![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What structure provides water, amino acids, and lipids as food to bacteria?
|
sweat (sebaceous) glands
|
|
|
What is the normal pH of skin?
It is acidic or basic? |
pH 4 to pH 6.5; slightly acidic
|
|
|
What skin layer contains dead cells?
|
Epidermis layer
|
|
|
Why is skin described as unstable?
|
Because it has a lot of dry skin cells on the topmost layer that flake off easily
|
|
|
sebum
|
thick oily substance, secreted by the sweat (sebaceous) glands of the skin, that consists of fat, keratin and cellular debris
|
|
|
List the 3 kinds of organisms that are commonly in human skin flora.
|
Diptheroids
Staphylococcus aureus Fungi |
|
|
diptheroids (3)
|
Grow in hair follicles & break down sweat
Results in body odor Involved in acne |
|
|
staphylococcus aureus (s. aureus)
|
Salt tolerant gram (+) bacteria that grow on the outer surface of skin
|
|
|
Identify the fungus that is common in human skin flora.
|
Malassezia grows on human skin.
|
|
|
What bacteria causes boils when it reaches the hair follicle?
|
Staphylococcus aureus
|
|
|
folliculitis
|
infection of the hair follicle
|
|
|
furuncle
|
a boil; extension of folliculitis going into the surrounding tissue
|
|
|
carbuncle
|
a number of boils (mass) in the same location; can potentially infect organs
|
|
|
abscess
|
symptom consisting of a localized collection of pus (dead neutrophils) surrounded by inflamed tissue
|
|
|
List the 2 bacterial skin infections discussed in class.
|
Staphylococcus aureus infections
Borrelia burgdorferi |
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus
Infection/Disease caused Side FX How does it spread? Rx |
Causes infection of hair follicles, i.e. boils, carbuncles
Side FX: Swelling, redness Spreads by getting into hair follicles & sebaceous glands; may spread by human contact Rx: Must be drained by of pus and individual must be given antibiotics |
|
|
Borrelia burgdorferia
Infection/Disease caused Side FX How does it spread? Rx |
Causes Lyme disease
Side FX: (1 wk) large circular rash, fever, muscle pains, enlarged lymph nodes, (2-8 wks) dizziness, paralysis, headaches, (6 months) arthritis and joint problems Spread via ticks, which act as vectors for disease RX: Ampicillin if caught soon enough |
|
|
Where is borrelia burgdorferia prevalent? Why?
|
It is most common in the northeast and in the mountains (northern CA) because deers reside there.
|
|
|
What is unique about borrelia burgdorferia compared to other prokaryotes?
|
It is a spirochete with a "linear genome".
|
|
|
List the 2 viral skin diseases discussed in class. What virus causes these diseases?
|
Chickenpox = Herpesvirus family
Measles = Rubeola virus German measles = Rubella virus |
|
|
Chickenpox = Herpesvirus family
Side FX How does it spread? Prognosis Rx |
Side FX: itchy red spots and blisters
Spreads via tiny droplets in the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes Most recover, except for infants & immuno-compromised individuals RX: Vaccination |
|
|
What is reactivation of chicken pox called?
|
Shingles
|
|
|
Measles = Rubeola virus
Side FX How does it spread? Prognosis Rx |
Side FX: fever, cough, swollen eyes, fine red rash
Spreads via tiny droplets in the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes Most recover, but can be dangerous due to secondary disease, such as pneumonia RX: Vaccination |
|
|
German measles = Rubella virus
Side FX How does it spread? Prognosis Rx |
Side FX: mild cold symptoms, fine red rash
Spreads via tiny droplets in the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes Most recover, but it can be very dangerous for pregnant women RX: Vaccination |
|
|
Why is the rubella virus so dangerous for pregnant women?
|
If pregnant women are exposed during the first 6 weeks, abnormal development (i.e. deafness) of the fetus usually occurs
|
|
|
Which is more dangerous: rubeola virus (measles) or rubella virus (German measles)?
|
Rubeola virus (measles)
|
|
|
List the 5 structures of the upper respiratory system.
|
Ears
Eyes Nose Throat Mouth |
|
|
List the 3 structures of the lower respiratory system.
|
Trachea
Bronchial tubes Lungs |
|
|
What structure causes the respiratory system to be moist?
|
Goblet cells release mucous all the time.
|
|
|
What structure in the URS moves objects either out of the mouth or down to the stomach?
|
Cilia
|
|
|
List the 2 URS bacterial diseases discussed in class.
|
Streptococcus pyrogenes = Strep throat
Corynbacterium disptheriae = Diptheria |
|
|
Corynbacterium disptheriae = Diptheria
Side FX How does it spread? Prognosis Rx |
Side FX: fever & sore throat, swelling of neck, coating of throat w/ whtie membrane
Spreads via tiny droplets in the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes Prognosis depends on location of infection; 10% death rate RX: Penicillin (for bacteria) and antitoxin |
|
|
Streptococcus pyrogenes = Strep throat
Side FX How does it spread? Prognosis Rx |
Side FX: fever & sore, red throat
Spreads via tiny droplets in the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes Most recover; individuals feel better within 24 hours of taking antibiotics RX: Penicillin |
|
|
What is the rare disease caused by streptococcus pyrogenes?
|
Necrotizing fasciitis (flesh-eating disease), which has a death rate of 30–50%
|
|
|
Streptococcus pyrogenes = Necrotizing faciitis
Side FX How does it spread? Prognosis Rx |
Side FX: severe pain, swelling, fever
Spreads by entering open wound Death rate of 30–50% Rx: Amputate area of infection, antibiotics, IV immunoglobulin |
|
|
How does this s. pyrogene membrane protein function?
C5a peptidase |
Destroys C5a, an enzyme involved in chemotaxis
|
|
|
How does this s. pyrogene membrane protein function?
Capsule |
Contains hyaluronic acid, which is only supposed to be in humans
|
|
|
How does this s. pyrogene membrane protein function?
M protein |
Degrades C3b, an enzyme that marks bacteria for opsonization
|
|
|
How does this s. pyrogene membrane protein function?
F protein |
Attaches to host cells
|
|
|
How does this s. pyrogene membrane protein function?
G protein |
Binds to Fc region of IgG, which is an antibody
|
|
|
List the 4 s. pyrogene secreted proteins.
|
DNAses
Streptolysins O and S SPE Proteases |
|
|
How does this s. pyrogene secreted protein function?
Streptolysins S and O |
Lyse blood cells
|
|
|
How does corynbacterium diptheriae infect a person?
|
AB exotoxins released by the bacteria spread through blood and deactivate EF-2, which results in paralysis
|
|
|
Identify the function of EF-2 (elongation factor-2).
|
involved in translocation and synthesizing proteins
|
|
|
Describe the vaccine for diptheria.
|
Vaccine acts on exotoxin with formalin
|
|
|
Identify and define the viral URS infection discussed in class
|
Rhinovirus/Picornavirus = Common cold
Rhinovirus/Picornavirus - non-enveloped ss RNA |
|
|
Rhinovirus/Picornavirus
How does it spread? Prognosis Rx |
Spreads via tiny droplets in the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes
RX: Pleconaril may help |
|
|
How does the drug pleconaril function?
|
It binds to the hydrophobic pockets on capsid, which results in changes of the bacteria's 3D conformation thus preventing viral uncoating.
|
|
|
Identify and define the bacterial LRS infection discussed in class
|
Pneumonia - inflammed and fluid-filled lungs; 4 diff. types caused by diff. bacteria
|
|
|
List the 4 bacteria that cause pneumonia.
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Klebsiella pneumoniae Mycoplasma pneumoniae Legionella pneumoniae |
|
|
Identify and define the first viral LRS infection discussed in class.
|
Hantavirus = Hantavirus flu
hantavirus - enveloped virus w/ 3 (- (ss) RNA segments |
|
|
Hantavirus = Hantavirus flu
Side FX How does it spread? |
Side FX: fever, vomiting, diarrhea, cough, shock, death
Spreads via inhalation of air contaminated with urine/feces of rodents |
|
|
Where is the hantavirus prevalent?
|
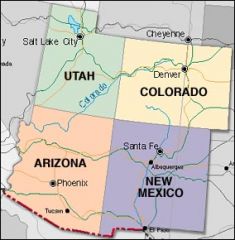
In the 4 corners area of the United States
|
|
|
Identify and define the second viral LRS infection discussed in class.
|
Influenza A - influenza (flu)
influenza A - enveloped virus with segments of (-) (ss) RNA |
|
|
Influenza A - influenza (flu)
|
Side FX: head & body ache, fever, muscle pain, cough, excess mucous, chills, malaise, vomiting
Spreads via air or by touching infected inanimate objects; virus can infects hours after removed from host Most recover in 10 days or so Rx: Vaccination |
|
|
Where is influenza A naturally found?
|
Wild birds
|
|
|
List the 2 protein spikes found on influenza A.
|
Hemaglutinin
Neuramindase |
|
|
Why must new influenza vaccines be made on a yearly basis?
|
Due to antigenic drift
|
|
|
antigenic drift
|
A mechanism for variation utilized by viruses that involves the accumulation of mutations within the antibody-binding sites
|
|
|
In order for s. pyrogenes to cause necrotizing faciitis, what exotoxins must be present?
|
Exotoxin A acts as superantigen and anti-shock.
Exotoxin B acts as protease. |
|
|
cyanosis
|
a blue coloration of the skin and mucous membranes due to lack of oxygen
|
|
|
Identify the 2 ways influenza A can kill a human.
|
Quickly and directly with viral pneumonia aka "burning of the lungs".
Slowly and indirectly by stripping the body of its defenses, which lets bacteria into the body, thus causing pneumonia. |
|
|
What do autopsies tell us about the influenza infections?
|
Autopsies show that all organs are infected/
|
|
|
Influenza mutates so fast that...
|
99% of the 100,000-1 million new viral particles that burst out of host cell are too defective to invade another cell
|
|
|
TRUE / FALSE
Mutated particles can be more deadly or less deadly. |
TRUE
|
|
|
When was the influenza virus in its most deadly form?
|
During the 1918 flu pandemic, in which it spread worldwide
|
|
|
1918 Flu Pandemic
Where did it begin? |
Haskell County, Kansas
|
|
|
1918 Flu Pandemic
Identify the 3 waves of the disease. |
Began in early 1918
June-Dec 1918: Soldiers spread the disease overseas to other soldiers & their families Last wave in early 1919 |
|
|
1918 Flu Pandemic
How many people did it kill worldwide? |
50-100 million, more than any disease in history
|
|
|
1918 Flu Pandemic
What was unique about this disease and how it affected young adults? (2) |
Young adults (25-29) had the most deaths.
8-10% of the world's young adult population died. |
|
|
List the 5 structures of the upper alimentary system.
|
Mouth
Esophagus Salivary glands Stomach Note: MESS |
|
|
List the 5 structures of the lower alimentary system.
|
Pancreas
Intestines Liver Note: Take a PIL |
|
|
Identify and define the bacterial upper alimentary infection discussed in class.
|
Vibrio cholera = Cholera
vibrio cholera - gram (-) bacteria rod |
|
|
Identify the function of the AB exotoxin that is released by vibrio cholera.
|
A fragment turns on cAMP production
B fragment binds to cells of small intestine |
|
|
What is the result of the A fragment (of the AB exotoxin) keeping cAMP on?
|
With cAMP being on continuously, it causes water to leave cells continuously.
Individual dies of dehydration. |
|
|
What is the Rx for cholera?
|
Vaccination and having a clean water/sanitation system
|
|
|
Identify and define the viral upper alimentary infection discussed in class.
|
Paramyxovirus family = Mumps
paramyxovirus family - enveloped 1 segment (ss) RNA |
|
|
Paramyxovirus family = Mumps
Side FX How does it spread? Prognosis Rx |
Side FX: fever, headache, swelling of parotid glands
Spreads via tiny droplets in the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes Most children recover w/ no problems; causes problems in adults Rx: Vaccination or survive disease |
|
|
What problems do males get from getting mumps?
|
If male gets mumps after puberty, they may become sterile b/c virus goes to testes.
|
|
|
What problems do pregnant females get from getting mumps?
|
Pregnant women can miscarriage.
|
|
|
Identify and define the viral lower alimentary infection discussed in class.
|
Hepatitis B virus = Hepatitis B
It is a DNA virus. |
|
|
What is unique about the hepatitis B virus?
|
It uses reverse transcriptase even though it is a DNA virus.
|
|
|
Hepatitis B virus = Hepatitis B
Side FX How does it spread? Prognosis Rx |
Side FX: fatigue, fever, nausea
Spreads via blood, blood products, and semen Leads to the destruction of liver and eventually death Rx: Vaccination, but there is no cure once contracted |
|
|
List the 3 structures of the nervous system.
|
Brain
Spinal cord Meninges |
|
|
Identify and define the first viral nervous system infection discussed in class.
|
Neisseria meningitidis = Meningococcal meningitis
neisseria meningitidis - gram (-) rod |
|
|
Identify and define the second viral nervous system infection discussed in class.
|
rhabdovirus family = Rabies
rhabdovirus family - bullet-shaped, enveloped, (ss) (-) RNA virus |
|
|
Identify and define the wound infection discussed in class.
|
Clostridium Tetani = Tetanus aka "lockjaw"
clostridium tetani - gram (+) rod |
|
|
What is the exotoxin released by the clostridium tetani virus? What is its function?
|
Tetanospasmin travels trough body and prevents neurons from controlling muscles; muscles kept in contracted position
|
|
|
Identify and define the blood infection discussed in class.
|
Yersinia Pestis = Black Death aka Plague
yersinia pestis - gram (-) rod |
|
|
Yersinia Pestis = Black Death aka Plague
Side FX How does it spread? Prognosis |
Side FX: enlarged lymph nodes, fever, shock, cough, bloody sputum
Spreads by fleas attacking humans and rodents Death occurs 80% of the time |
|
|
Identify the function of P1a in yersinia pestis.
|
Protease that dissolves blood clots in and destroys C3b and C5a
|
|
|
Identify the function of F1 in yersinia pestis.
|
Gene expressed only at high temps, i.e. in the human body
Leads to capsule production. Capsules are harder for the body to fight. |
|
|
Identify the function of the Yops protein in yersinia pestis. (3)
|
Destroys actin filaments in host cells
Prevents release of cytokines from being released *** Induces apoptosis |
|
|
What pneumonia-causing bacteria is most prominent in nosocomial infections?
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae
|
|
|
What pneumonia-causing bacteria that does NOT have a cell wall?
|
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
|
|
|
Why won't penicillin work on Mycoplasma pneumoniae?
|
It doesn't have cell walls.
|
|
|
How does Mycoplasma pneumoniae affect our bodies?
|
It attaches to epithelia cells and prevents cilia function.
|
|
|
How does legionella pneumophilia affect our bodies?
|
It enters and lives in our phagocytes
|

