![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
variolation
|
Inoculation with smallpox.
scratch pus from smallpox lesion into skin ground dried smallpox scabs vaccination: Inoculation of cowpox into skin vaccines confer artificial active immunity |
|
|
Inactivated and Attenuated Whole Agent Vaccines
|
wild-type (virulent) strain … must be killed (inactivated if virus)
or attenuated (weakened) strain …is usually live (infectious if virus) inactivated poliovirus (Salk) infectious poliovirus (Sabine) killed Yershinia pestis (plague) live Mycobacterium tuberculosis infectious measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) infectious varicella virus (chickenpox) infectious vaccinia virus (smallpox) inactivated rabies virus inactivated hepatitis A virus |
|
|
Infectious (live) verses Inactivated (killed)
|
organisms multiply (simulate natural infection with WT)
increase dose spread to other people stimulate both AMI and CMI back mutation to virulence |
|
|
Toxoids
|
inactivated toxins
DTaP diphtheria: purified diphtheria toxoid pertussis: acellular fragments of B. pertussis tetanus: purified tetanus toxoid 3 disease vaccine |
|
|
Subunit Vaccines
|
immunize verses one antigen of agent that causes disease or can prevent disease
EX Meningococcal meningitis purified polysaccharide from N. meningitidis Haemophilus influenzae type b meningitis -polysaccharides conjugated with protein Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine-Streptococcus. pneumoniae antigens conjugated with protein Influenza-Purified envelope spikes HA and HN |
|
|
recombinant vaccines
|
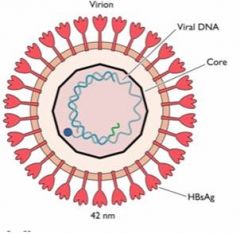
Hepatitis B
HepB surface antigen HBsAg Gene inserted in diploid cell line Safe compared to inactivated virus from patient serum |
|
|
Immunization Schedule
|

Person acquires artificial active immunity
herd immunity results when most of a population is immune to a disease. |
|
|
Antibody Titer
|

the concentration of antibodies against a particular antigen
determine level of antibody in patients serum acute vs convalescent stage |
|
|
Precipitation Reactions
|
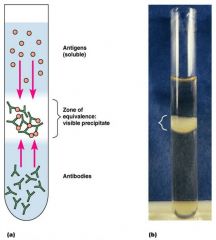
soluble antigens (solution)
ID antigen ID antibody |
|
|
Viral Hemagglutination
|
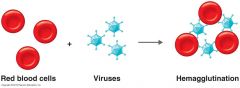
Viral hemagglutination : agglutination of RBCs.
ID viruses that agglutinate RBCs Influenza virus agglutinates chicken red blood cells Hemagglutination is a positive test for virus |
|
|
Viral Hemagglutination Inhibition
|
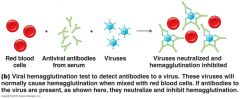
tests for antibodies in patient serum
antibody prevent virus from agglutinating RBCs No hemagglutination is a positive test for antibody |
|
|
Toxin Neutralization
|
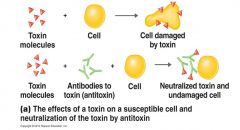
|
|
|
Complement fixation test
|
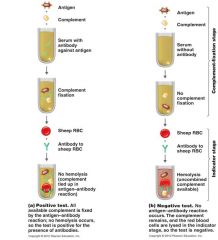
|
|
|
Fluorescent Antibody Techniques (Direct and Indirect)
|
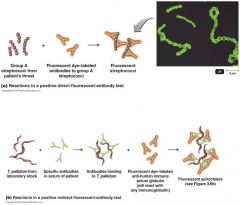
|

