![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lab 12: bacteriostatic |
capable of stopping the growth of bacteria |
|
|
Lab 12: bactericidal |
capable of causing bacterial cell death |
|
|
Lab 12: Disinfectants |
chemical agents used on nonliving surfaces |
|
|
Lab 12: Antiseptics |
chemical agents gentle enough to be used on living tissues. |
|
|
Lab 12: Why is Gram negative more resistant than gram positives to chemical control agents. Give an example of genus bacteria. |
Gram negative's outer membrane makes it more resistant to chemical control agents.
For ex: Mycobacterium are difficult to control because of their waxy lipid in cell wall. Clostridium for their endospores. Pseudomonas have plasmids that can inactivate many chemical agents. |
|
|
Lab 12: What is the oxidizing agents we used? And how does it work on bacteria? |
We used Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2). It pulls electrons off proteins and membranes and cause the bacterial cell to lyse. Also breaks disulfide bonds. |
|
|
Lab 12: What is the halogens used? And how does it work on bacteria? |
Bleach and sodium hydrochlorite is what we used. It pulls electrons off proteins and membranes, causing the cell to lyse. |
|
|
Lab 12: What is the alcohol used? And how does it work on bacteria? |
Ethanol, isopropanol is what we used. It dissolved lipids in cell membranes and cause proteins to denature. |
|
|
Lab 12: What is the phenols used? And how does it work on bacteria? |
We used Amphyl. It denatures proteins and dissolve lipids. |
|
|
Lab 12: What were the bacteria used in this experiment? |
Bacillus subtilis (gram + spore former) Staphylococcus aureus (gram +) |
|
|
Lab 13: UV light can form what covalent bonds? |
They can cause Thymines to covalently bond and create "Thymine dimers". |
|
|
Lab 13: Is UV light a weak or strong radiation? |
It is a weak radiation. It's long wavelength makes it difficult to penetrate objects. It can go through cells and membranes. |
|
|
Lab 13: How does bacteria decrease UV absorption? |
1. pigmentation 2. capsule 3. spore formation |
|
|
Lab 14: Another name for disc diffusion? |
kirby bauer test |
|
|
Lab 14: What ager did we use and why? |
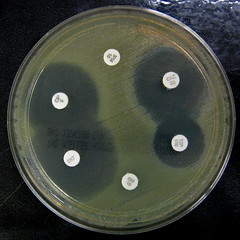
Mueller Hinton agar. It doesn't inhibit activity of certain antibiotics. |
|
|
Lab 14: Antibiotic Resistant |
-Penicillin will tell you that it works with Gram (+) -Ampicillin will effect both +/- and inhibit both gram +/- |
|
|
Lab 14: What can you not tell by disc diffusion? In other words, what information does it not tell you? |
Doesn't determine MIC (minimal inhibitory concentration). Only E-test determines MIC. |
|
|
Lab 15: What are the control for the Pathogenic Cocci experiment? |
Micrococcus luteus, or nonpathogenic selective media. |
|
|
Lab 15: Biochemical test growth medium can either be what? Define the two. |

Selective: encourage growth of some bacteria while inhibiting growth of others. (ex: mannitol salt agar selects for salt tolerant bacteria) |
|
|
Lab 15: Mannitol Salt Agar |
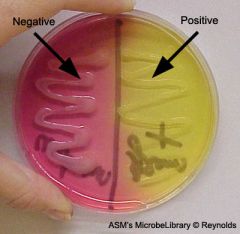
-selective and differential -determine if bacteria can ferment sugar mannitol while in presence of 7% NaCl salt (is the bacteria halogenphile?) |
|
|
Lab 15: Glucose Fermentation Test |

-selective is glucose, differential is phenol red -Red --> yellow = positive for glucose ferm. pH drops, it is acidic. -Red only = negative for glucose ferm. -durham tube traps gas bubble
|
|
|
Lab 15: Esculin Hydrolysis Test |
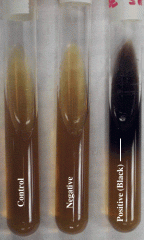
-converting esculin to esculetin. -black= positive result -esculetin reacts with ferric citrate. |
|
|
Lab 15: Hemolysis/Blood Agar |
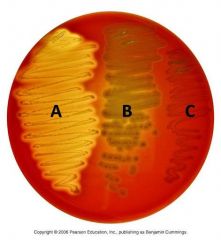
A: Beta
Streptococcus produce enzymes that lyse RBC |
|
|
Lab 15: Coagulase test |

solid serum = positive ex: staph. aureus gives you (+) results, staphococcus epidermidis gives you (-) results |
|
|
Lab 16: Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB) |
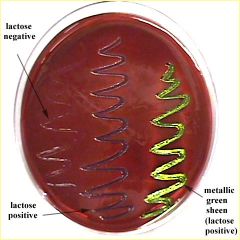
-is selective (lactose) and differential (dye) -works on enterobacteriacea -inhibit Gram (+) growth (ex: Serratia, Proteus, Shigella) -vigorous ferm = green (E. coli) -negative ferm = grey (serratia, proteus, shigella, salmonella) |
|
|
Lab 16: MacConkey Agar |

-test for enteric bacteria (gram neg rod) -selective (lactose, bile salts, crystal violet) -differentiate ( neutral red) -positive (lac ferm) = brick red colonies -negative (no lac ferm) |
|
|
Lab 16: Citrate Test |

-Test to see if bacteria can use citrate as a carbon source. Alkaline is produce giving a alkaline pH. -selective ingredient (citrate), differential (bromthymol blue) -Green = negative result -Blue = positive result |
|
|
Lab 16: Urease |

-it is a differential test (ph indicator phenol red), to see if bacteria can hydrolyze urea with enzyme urease. -negative = yellow |
|
|
Lab 16: Liquid medium |
-yellow + gas (durham tube) = positive -lactose = gas in tube -glucose = no gas |
|
|
Lab 16: Sim test |

-SIM (Sulfur - indole - motility) -motility: growth call “swarming” -indole: red ring is the presence of tryptophanase -H2S production: black = positive result, presence of H2S
-(A) E. coli is (-) for black, (+) for indole -P. mirabilis is (+) sulfur reduction, (+) motility
|
|
|
What is ELISA? |
-ELISA is a test that use antibody and color change to detect a substance. 2 molecules interact: antibody + antigens
|
|
|
What is a plaque? |
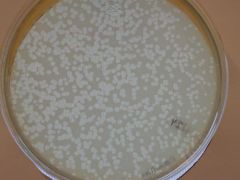
Clearance of bacteria due to bacteriaphage. Virus kills bacteria population. |

