![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
pure culture |
a culture that contains one type of microorganisms |
|
|
subculture
|
microorganism that are grown in one culture are moved to another culture for further purify it
|
|
|
mixed culture
|
contain two or more microorganisms easily differentiated microbes
|
|
|
contaminated culture
|
are culture that was once pure but now contains unwanted unidentified microbes
|
|
|
fastidious
|
microbes that contain specific growth factors and complex nutrients growth
|
|
|
quadrant streaking
|
method to dilute and separate individual microbes in order well isolate, pure colonies
|
|
|
colony
|
a population of microbes on a solid growth media. consisting of aggragation of molecules arising from a single parent cell
|
|
|
simple stain
|
single basic positively charged dye to add color to microbial cells so that they can be easily seen. as a result all are stained the same color
|
|
|
differential stain
|
uses two basic positively charged dyes to distinguish between two different microbes groups or structures by color reaction. as result these groups are stained in two contrasting colors
|
|
|
negative stain
|
uses single acidity negativity charged dye to color the background, leaving the microbe unstained. cells appear colorless against a stained background
|
|
|
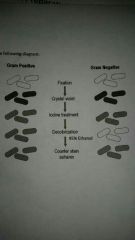
gram stained
|
.
|
|
|
procedural negative stain
|

|
|
|
procedural gram stain prep
|

|
|
|
bacterial smear prep procedures
|

|
|
|
simple stain prep procedures
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
Spore stain scaeffer method. procedures
|

|
|
|
study and identify
|

|
|
|
what is the purpose of heat fixation?
|
the heat coagulates the microbes protiens causing bacteria to stick to slide
|
|
|
what is obtained from simple staining
|
cell size shape and arrangement
|
|
|
why is acid fast stain useful in medicine?
|
Since few microorganisms are acid-fast the stain is useful when is it is suspected that a disease caused by unknown acid fast pathogen
|
|
|
Why is heat needed for a first step of acid fast staining method
|
The cell walls of acid fast bacteria contain thick and waxy layer of mycolic acid which is responsible for a high degree of resistance to chemicals and dyes. steam heat drives the primary stain carbon fuchsin into the acid fast cell walls
|
|
|
during the acid fast stain procedure what color do acid fast and non acid fast bacteria stain
|
Pink acid-fast and blue non-acid fast
|
|
|
Name two genara of acid fast bacteria
|
mycobacterium and nocardia
|
|
|
Name one disease caused by mycobacterium
|
Tuberculosis leprosy nocardosis
|
|
|
Why is steam heat used with the Malachite green in the endospore stain
|
Spores are surrounded by 6 cell walls spore coats which make them resistant to harsh conditions steam heat drive the primary stain malachite green through these four coats
|
|
|
What is an older culture 5 day of Bacillus needed for the end of spore stain
|
spores form under harsh conditions such as during nutrient depletion as a result and older culture is more likely to produce spores
|
|
|
During the end of spore stain procedure what color do the spores and vegetative cells stained
|
Green spores and pink / red vegetative cells
|
|
|
Name two generas of bacteria that produced endospores
|
Bacillus and Clostridium
|
|
|
Name one disease caused by endospore forming bacteria
|
Anthrax tetanus and botulism
|
|
|
Why doesn't the negative stain the nigrosin colorize the cells
|
Negatively charged acidic dyes are repelled by the negatively charged bacterial surface forming a deposit around the organism as a result the background is stained and the microbe is transparent
|
|
|
What is the purpose of negative staining
|
To determine the morphology and arrangement of bacteria to delegate to withstand heat fixing
|
|
|
During the Gram stain what is the purpose of the moredant iodine
|
Iodine forms an intracellular complex with crystal violet making the dye molecules larger and less likely to leave the gram-positive cell during subsequent washings. as a result the Mordant enhances the retention of a crystal violet in Gram positive bacteria
|
|
|
During the Gram stain why is decolorization 95% of alcohol and most critical step
|
During decolorization gram-negative bacteria lost the crystal violet stain while gram positive cells are not decolorize this is what makes the Gram stain differential however over decolorization can lead to misleading results since overexposure to alcohol can also strip crystal violet from cram positive cells making them up here gram negative
|
|
|
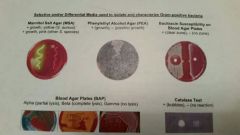
What makes mannitol salt agar MSA selective and differential what does MSA select for |
It selects for bacteria that tolerate 7.5% NaCI differentiates between bacteria according to its ability to ferment mannitol it is used to isolate staphylococcus distinguish between individual species for example staphylococcus epidermidis viruses versus Staphylococcus aureus
|
|
|
What bacteria selectively grow on PEA alcohol how does it selectively inhibit other bacteria
|
It selects for the growth of gram-positive bacteria it inhibits or slows down the growth of gram-negative bacteria by interfering with DNA synthesis
|
|
|
What type of media is blood agar how does alpha beta and gamma hemolysis appear on blood agar plate
|
It is differential enriched media that characterizes bacteria according to its ability to lysis red blood cells 3 results can be observed alpha a greenish hue appears around a colony due to the parcel lysis of red blood cells deta a clear zone appears around the colony due to the complete list of red blood cells gamma no change results due to the presence of non hemolytic bacteria
|
|
|
What type of information is gained from a positive catalase test
|
A positive test indicates that bacteria contain the ends I'm capable of breaking down hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen
|
|
|
What is the purpose of bacitration susceptibility
|
this antibiotic sensitivity test can be used to differentiate between bacteria for example Staphylococcus is resistant to while microcroccus caucus is sensitive
|
|
|
fastidious
|
requires specific growth factors
|
|
|
Name 5 I's of bacteria culture
|
insolation, incubation , isolation,inspection and identification
|
|
|
colony characteristics
|
size, form, shape, properties, texture, elevation
|
|
|
complex media purpose
|
used to grow majority of bacteria, contained nutrients released by patial digested yeast, beef, soy and protiens
|
|
|
Chemically defined synthetic media
|
Used to grow fast fastdious bacteria that require specific growth factors and nutrients its exact chemical composition is known
|
|
|
Selective media
|
favers growth of specific micro organisms and inhibits growth of un- wanted ones
|
|
|
Differential media
|
Distinguishes between groups of microorganisms based on different chemical reactions and appearances
|
|
|
Enrichment media
|
Supplemented with blood serum or other growth factors to promote the multiplication of specific microorganisms
|
|
|
Reducing media
|
Contains compounds that bind free oxygen and remove it from the medium used to grow anaeroboc microorganisms
|
|
|
Fermentation media
|
Contains carbohydrates that contain converted acids plus a pH indicator to monitor acid production a byproduct of fermentation
|
|
|
5 approches for identifying microorganisms
|
macroscopilly, Microscopically, biochemically, immunologically and genectic analysis
|
|
|
Why can't all microorganisms grow on a general purpose media
|
Microbes often require specific growth factors Fast Eddie is bacteria require specific growth factors conditions and may be unable to grow on a general purpose media
|
|
|
How can you tell if a culture has been contaminated
|
At the macroscopic level after growth on solid media you might observe colonies that appear different from known microorganism at the microscopic level after staining a sample you might observe cell shape and arrangement that differ from the known microorganisms
|
|
|
What is the purpose of using aseptic technique
|
Aseptic technique refer to the methods of handling microbial cultures patient specimens and other sources of microbes in a way that prevents infection of the handler and others who may be expose it prevents the introduction of unwanted microorganisms in a culture or environment
|
|

|

|
|
|
identify
mannitol salt agar phenylethyl alcohol agar blood agar plate catalyst test |
|
|
|
mannitol agar
|

|
|
|
phenylethyl alcohol agar (pea)
|

|
|
|
bacitracin susceptibility on blood agar plates
|

|
|
|
blood agar plates (BAP) Alpha Beta and Gamma
|

|
|
|
catalase test
|

|

