destroys cell wall of bacteria |
-Antimicrobial peptides (defensins)- Dermicidins - broad spectrum -lysozyme- destroys cell wall of bacteria |
|
|
|
_________ secreted by oi glands, lower skin pH to a level (pH___) inhibitory to many bacteria. |
pH5 |
|
|
|
_________ ___________ line all body cavities open to environment.
|
mucous membranes |
|
|
|
Mucus secreting ______ _______, secrete antimicrobial peptides (________), nasal mucus contains ________.
|
goblet cells defensins lysozyme |
|
|
|
The lacrimal apparatus; a group of structures that produce and drain tears, blinkin spreads tears and _________ surface of the eye, _________ in tears destroys bacteria.
|
Lysozyme |
|
|
|
Vitamin B5, folic acid, precursor of vitamin K are provided by the ________ _________.
|
normal microbiota |
|
|
|
activities of _______ _________ make it hard for pathogens to compete. |
normal microbiota |
|
|
|
Animals raised in an _______ environment (free of all other organisms and viruses) are slower to defend themselves when exposed to a _________. |
axenic
|
|
|
|
__________ _________, present in skin, mucous membranes, and neutrophils; are triggered by sugar or protein molecules of the pathogens. |
Antimicrobial peptides |
|
|
|
_________ __________, work in several ways (punch holes in cytoplasmic membranes, interrupt internal signaling or enzymatic action, and __________ factors that recruit leucocytes).
|
chemotactic factors |
|
|
|
the _________/________ _________ line of defense operates when the pathogens penetrate the skn or mucous membranes. |
second/innate immunity |
|
|
|
_________ line of defense, composed of -phagocytes -antimicrobial chemicals .peptides .complement .interferons -fever -Inflammation |
second |
|
|
|
_______- mostly water containing electrolytes, dissolved gases, nutrient, and proteins. _______- is the fluid remaining when Clotting factors are removed from plasma. |
serum |
|
|
|
________-, incules iron- binding proteins transferrin, ferritin, siderophores, actoferrin, hemolysin), complement proteins and antibodies.
|
Serum |
|
|
|
Three types of ________ _________ in blood: -erythrocytes -platelets -leukocytes |
formed elements |
|
|
|
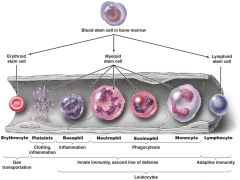
________________, are dividen into granulocytes and agranulocytes. |
leukocytes |
|
|
|
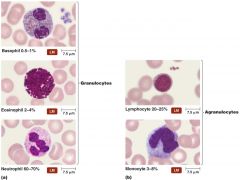
three types of granulocytes that contain large granules that stain different colors
|
basophils eosinophils neutrophils |
|
|
|
neutrophils are also call _______________ ____________ (PMNs)
|
polymorphonuclear leukocytes |
|
|
|
relative percentages of granulocytes -neutrophils -basophils -eosinophils agranulocytes -monocytes -lymphocytes |
|
|
|
|
Differential white blood cell count can signal signs of disease. -___________ _________ indicate allergies or parasitic worm infection -bacterial diseases often show increase in __________ and __________. -viral infections show increase in ____________ |
increased eosinophils leukocytes and neutrophils lymphocytes |
|
|
|
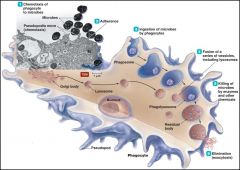
phagocytosis can be divided into 6 stages.... 1._________- movement of cell towards chemical stimulus 2._________- attachment to microgorganisms 3.__________- They extend pseudopodia, engult the microbe- phagosome 4.__________- complete in 10-30 minutes 5._________- Phagolysosome contains enzymes, hightly reactive and toxic forms of oxygen, low pH 5.5 6.___________: exocytosis- elimination of phgosomes, antigen processing and presentation on membrane |
1. chemotaxis 2. adherence 3. ingestion 4. maturation 5. killing 6 elimination |
|
|
|
nonphagocytic killing killing by eosinophils- -attach __________ _________ by attaching to their surface -____________ (elevated esosinophils) is often indicative of a helminth infestation. |
eosinophilia |
|
|
|
NK cells / natural killer lymphocytes. - secrete _______ onto surface of virally infected cells and tumors |
toxins |
|

