![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ubiquitous
|
Found anywhere |
|
|
Microorganisms |
Too small to see with the naked eye |
|
|
Microbiology |
The study of microorganisms |
|
|
Robert Hooke |
1). First to describe MOs 2). Seen Blue Mold ( a fungus) 3). While using a crude microscope to look at a thin slice of cork, Hooke saw tiny room-like structures that he named cells. |
|
|
5 types of MOs |
1). Protozoa 2). Bacteria 3). Virus 4). Algae 5). Fungi |
|
|
Cell Theory
|
1). All living things are made of cells.
2). Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3). Living cells come only from other living cells. |
|
|
Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek |
1). Invented single lens microscope 2). First to see bacteria, which he described smaller than molds |
|
|
Spontaneous Generation |
Living organisms came from nonliving matter or a "vital force" |
|
|
Biogenesis |
Living cells arise only from pre-existing cells
|
|
|
Louis Pasteur pt. I |
1). Used Swan Neck Flask experiment to prove that "If no life exists, then no life will arise" 2). Disproved Spontaneous Generation 3) Developed pasteurization and sterilization |
|
|
Swan Neck Flask Experiement |
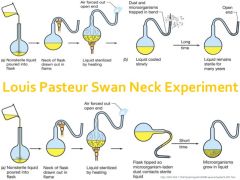
|
|
|
What is the Golden Age of MOs and when was it? |
When: (1857- 1914) Began with Pasteur's work What: An explosion of discoveries and rapid advances in microbiology. Microbiology was established as a science |
|
|
Joseph Lister |
1). Surgeon 2). Conducted the first ANTISEPTIC surgery |
|
|
Antiseptic |
substances that prevent the growth of disease-causing microorganisms
|
|
|
Robert Koch |
1). Investigated the anthrax disease 2). Studied the bacteria that causes tuberculosis and cholera 3). Formulated Koch’s postulates 4). Developed techniques for obtaining a pure culture 5) Invented Petri Dish |
|
|
Koch’s postulates
|
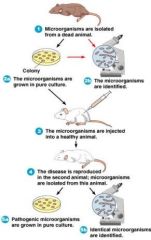
A series of critical procedures to link specific MOs to specific diseases |
|
|
Limitations to Koch's Postulate |
1). Can not always satisfy all postulates for every disease 2). Only applies to infectious diseases (caused by living organisms) 3). Animal model: may cause ethical issues 4). Asymptomatic Carriers 5). Not all MOs can grow in lab medium |
|
|
Pure Culture |
only one strain or clone is present
|
|
|
Asymptomatic Carriers
|
A healthy person who's body has a strong immune system that can contol pathogens |
|
|
Germ Theory of Disease |

1). MOs= Germs 2). MOs could cause diseases 3). Specific MOs causes Specific diseases |

