![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What bacteria uses altered permeability as its mechanism of resistance?
|
Pseudomonas, resistance to aminoglycosides
|
|
|
What bacteria uses altered receptors or binding proteins as a mechanism of resistance?
|
S. pna
MRSA |
|
|
To determine antibiotic resistance, one must have a pure culture in log-phase growth, which is usually what?
|
18-24 hours old
|
|
|
What is 0.5 McFarland?
|
Barium sulfate standard equal to the turbidity of 10^8 bacteria/ml
|
|
|
How many days of QC are needed to implement a new method?
|
20 consecutive days, using ATCC (known) strains
Then weekly QC on all lots |
|
|
What to do if the weekly QC is OUT OF CONTROL!
|
- Inform supervisor
- Repeat test - If repeat is normal, move on - If repeat not ok, investigate and repeat x 5 (all must be ok) |
|

What is the preferred agar for a Kirby Bauer test and why?
Plate diameter and depth? |
Mueller Hinton agar
Specially balanced with the proper amounts of Ca++, Mg++ (Too much concentration can give FALSE RESISTANCES TO AMINOGLYCOSIDES) 150mm diameter, 4mm depth |
|
|
Can you compare zones of inhibition between antibiotics using a Kirby Bauer?
|
NO!! Never compare zone sizes. CLSI charts tell sensitive/resistant/intermediate based on unique zone sizes for each antibiotic
|
|
|
What is the difference between MIC and MBC?
|
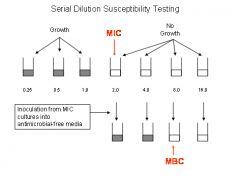
MIC: lowest concentration of antibiotic that inhibits growth
MBC: lowest concentration of antibiotic that kills 99.9% of original inoculum (subculture the "no growth" from MIC) |
|
|
What is "Antibiotic tolerance"?
|
(MBC / MIC) >= 32
BAD! Can't kill the organism but can inhibit it |
|
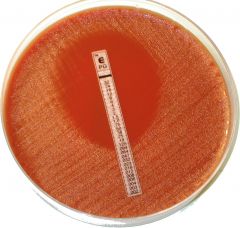
When would we use e test over KB?
|
E tests are good for fastidious organisms
Also, e test directly gives MIC |
|
|
What % of haemophilus is resistant to ampicillin, via disk test for B-lactamase detection?
|
28%
|
|
|
What is the primary mechanism for PCN resistance in B frag?
|
B lactamase. Test with disk test for B lactamase
|
|
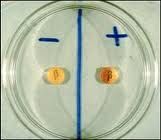
What is the chromogenic cephalosporin used for the disk test for B lactamase detection?
|
Nitrocefin. turns from yellow to red in the presence of B lactamase
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of resistance in MRSA?
|
mecA gene encodes PBPs (Pcn binding proteins)
|
|
|
What drug do we test in the lab for MRSA?
|
Oxacillin (actually now we mostly use cefoxitin for increased sensitivity)
|
|
|
How to increase sensitivity of MRSA detection?
|
Adding 4% NaCl to the agar
Using cefoxitin instead of oxacillin |
|

What is this test?
|
D test
Tests inducible clindamycin induction (Clinda can be induced to resistant when certain enzymes are present. Must to D test for all organisms resistant to erythromycin but susceptible to clinda) Report as resistant by induction |
|
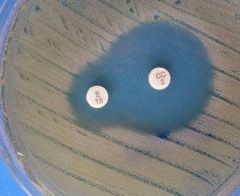
Is this a positive D test?
|
NO.
Report at susceptible by induction |
|
|
All enterococcus is naturally resistant to?
|
Cephalosporins
Clindamycin TMP/SXT |
|
|
How to treat enterococcus endocarditis?
|
AMP & GENT
Enterococcus shows SYNERGY with aminoglycosides |
|
|
What drugs do we use to treat VRE?
|
Linezolid,
Synercid |
|
|
What is the mechanism of resistance in VRE?
|
Plasmid mediated; bypasses metabolic block
|
|
|
What organisms can have ESBLs?
|
E coli
Proteus Klebsiella |
|
|
Mechanism of resistance in ESBL?
|
mobile plasmids!
|
|
|
If ESBL is detected, what should you report? treat with?
|
Report as R to all cephalosporins and penicilins
Cephalomycins ARE susceptible (Cephamycin) Treat with Imipenem; Pip/Tazo (blocks B lactamase function) |
|
|
Test for ESBL?
|
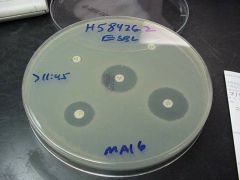
Double disk test
(Organism will be resistant to cephalosporin, but SUSCEPTIBLE to cephalosporin PLUS clavulinic acid |
|
|
What is a KPC?
|
Klebsiella producing carbapenemase
BIG PROBLEM! No drugs to treat this! Resistant to carbapenems and B lactamases |
|
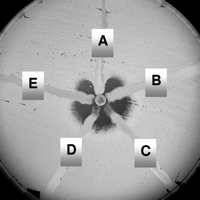
Test for a KPC? (which ones are KPCs?
|
Modified Hodge Test
A, B, E are KPCs: they hug the disk (subjective. best test is molecular...) |
|
|
How do we test S. pna resistance to PCN?
|
OXACILLIN! (because more sensitive)
- If resistant, confirm with MIC testing Or could just do MIC testing as first step (but many smaller labs cannot) |
|
|
What is unique about S. pna PCN resistance?
|
Different MIC values based on site!
CNS: R if greater than 2 mcg/ml Resp or blood: 8 mcg/ml |
|
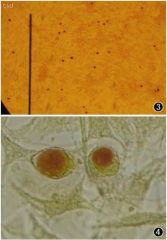
what is this
|
Chlamydia. Old test - stain vacuoles with IODINE
|
|
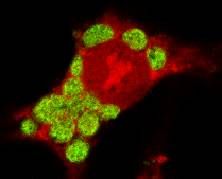
Chlamydia DFA - what is staining?
|
ELEMENTARY BODIES!
|
|
|
What is EIA and give an example of what organism it was used for?
|

Enzyme immunofluorescence
C Diff! (though now use PCR. EIA was 60% sens!) |
|
|
What is endotoxin A in C Diff? B?
|
Endotoxin A: Enterotoxin, FLUID
Endotoxin B: Cytotoxin |
|
|
What is the hypervirulent strain of C Diff?
|
NAP1 strain
|
|
|
What to do if your negative control is positive in an amplification?
|
Contaminated! Invalid run. Cannot report results.
Must return to ORIGINAL specimen |
|
|
What is an internal amplification control?
|
tests to see if amplification occurred in a specific patient (PATIENT SPECIFIC!)
Can have inhibitors (Vagisil, etc). Invalidates PATIENT, not the whole run |

