![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
3 major groups of fungi
|
mushrooms, yeasts, and molds
|
|
|
Specific Risk Factors
for Opportunistic Fungal Infxns |
broad spectrum antibiotics
radiation/chemotherapy corticosteroids surgery catheterization Micro-37-ppt-9 |
|
|
Fungal Cell Wall Components
|
Chitin
Beta Glucan Mannan Micro-37-ppt-15 |
|
|
Chitin
|
Rigid Polysaccharide Component of Fungal Cell Wall
Micro-37-ppt-15 |
|
|
Beta Glucan
|
Fungal Cell Wall Component
Micro-37-ppt-15 |
|
|
Mannan
|
Fungal Cell Wall Component
Micro-37-ppt-15 |
|
|
Fungal Membrane Antimicrobial Target
|
Ergosterol/zymosterol
Micro-37-ppt-15 |
|
|
Thermal Dimorphic
Conversion |
When a fungus grows as yeast at one temp and mold at another (eg 25 C vs 37C)c
|
|
|
Yeast
|
Oval fungal cell that reproduces through budding
Micro-37-ppt-20 |
|
|
encapsulated yeast
|
"Automatically go for cryptococcus"-
Micro-37-ppt-25 |
|
|
Pseudohypha
|
elongated yeast cell
occurs when budding yeast cells fail to detach increased SA: better adherence to human tissue larger cell: more resistant to phagocytosis Micro-37-ppt-26 |
|
|
Germ tube
|
elongated appendage growing from a yeast cell,
a virulence factor for adhesion and invasion (proteases) Only C. albicans and C dubliniensis capable of forming germ tube Micro-37-ppt-29 Micro-39-pdf-3 |
|
|
Mold
|
Multicellular filamentous colony
Micro-37-ppt-31 |
|
|
Hypha
|
long filament of cells, characteristic of mold
(compare to pseudohyphae, characteristic of yeast) Micro-37-ppt-37 |
|
|
Hyphal Septation of
Aspergillus, Rhizopus, Mucor |
Aspergillus is septate
Rhizopus and Mucor are not Micro-37-ppt-39 |
|
|
Mycelium
|
mat of hyphae (mold)
Micro-37-ppt-41 |
|
|
Fungal Spores
|
Aka sporangiospores
Asexual Reproduction Produced within the Sporangium (Sac) on the end of the sporangiophore (Stalk) Micro-37-ppt-44 |
|
|
Sporangium
|
The sac which contains fungal spores (aka sporangiospores)
An asexual reproductive structure, located on the end of a sporangiophore (stalk) Micro-37-ppt-44 |
|
|
Sporangiophore
|
Stalk which bears the sporangium (sac) full of spores (aka sporangiospores, asexual reproduxn)
Micro-37-ppt-44 |
|
|
Conidium
|
Non-ensaculated cluster of spores (conidiospores) on the end of a conidiophore (stalk).
Micro-37-ppt-49 |
|
|
Conidiophore
|
The hyphal stalk of a mold which bears the conidium (a non-ensaculated cluster of spores (conidiospores))
Micro-37-ppt-50 |
|
|
Fungi with Conidium
|
Penicillin and Aspergillis
Micro-37-ppt-53 |
|
|
Arthroconidium
|
Spore prodxn via hypha fragmenting
Micro-37-ppt-56 |
|
|
Chlamydoconidium
|
Spore prodxn via swollen hypha
like bacterial endospores: suvival mode. don't see in ts unless almost dead. don't see in clture for weeks. Candida Micro-37-ppt-56 |
|
|
Microcondium
|
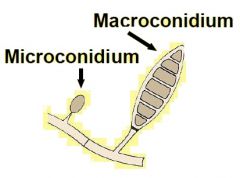
Organism: Trichophytion (dematophyte)
unicellular spore bud (dematophyte) Micro-37-ppt-63 |
|
|
Macroconidium
|
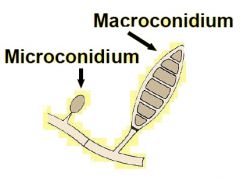
Organism: Microsporum (dematophyte)
multicellular spore bud Micro-37-ppt-63 |
|
|
Blastoconidium
|
Spore prodxn via by budding
Candida Micro-37-ppt-56 |
|
|
Mycosis
|
fungal disease: produces inflammation and granulomas
No toxigenic virulence factors (eg, exotoxins, endotoxins) are associated with a mycosis. Micro-37-ppt-72 |
|
|
Systemic/Endemic Mycoses
|
Coccidiodomycosis
extremely serious Micro-37-pdf-7 |
|
|
Superficial Mycoses
|
Thrush and Dermatophytes
Micro-37-pdf-7 |
|
|
Subcutaneous Mycoses
|
Sporotrichosis and Myetoma
Micro-37-pdf-7 |
|
|
Opportunistic Mycoses
|
Candidaisis and Crytpococcosis
Micro-37-pdf-7 |
|
|
Madura foot
|
Gross Manifestation of Subcutaneous Mycoses
Micro-37-ppt-78 |
|
|
What Patients Get
Candidia Mucosal Infections |
Pts with Immunosuppression, contraceptive, antibiotics
Micro-37-ppt-78 |
|
|
What Patients Get
Candidia Skin Infections |
elderly & obese: moist areas of folded skin
Micro-37-ppt-78 |
|
|
Candidal paronychia
|
localized inflammation around the nails
Micro-37-ppt-78 |
|
|
Systemic Candidiasis
|
Respiratory, UTI, candidemia
Micro-37-ppt-78 |
|
|
Virulence Attributes of Candida
|
Adherence to tissue & prosthesis (biofilms)
Form germ tubes & hyphae (tissue invasion) Extracellular enzymes: phospholipase, proteinase, hemolysin (break down tissue) Micro-37-ppt-87 |
|
|
Growing Fungi in the Lab
|
•Aerobes for most part
•Submit suitable specimens •Safety cabinets for molds •Avoid inhaling spores •Yeasts grow rapidly, identified biochemically •Molds may require weeks to mature, identified structurally Micro-37-ppt-93 |
|
|
What Patients get Oral Candidiasis
|
Pt's with
chornic local irritant ill-fitting or poorly maintained appliances pts with disturbed oral microbiota Micro-37-pdf-8 |
|
|
Cryptococcus
Features Patients |
Polysaccharide Encapsulated yeast resistant to immune defenses.
Oral infections seen in HIV patients. Micro-37-pdf-8 |
|
|
Common Media for Fungi Growth
|
•Sabouraud agar
•Potato dextrose agar Micro-37-ppt-94 |
|
|
Staining Skin Scrapings of Fungi
|
10% KOH (clears tissue) for direct observation
Gram Stain Chlorazole Black (India Ink & KOH) "I cannot stress enough how fast a physicaln can emake a presumptive dx just by using a scraping or lesion under the microscope" -Dr. J Micro-37-ppt-94 |
|
|
Ketoconazole-itraconazole
|
Anything with an azole inhibits ergosterol synthesis
Used vs Candida Micro-37-ppt-97 |
|
|
Amphotericin B
|
A Polyene (like nystatin)
Targets ergosterol to cause membrane damage. Used vs. Systemic Fungi Micro-37-ppt-97 |
|
|
Griseofluvin
|
Targets MT's to interfere with mitosis
Used vs dermatophytes Micro-37-ppt-97 |
|
|
Flycytosine
|
interferes with DNA and protein synthesis
Micro-37-ppt-97 |
|
|
Terbinafine
|
Used vs. dermatophytes
Inhibits ergosterol synthesis Micro-37-ppt-98 |
|
|
Caspofungin
|
Used vs Candida & Aspergillus
Inhibits glucan synthesis (cel wall) Micro-37-ppt-98 |
|
|
Endemic Mycoses Ranges
|
image
Micro-39-ppt-3 |

