![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Filamentous Appendages |
Composed of protein subunits that form a helical chain. |
|
|
Flagella |
Provides the most common mechanism of motility. |
|
|
Pili |
Extracellular. Multiple forms and functions. Allow cells to: -Adhere to surfaces. -Exchange genetic info ("sex"). -Be motile.
|
|
|
Capsule |
Made of polysaccharide. Distinct and gelatinous. Allows bacteria to adhere to specific surfaces. Allows some bacteria to evade immune defense mechanisms and thus cause disease (pathogenicity). |
|
|
Slime Layer |
Diffuse and irregular. Allows bacteria to adhere to specific surfaces. |
|
|
Cell Wall |
PG. Provides rigidity to bacterial cell walls, preventing cells from lysing. |
|
|
Gram Positive |
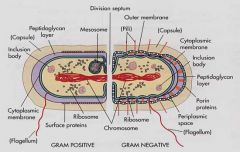
Thick PG layer containing teichoic acids and lipoteichoic acids. |
|
|
Gram Negative |
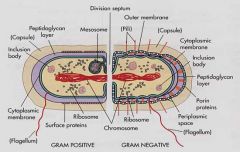
Thin PG layer surrounded by an outer membrane. The outer membrane is composed of lipolysaccharide. |
|
|
Cytoplasmic Membrane |
Phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins. Surrounds the cytoplasm. Separating it from the outside environment. Also transmits external environment info to inner cell. |
|
|
DNA |
Contains the genetic information of the cell. |
|
|
Chromosomal DNA |
Carries genetic info REQUIRED by the cell. Typically a double stranded DNA molecule. |
|
|
Plasmid DNA |
Extra-chromosomal circular DNA molecules. Generally carries extra genetic info that is only advantageous to the cell in certain situations. |
|
|
Endospore |
Dormant cell. Generally extraordinarily resistant to: -heat -toxins -UV radiation -dessication
|
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
Involved in cell reproduction. Holds cell shape. |
|
|
Gas vesicles |
Small rigid structures that provide buoyancy to the cell. |
|
|
Granules |
Accumulations of high molecular weight polymers, synthesized from a nutrient available in relative excess. |
|
|
Ribosomes |
Involved in protein synthesis. 2 subunits: 30S and 50S. Join together to form the 70S ribosome. |
|
|
Myxobacteria |
-travel in packs -release enzymes and break down organic materials as a swarm -have fruiting bodies that are visible to the human eye when in unfavorable conditions
|
|
|
Negative Staining |
-acidic -burns up specimen and leaves on image on the dark background |
|
|
Simple Stains |
-basic dye -easy contrast increase on transparent backgrounds -non-differential |
|
|
Aquaporin |
Membraneous pore proteins that specifically allow water molecules through the cells membrane. |
|
|
Differential Stains |
Stain methods that stain specific cells different ways, making them easier to identify. 2 types: -Gram Staining -Acid-fast Staining |
|
|
Gram Staining |
Identifies two types of cells: -Gram Positive (Purple) -Gram Negative (Pink)
|
|
|
Gram Positive |
-Purple -Thick peptidoglycan layer |
|
|
Gram Negative |
-Pink -Thin peptidoglycan layer -Perriplasm |
|
|
Periplasm |
Gel-like material that fills the region between the cytoplasmic membrane and the outer membrane of Gram Negative bacteria. |
|
|
Transport Systems |
Protein mechanisms that transport nutrients and other small molecules across the cytoplasmic membrane.
*chemicals that interfere with transport systems unique to certain (prokaryotic) cells can be used to selectively destroy those cells without harming human cells that lack the same specifically targeted transport system. |
|
|
Prokaryotic Cells |
-smaller than eukaryotic cells -high SA:V ratio, making it easier to divide and thus reproduce. -vulnerable to: ____-predators ____-parasites ____-competitors
such disadvantages encouraged them to evolve unique features to cope |
|
|
Eukaryotic Cells |
-more complex -most cellular processes take place in membrane bound environments (organelles). -Have nuclei |
|
|
Light Microscope |
-(1000x) -easy to observe cells |
|
|
Electron Microscopes |
-use electrons instead of light to produce the magnified image -(100,000x) -2 types: ____-Transmission ____-Scanning |
|
|
Electron Transmission Microscopes |
-beam of electrons THROUGH specimen -elaborate preparation |
|
|
Electron Scanning Microscopes |

-beam of electrons scans back and forth OVER specimen -High surface detail -3-D effect |
|
|
Atomic Force Microscopes |
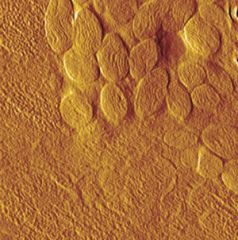
-Produce images of individual atoms -an ultra sensitive probe senses even the slightest movements in the sample. -produces a map showing bumps and valleys of the atoms on the surface of the specimen |
|
|
Bright Field Microscopy |
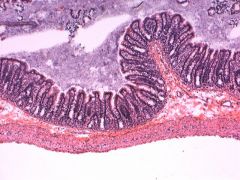
-Illuminates field of view evenly -most common |
|
|
Dark Field Microscopy |
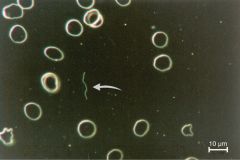
-light is directed towards the specimen at an angle -unstained cells easier to see -organisms bright against dark background -Treponima pallidum (Syphilis) |
|
|
Phase Contrast Microscopy |
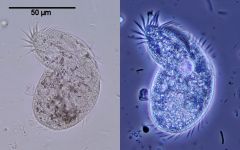
-increases contrast by amplifying differences in the refractive index. -makes unstained cells easier to spot -Paramecium bursaria (green algae symbiont) |
|
|
Differential Interference Contrast Microscopy |

-2 light beams pass through specimen and then recombine -image appears to be 3-D |
|
|
Refractive Index |
-Measure of the relative speed of light (c) as it passes through a medium |
|
|
Contrast |
-affects ease of visibility |
|
|
Capsule Stains |
-negative stains for viscous capsules that don't take up certain stains -BG stained |

