![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 4 basic tissues of the body? |
Epithelium Connective tissue Muscle Nervous tissue |
|
|
What is the embryonic derivation of muscle tissue? |
mesoderm |
|
|
How would you classify the three basic muscle types in terms of voluntary/involuntary and striated/smooth? |
skeletal: voluntary and striated cardiac: involuntary and striated smooth: involuntary and smooth |
|
|
Know these terms: Sarcolemma Myofibril Myofilament Sarcomere Sarcoplasm Sarcoplasmic reticulum T-tubules Sarcosomes |
Sarcolemma: cell membrane Myofibril: contractile unit of the cell Myofilament: contractile unit within myofibril Sarcomere: from Z to shining Z Sarcoplasm: cytoplasm Sarcoplasmic reticulum: ER T-tubules: extension of sarcoplasmic reticulum Sarcosome: mitochondria |
|
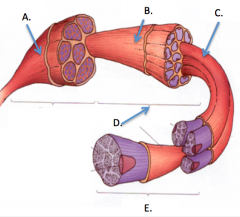
|
A. Epimysium B. Perimysium C. Endomysium D. Fasicle E. Fiber/muscle cell |
|
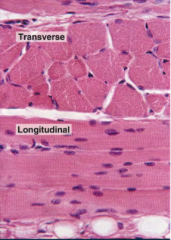
What tissue type is shown? |
Skeletal muscle |
|
|
What are some histologically identifying characteristics of skeletal muscle? |
regular striations peripherally located nuclei acidiphilically stained cytoplasm |
|
|
What are satellite cells? Where can they be found? |
stem cells within skeletal muscle located between sarcolema of muscle cell and basement membrane. (typically can't be seen with light microscope) |
|
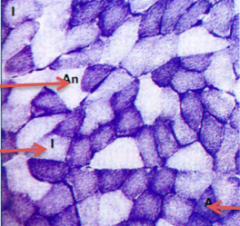
What type of cell is indicated by each red arrow (give name and type)? |
top: Fast twitch/Type 2B middle: Intermediate/Type 2A bottom: Slow twitch/Type 1 |
|
|
Describe slow twitch skeletal muscle fibers in terms of: fatigue resistance speed metabolism number of mitochondria myoglobin concentration |
very fatigue resistant slow aerobic metabolism (oxygen) lots of mitochondria lots of myoglobin (stains darker) |
|
|
Describe fast twitch skeletal muscle fibers in terms of: fatigue resistance speed metabolism number of mitochondria myoglobin concentration |
fatigue easily fast anaerobic metabolism (no oxygen) fewer mitochondria (don't need for metabolism) less myoglobin |
|
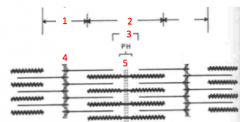
replace each number with the correct letter label |
1. I 2. A 3. H 4. Z 5. M |
|
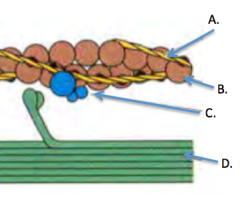
|
A. Tropomyosin B. Actin C. Troponin D. Myosin |
|
|
What is the purpose if titin in skeletal muscle? |
Holds the sarcomere together. Extends from the Z line, through the thick myofilament (myosin), to the M line. Very elastic Regulates the amount of contraction allowed
|
|
|
Describe the connective tissue that makes up the Endomysium, Perimysium, and Epimysium |
Endomysium: loose connective tissue Perimysium: dense irregular connective tissue Epimysium: dense irregular connective tissue |
|
|
Epimysium surrounds the ___________ |
whole muscle (blends with fascia) |
|
|
Perimysium surrounds the ___________ |
muscle fasicle (collection of muscle fibers) |
|
|
Endomysium surrounds the _____________ |
muscle fiber (individual cell level) |
|
|
what tissue makes up tendons? |
dense regular connective tissue |
|
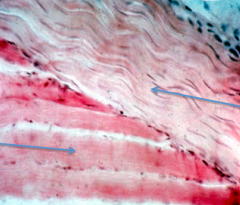
name each tissue |
top: tendon, made from dense regular connective tissue, very regular arrangement of collagen bottom: skeletal muscle |
|
|
In skeletal muscles, nerves, arteries, and veins will branch and go as deep as the ___________. Lymph vessels are only found as deep as the _____________. |
Endomysium Perimysium |
|
|
define a motor unit |
All the muscle cells innervated by a single motor neuron |
|
|
What is a muscle spindle? What does it do? |
sensory organ derived from skeletal muscle lies parallel to muscle cells, within the perimysium detects stretch in muscle, communicates with the CNS |
|
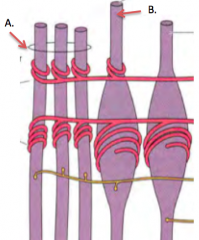
Name the specialized cells within the muscle spindle |
A. Nuclear chain fiber B. Nuclear bag fiber |
|
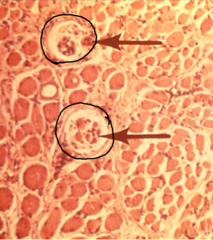
what cells are circled? what type of tissue is surrounding these cells? |
Skeletal muscle spindles Connective tissue capsule and skeletal muscle |
|
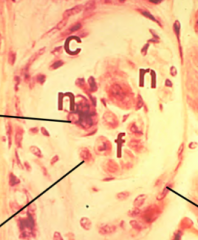
what kind of cell is this? what are the lines pointing to? |
Skeletal muscle spindle Nuclear bag fiber Nuclear chain fiber Connective tissue capsule |
|
Don't forget this stuff. Just look at it for a minute |
Freebie! |
|
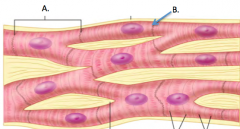
|
A. Cardiac muscle cell B. Intercalated disc |
|
|
What are some histologically identifying characteristics of cardiac muscle? |
striated 1 centrally located nucleus branched intercalacted discs
|
|
|
what is functional syncytium? |
cardiac muscles cells are connected through gap junctions, so that depolarization travels quickly through cells |
|
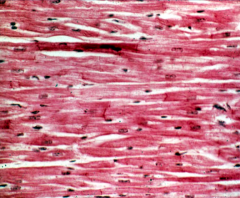
What type of tissue is shown? |
Cardiac muscle |
|
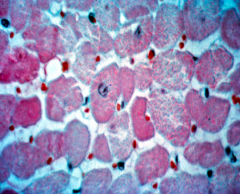
What type of tissue is shown? |
Cardiac muscle |
|
|
What are some histologically identifying characteristics of smooth muscle? |
spindle shaped nucleus can be spiral shaped when cell is contracted, is centrally located cytoplasm stains acidiphilically
|
|
|
How are contractile filaments arranged differently in smooth muscle vs. skeletal or cardiac? |
No T-tubules No troponin tend to have more myosin filaments run the length of the cell, but not in any sort of regular arrangement.
|
|
|
Skeletal and cardiac muscle has 3 types of connective tissue (endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium). What does smooth muscle have? |
Endomysium, no perimysium or epimysium |
|
|
How is smooth muscle stimulated? |
Innervation by nerves (mostly autonomic nervous system, not to every cell) stretch irritants hormones |
|
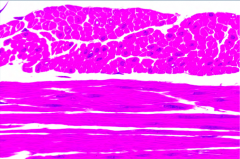
What tissue is shown on top? On bottom? |
Both are smooth muscle |
|

Name this tissue |
Smooth muscle note that the nuclei are oblong, but not pencil thin |
|
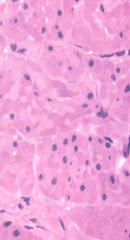
Name this tissue |
Smooth muscle |
|
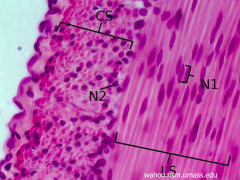
Name this tissue |
Smooth muscle |
|
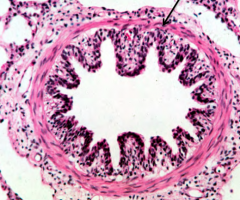
what type of tissue is indicated by the arrow? |
Smooth muscle |

