![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
3 lens and their functions for compound light microscopy
|
Condenser lens:
-focuses light onto plane of specimen Objective lens: -picks up from specimen, focused on focal plane where it is magnified. Ocular lens: -magnifies image from objective focal plane |
|
|
Magnification
|
Objective X Ocular lens
magnification for a 10X objective lens and typical 10 X ocular lensmagnification: 10 X 10 = 100 X |
|
|
Resolution
|
The minimum distance b/w 2 distinguishable objects
|
|
|
Ways to change the resoultion
|
(want to decrease D) by changing alpha or angular aperture (moving objetive lens closer to specimen), using oil (refractive index N is 1.5 for oil) or using blue light
|
|
|
Difference b/w air and oil for microscopic resolution
|
Air has a N=1 and maximum resolution is 0.3 micro meters
for oil N=1.5 and you can get 0.2 micro meters |
|
|
The limit of resolution by light
microscopy is ________ , regardless of the magnification |
0.2 µm
|
|
|
Electron microscopy (EM) vs LM
|
TEM resolution is as little as 1 nano meter and resolving power is 200x better than LM
|
|
|
TEM and SEM are used to reveal cell and tissue____
|
ultrastructures
|
|
|
The thickness of tissue thin sections for light microscopy is usually 4-5 µm so that each section encompasses ___ layer (s) of cells
|
a single
layer of cells in the tissue |
|
|
Examples of basophilic cells
|
DNA and RNA (due to phosph ion)
|
|
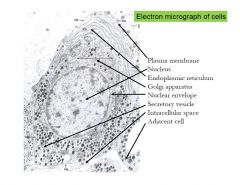
Electron Micrograph of cell
|
Electron micrograph of cell
|
|
|
Haemotoxylin and Eosin (H&E)
color and pH properties |
-Haemotoxylin is blue
and basic so it binds to negative ions -Eosin is pink and is acidic so binds to positively charged structures |
|
|
Acidophilic structures
|
collagen, cytoplasm, eosinophilic granules
|
|
|
Major cellular components seen clearly with light microscope
|
plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, nucleoli
|
|
|
Protiens suspended or intrinsic to phospholibid bilayer are (stationary/fluid) and (rigid/flexibile)
|
Fluid and flexible
|
|
|
Plasma Membrane is made of
|
Protiens (1/2 total mass) and glycocalyx
|
|
|
Types of membrane proteins
|
intrinsic and extrinsic
|
|
|
Glycocalyx description
|
carbohydrate layer that covers external membrane composed of glycoproteins and glycolipids
|
|
|
Glycocalyx functions
|
plasma membrane component that aids in cell recognition intercellular adhesion, and mechanical and chemical protection of brush border
|
|
|
Histones
|
nucleoproteins include these small positively charged proteins that control extent of DNA coiling
|
|
|
Two types of DNA chromatin
|
Heterochromatin and Euchromatin
|
|
|
How to distinguish heterochromatin and euchromatin
|
hetero- tightly coiled, inactive chromatin, DARK irregular clumps
Eu- LIGHTly staining chromatin made up of the DNA being actively transcribed to make mRNA |
|
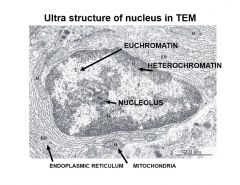
ultra structure of nucleus in TEM
|
Ultra structure of nucleus in TEM -notice euchromatin being lighter and heterochromatin being darker
|
|
|
In a H&E stained slide what color would you expect nucleus to be?
|
Dark Blue
|
|
|
Smooth ER
|
vesicles or cisternae
prominent in liver and cells than are involved in lipid and steroid synthesis STEROID- LIPIDS stores Ca |
|
|
Rough ER
|
has RIBOSOMES on flattened membrane of vesicles and cisternae-- site of PROTEIN SYNTHESIS, protien folding and where glycosylation
|
|
|
Where is portein glycosylation intiated?
|
rER
|
|
|
Ribosome fx
|
Site of protien synthesis (made up of proteins and rRNA)
|
|
|
Golgi structure
|
stacked saccules with peripheral dialations
|
|
|
Golgi's functional polarity membrane flow is made up of what two faces? How do you distinguish the faces?
|
Immature (Cis= convex)- where transfer vesicles arrive
Mature (trans= concave side) where secretory vesicles bud from Golgi |
|
|
Golgi funcitons
|
maturation of various proteins, packaging secretory vesicles
|
|
|
Mitochandria basics
|
contain DNA for synthesis of (mitochondrial specific) enzymes, making enzymes of TCA cycle
|
|
|
Relationship b/w cell energy and number of mitochondria found in cell
|
Cells with high energy requirements have more mitochondria (skin is stationary so has less and muscle cell has the most even over nerve cell)
|
|
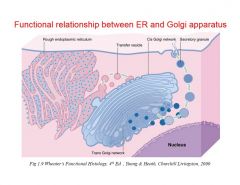
Functional relationship between Golgi and ER
|
Functional relationship between Golgi and ER
|
|
|
Lysosomes
|
vesicles filled wiht acidic hydrolytic enzymes
|
|
|
Three types of lysosoomes
|
primary (the ones budding off Golgi)
seconary (primary fused iwht endosomes Autophagosomes -lysosomes that have fused with worn out organelles |
|
|
Secondary lysosomes are also called and can be distinugished from primary because
|
endolysosomes or phagolysosomes
distinguish bc they have more stuff in tehm more material inside lysosome |
|
|
Endocytosis
|
invagination at the cell surface-formation of an endosome (pino= fluids and phago=particles) and can have receptor mediated endocytosis
|
|
|
Exocytosis
|
Intracellular vesicle binds to cell membrane fuses and opens
|
|
|
Peroxisomes
|
Found in liver and kidneys and just like lysosomes but derived from rER instead of Golgi
|
|
|
Cytoskeleton
|
organized as microfilaments or microtubules and helps cell maintain shape and move and faciliates division and transport or attachment
|
|
|
microtubules
|
pipe-like organization of end-end units of tubulin
PIPE like structure |
|
|
Centriole structure
|
contian 9 sets of microtubule organized pipe like
|
|
|
Cilia and flagella
|
9 sets of doublets surrounding pair of single microtubules for movement
|
|
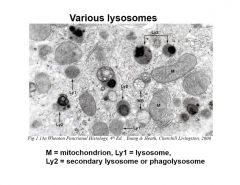
Various lysosomes
|
Notice primary and secondary differences
|
|
|
Filaments of cells
|
Thin (micro) Intermediate and Thick
|
|
|
Examlples of three types of filaments
|
thin= actin
intermediate= desmin, keratin, vimentin thick= myosin |
|
|
How melanocytes appear on H&E stain
|
brown in color
|
|
|
Review major processes during cell cycle phases
|
prophase-migration of centrioles
metaphase-chromatin on equatorial plate anaphase/karyokinesis-sister chromatids separate and migrate towards poles telo- reorganize cytokinesis- cleavage furrow and division |
|
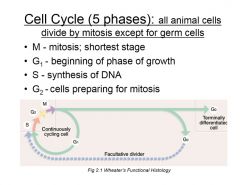
cell cycle
|
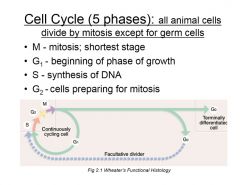
cell cycle
|
|
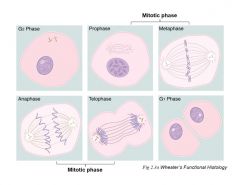
phases
|
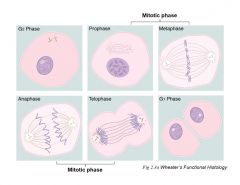
phases
|

