![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Actinomycetes
|

|
|
|
Life Cycle of Actinomycetes
|

|
|
|
Actinomycetes on growth medium
|

|
|
|
Actinomycetes: Motility & Forms
|

|
|
|
Ecological Significance of Actinomycetes
|

|
|
|
Phylum Actinobacteria
|
consists of actinomycetes and their high G + C gram-positive relatives
|
|
|
Characteristics of Actinobacteria
|
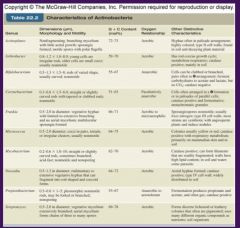
|
|
|
Genus Micrococcus
|

|
|
|
Suborder Corynebacterineae
|

|
|
|
Corynebacterium
|

|
|
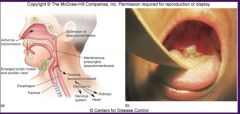
|
Diphtheria
|
|
|
Genus Mycobacterium
|

|
|
|
Structure of Mycolic acid
|

|
|
|
Important species of Mycobacterium
|
-M. bovis – tuberculosis in cattle and other ruminants
-M. tuberculosis – tuberculosis in humans -M. leprae – leprosy |
|
|
TB in the lungs
|
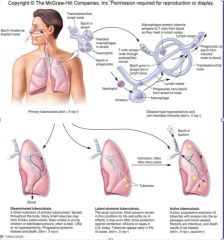
|
|
|
Genus Propionibacterium
|

|
|
|
Streptomycetes
|

|
|
|
Streptomycetes
|

|
|
|
Bifidobacterium bifidus
|

|
|
|
Class Bacilli
|
large variety of gram-positive organisms
|
|
|
Characteristic members of the Class Bacilli
|
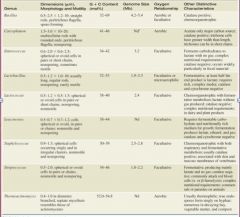
|
|
|
Order Bacillales, genus Bacillus
|

|
|
|
Anthrax
|

|
|
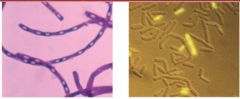
|
a. Bacillus anthracis (purple)
b. B. Cereus (greenish |
|
|
Family Staphylococcaceae
|

|
|
|
Antibiotic Resistant Staphylococci
|

|
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus
|

|
|
|
Bacterial skin diseases
|

|
|
|
Genus Listeria
|

|
|
|
Order Lactobacillales
|

|
|
|
Order Lactobacillales: largest genus - Lactobacillus
|

|
|
|
Order Lactobacillales examples
|
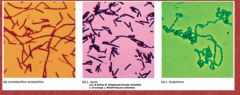
|
|
|
Importance of lactobacilli
|

|
|
|
Genus: Leuconostoc
|

|
|
|
Streptococci classifications
|

|
|
|
Properties of Streptococci and relative
Hemolysis |
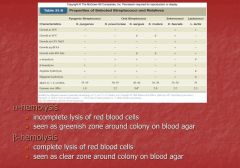
|
|
|
Images of Streptococci
|

|
|
|
Important streptococci, enterococci, and lactococci
|

|
|
|
Streptococcal infections
|

|
|
|
Streptococcal infections
|

|
|
|
Glomerulonephritis
|

|
|
|
Glomerulonephritis diagram
|
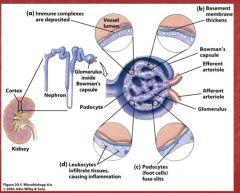
|
|
|
Streptococcus pyogenes
|
– streptococcal sore throat, acute glomerulonephritis, and rheumatic fever
|
|
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae
|
lobar pneumonia and otitis media
|
|
|
Streptococcus mutans
|
dental caries
|
|
|
Enterococcus faecalis
|
opportunistic pathogen (urinary tract infections and endocarditis)
|
|
|
Lactococcus lactis
|
production of buttermilk and cheese
|
|
|
Biochemical cycling
|

|
|
|
Carbon Cycle w/bacteria
|
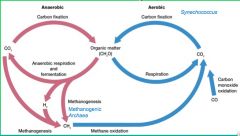
|
|
|
N Cycle
|

|
|
|
Nitrogen cycle products etc
|

|
|
|
Anammox process
|

|
|
|
Nitrogen Cycle Diagram
|
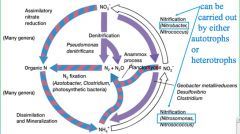
|
|
|
Phosphorous Cycle
|

|
|
|
Phosphorus cycle Diagram
|
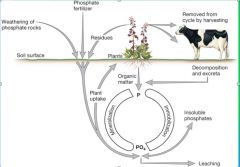
|
|
|
Sulfur cycle
|

|
|
|
Sulfur cycle diagram
|
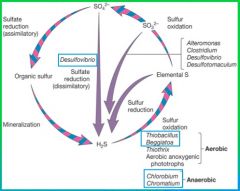
|
|
|
Interaction of Element Cycles
|

|
|
|
Winogradsky column
|
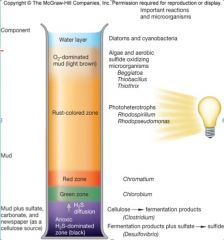
|
|
|
Functions of microorganisms in ecosystems
|

|
|
|
Microbial Interactions
|

|
|
|
Microorganism-Insect Mutualisms
|

|
|
|
protozoan-termite mutualism
|
-termite provides food for protozoan
-protozoan digests cellulose in wood particles, providing nutrients for termite |
|
|
Tube Worm (Riftia)-Bacterial Relationships
|

|
|
|
Tube Worm Diagram
|
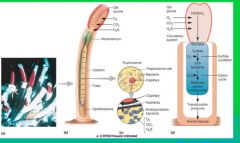
|
|
|
The rumen ecosystem
|

|
|
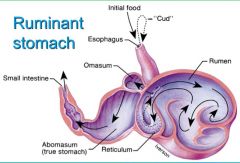
|
ruminant and microbial community have a mutualistic relationship
-specific interactions occur within the microbial community in cows, acetate, CO2, and H2 are used by methanogenic archaea to generate methane (CH4), a greenhouse gas -methane released by belching |
|
|
Commensalism
|
one organism benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped
commensal --organism that benefits |
|
|
An Example of Commensalism
|

|
|
|
More examples of commensalism
|

|
|
|
Parasitism
|

|
|
|
Another example Balance between Host and Parasite
|

|

