![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
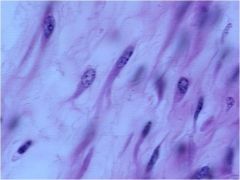
|
mesenchymal cells: stem cells of bone and cartilage |
|
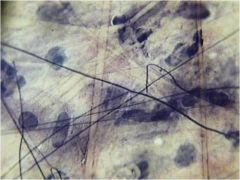
|
CT: collagenous fibers; fibroblast nucleus; elastic fibers |
|
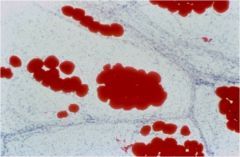
|
adipocyte |
|
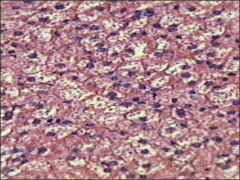
|
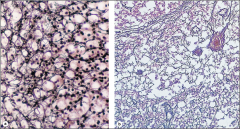
brown adipose tissue; multilocular (multiple lipid droplets); heat generation; many mitochondria |
|
|
brown adipose tissue |
|

|
collagen; Many cells synthesize collagen –fibroblasts, chondroblasts, osteoblasts, odontoblasts, others; Procollagen is formed in the fibroblast; high tensile strength |
|
|
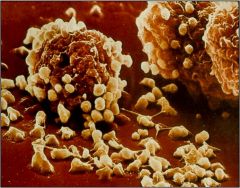
degranulation of mast cells |
|
|
dense ct |
|
|
elastic fibers; capable of stretching; Aorta and elastic arteries,lungs, vocal cords, dermis, pinna of ear, epiglottis; Produced by fibroblasts andsmooth muscle |
|
|
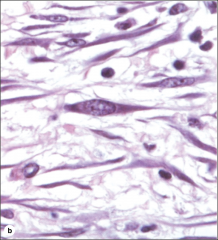
fibroblasts: form collagenous, elastic, and reticular fibers of the matrix |
|
|
fibroblasts: resident cells of ct |
|
|
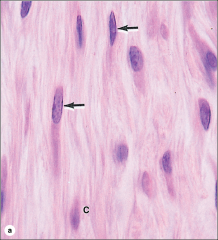
dense ct: fibrocytes found in tendons, ligaments, cornea |
|
|
glycoproteins: fibronectin and laminin; make up ground substance |
|
|
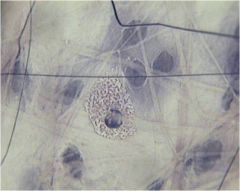
mast cell |
|
|
mast cells; resident cells of ct; release granules that cause symptoms of allergy |
|

|
mucous or embryonic ct; contains mesenchymal cells |
|
|
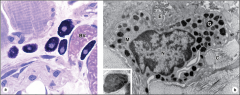
network of reticular fibers |
|
|
reticular cells (fibroblasts) in lymph node |
|
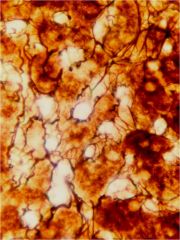
|
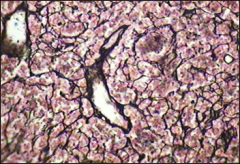
reticular fibers: using silver stain;Collagentype 3 is synthesized by reticular cells(fibroblasts), liver cells, smooth muscle cell and skeletal muscle cells |
|
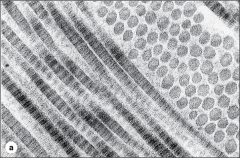
|
type 1 collagen |
|
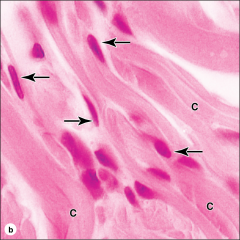
|
type 1 collagen; foundin bone, dentin, dermis, tendons (fibrocartilage); resists tensile forces |
|
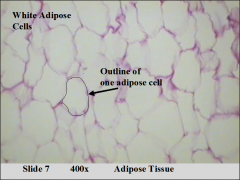
|
white adipose tissue; unilocular (one lipid droplet); energy storage; insulation; endocrine function: secrete leptin |
|
|
reticular fibers: produced by modified fibroblasts (reticulocytes) |
|
|
acinar adenomeres |
|
|
apocrine method |
|
|
apocrine method |
|
|
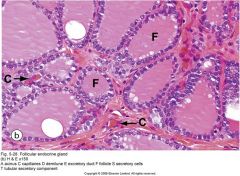
follicular endocrine gland |
|
|
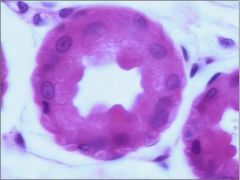
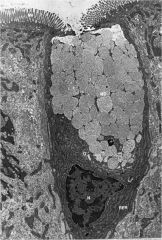
goblet cell: mucinogen granules seen at apical surface |
|
|
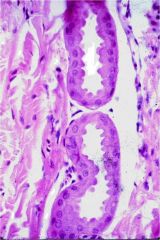
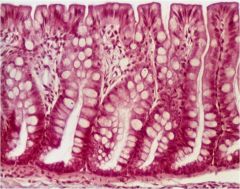
goblet cells and tubular adenomeres |
|
|
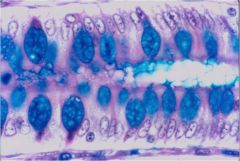
goblet cells: secrete mucinogen granules |
|
|
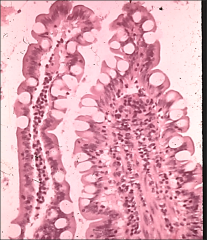
goblet cells in GIT |
|
|
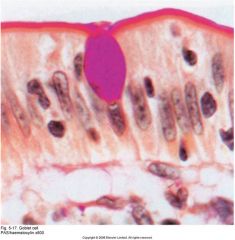
goblet cell: unicellular |
|
|
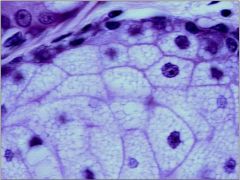
sebaceous gland/holocrine method |
|
|
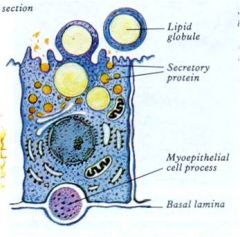
mammary gland: merocrine and apocrine method |
|

|
merocrine method |
|
|
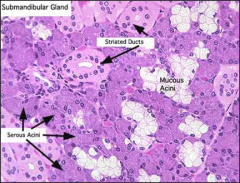
mixed gland (salivary): mucus and serous |
|
|
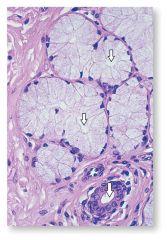
mucus gland |
|
|
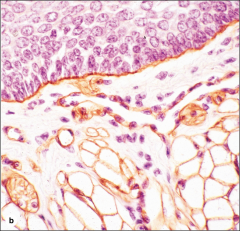
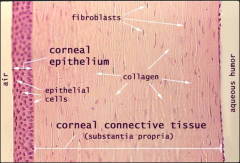
cornea: nonkeratinized stratified squamous |
|
|
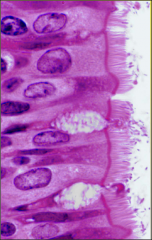
pseudostratified ciliated columnar |
|
|
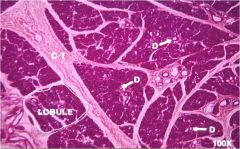
salivary gland with ducts |
|
|
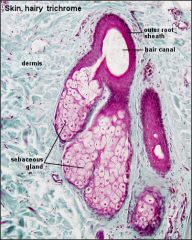
sebaceous gland with hair canal |
|
|
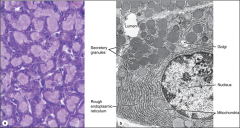
serous gland |
|
|
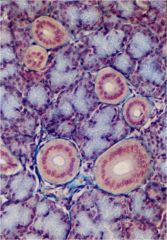
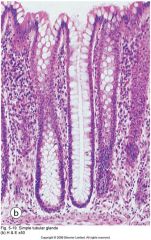
simple tubular gland in SI |
|
|
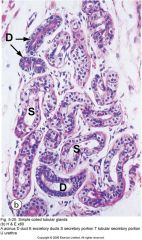
simple coiled tubular; sweat gland |
|
|
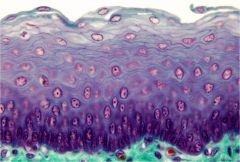
non keratinized stratified squamous; esophagus |
|
|
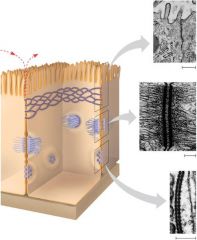
tight junction, desmosome, gap junction |
|
|
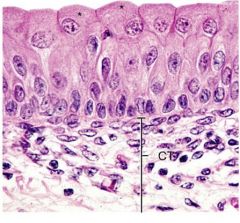
transitional; urinary passages |
|
|
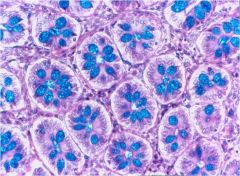
tubular adenomeres in LI |
|
|
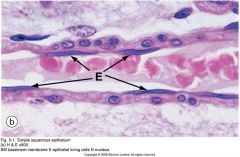
vascular endothelial cells |
|
|
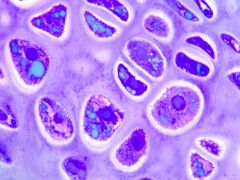
chondrocytes; ocupy lacunae; nucleus; well developed RER; cytoplasm rich in glycogen; lipid droplets present |
|
|
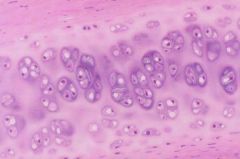
chondrocytes in hyalin; clustered in isogenous groups; territorial matrix is more basophilic due to more abundant GAGs |
|

|
from left to right: perichondrium in hyaline (contains fibroblasts), chondroblasts; chondrocytes |
|
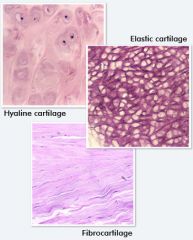
|
types of cartilage: classified based on amount of collagen or elastic fibers in extracellular matrix |
|
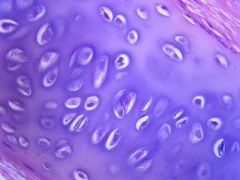
|
hylaine cartilage: reinforced by collagen type 2Fetal axial and appendicularskeleton; Growth plates – physis; Articular cartilage; Costo-chondral junctions; Nasal septum, larynx, trachealrings, bronchi. |
|
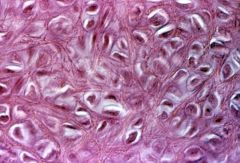
|
elastic cartilage: has perichondrium; chondroblasts and chondrocytes in lacunae; contains abundant elastic fibers-flexible; Found in the larynx (epiglottis and the corniculate andcuneiform processes of the arytenoid cartilage), in theexternal auditory canal and in the ear pinna. |
|
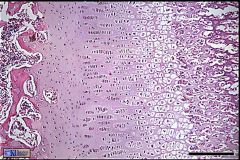
|
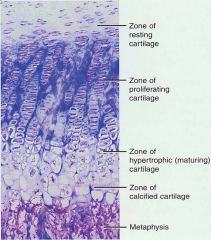
hyaline cartilage growth plate: (from the left) zone of resting/reserve cells; zone of proliferation; zone of hypertrophic cells (interstitial growth) |
|

|
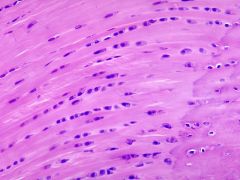
elastic cartilage; with perichondrium; grows occurs by both appositional and interstitial growth |
|
|
fibrocartilage: lacks perichondrium-cannot regenerate; contains chondrocytes and dense fibrous CT (collagen type 1); Found in intervertebral discs,menisci, insertions of tendons,mandibular symphysis, pubicsymphysis |
|

|
dense collagenous CT: contains inactive fibrocytes |
|
|
zones of hyaline growth plate |
|
|
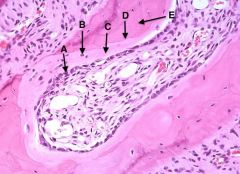
A. osteoblasts B. osteocytes C. osteoid - matrix that undergoes mineralization by deposition of inorganic salts (hydroxyapetite) to form bone D. cement line E. bone |
|
|
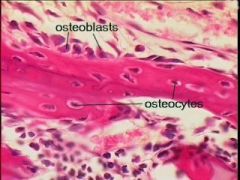
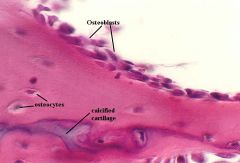
osteoblasts: matrix formation; secrete type 1 collagen; positioned external to osteoid matrix osteocytes: occupy lanucae; form gap junctions with neighboring cells; extend filopodia |
|
|
osteoblasts osteocytes |
|
|
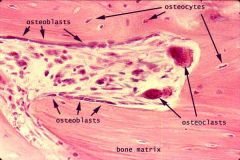
osteoclasts: digest bone; large, multi nucleated cells; originate from pluripotent stem cells in bone marrow |

