![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ocular lens (eye piece)
|
Remagnifies the image made by the objective lens.
|
|
|
Objective lenses
|
Primary lenses that magnify the specimen.
|
|
|
Body tube
|
transmits the image from the objective lens to the ocular lens.
|
|
|
Microbiology
|
The study of living things too small to be seen with the naked eye.
|
|
|
Types of Microorganisms
|
Bacteria, Archaea, Fungi, Protozoa, Algae, Viruses, Multicellular animal parasites.
|
|
|
Genus (genera plural)
|
First name and is always capitalized. A group of closely related organisms.
|
|
|
Specific epithet (species name)
|
is not capitalized. Subcategory of genus.
|
|
|
How are Bacteria beneficial?
|
Decomposer, fermentation, digestion, vaccination, antibodies, nitrogen, sulfur and carbon cycle, research.
|
|
|
How are bacteria harmful?
|
cause disease, mold
|
|
|
How to control light on microscope
|
Condensor, Iris Diaphragm, illuminator
|
|
|
Pieces to a Microscope
|
Base, stage, arm, body tube, condenser, iris diaphragm, objective lenses, ocular lens, course adjustment, fine adjustment.
|
|
|
Resolution or Resolving power
|
The ability of lenses to reveal fine detail.
|
|
|
Numerical Aperture
|
Function of wavelengths
|
|
|
Brownian Movement
|
Not true motility, moved by water molecules bumping into it.
|
|
|
Aseptic techniques
|
Procedures used to avoid introducing unwanted microbes and to prevent spreading microbes where they are not wanted.
|
|
|
Complex media
|
media for which the exact chemical composition varies slightly from batch to batch.
|
|
|
Turbid
|
When something becomes cloudy
|
|
|
Gram Stain
|
1. Apply primary Stain (crystal violet)
rinse with water 2. Apply mordant (Gram's iodine) rinse with water 3. Add decolorizing agent (ethanol or ethanol-acetone) rinse with water 4. apply secondary stain (safranin) rise with water |
|
|
Gram Positive
|
Lots of peptidoglycan, small amount of lipids, no lipid A, Teichoic acid. Stain purple.
|
|
|
Gram Negative
|
Small amount of peptidoglycan, lots of lipids, Lipid A, no teichoic acid. Stain red.
|
|
|
What happens when decolorize too much?
|
G+ will look like G-.
|
|
|
What happens when not decolorize enough?
|
G- would look purple.
|
|
|
What does peptidoglycan do in cells?
|
Gives structure to the cell wall.
|
|
|
Plant Kingdom
|
Don't move, energy from sun, produce organic molecules, somewhat flexible.
|
|
|
Animal Kingdom
|
MOve, energy from organic molecules, consume organic molecules, somewhat flexible.
|
|
|
Organic
|
Have carbon and hydrogen.
|
|
|
Prokaryotic
|
Primitive, no nucleus, no membrane-bound organelles, asexual reproduction, single circular chromosome, no histones, if flagella simple.
|
|
|
Eukaryotic
|
Nucleus, membrane bound organelles, sexual reproduction, pairs of linear chromosomes, histones, if flagella complex.
|
|
|
Whittaker
|
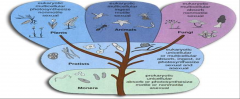
|
|
|
Capsule/Glycocalyx
|
Made of Polysaccharides and peptides. Can protect cell from dehydration. Cell can store extra nutrients here. Allows to stick to environment.
|
|
|
Taxis
|
Ability to move towards or away from stimulus.
|
|
|
Phototaxis
|
Ability for bacteria to move towards/away from light.
|
|
|
Fimbriae
|
Allow organisms to hold onto environment
|
|
|
Pilus
|
Allows to attach to another organism. Can pass DNA through it.
|
|
|
Axial filament
|
Allow spiral organisms to be mobile
|
|
|
What do bacteria need to survive and what do they turn into without it?
|
Cell wall. Will turn into cocci without it.
|
|
|
Plasma membrane
|
Essential for survival of bacteria. Semipermeable. A lot of metabolism happens on it. Many antibiotics target plasma membrane.
|
|
|
Cytoplasm
|
80 percent water. Nutrients floating in it. looks like plate of spaghetti but if stretch it out is one big circle.
|
|
|
Ribosome
|
Makes protein. For cell structure. Can be used for food.
|
|
|
Plasmid
|
Extra chromosomal circle of DNA which codes to make single product. Can code for enzyme to break down lactose. One thing that often passes through pilus.
|
|
|
Inclusion
|
Things that are extra such as phosphate, starch and lipids.
|
|
|
Endospore
|
Thick walled. Purpose is to resist adverse conditions in the environment. Only in rod shaped cells. When cells are dying produce an endospore.
|
|
|
How to grow bacteria
|
a. energy source
b. Carbon source c. Sulfur, Nitrogen, Phosphate d. Metallic elements e. vitamins f. water |
|
|
Prototroph
|
Use light for energy
|
|
|
Chemotroph
|
require organic molecules we eat
|
|
|
Woese
|
a. Domain
b.Kingdom c. Phylum d. Class e. Order f. Family g. Genus H. Spices |
|
|
Streptococci
|
chain of cocci
|
|
|
Diplococci
|
two cocci together
|
|
|
Tetrad
|
four cocci together
|
|
|
Staphylococci
|
cluster of cocci together
|
|
|
Streptobaccilli
|
Chain of bacilli
|
|
|
Maintenance media
|
Has basic ingredients that are needed to keep organisms alive. Doesn't show reaction.
|
|
|
Enriched media
|
Has extra nutrients. Used to grow bacteria rapidly or larger.
|
|
|
Fastidious organisms
|
need something extra or won't grow
|
|
|
Selective media
|
Inhibits some organisms from growing but allows others to grow.
|
|
|
Differential media
|
normally have a sugar, protein and ph indicator.
|
|
|
Microaerophilic
|
require small amount of oxygen
|
|
|
Facultative
|
can live with or without oxygen
|
|
|
Psychrophile
|
require cold temperature. 0 Celsius or less
|
|
|
Mesophile
|
require medium temperature. 25-40 Celsius
|
|
|
Thermophile
|
require warm temperature. 45-60 celsius.
|
|
|
Ways to count microorganisms
|
Counting chamber, spectrophotometer, dilutions.
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Organic catalyst that speed up reactions. made out of protein. Can easily be denatured because made out of protein.
|
|
|
Substrate
|
Something an enzyme acts upon
|
|
|
Holoenzyme
|
Apoenzyme + Coenzyme
|
|
|
Constitutive enzyme
|
Always present in cell. Used for what cells need frequently.
|
|
|
Adaptive or induced enzyme
|
Made only when substrate they act upon is present.
|
|
|
Total magnification
|
magnification of ocular x magnification of objective.
|
|
|
Similarities of prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells
|
a. made of same organic molecules (protein, carbs, lipids and nucleic acid)
b same metabolic pathways |
|
|
Anabolism
|
Single part --> complex whole (repair itself)
requires energy. |
|
|
Catabolism
|
Complex parts --> simple parts
releases energy. |
|
|
ATP
|
ADP + PO4 + E
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
loss of electrons. can happen by gaining oxygen.
|
|
|
Reduction
|
Gain of electrons. Gain hydrogen.
|
|
|
Photophosphorylation
|
taking light energy and turning it into ATP energy
|
|
|
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
|
When a substrate breaks down and in the process you gain ATP (Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle)
|
|
|
Oxidative Phosphorylation
|
substances are broken down (ETC)
|
|
|
Phosphorylation
|
Adding PO4 with a high E bond to something.
|

