![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the parts of the external ear?
|
The pinna and external auditory canal.
|
|
|
What are the different components of the pinna?
|
Cartilage, thin skin, hair follicles, sebaceous and sweat glands.
|
|
|
What are the components of the external auditory canal?
|
The same as the pinna (Cartilage, thin skin, hair follicles, sebaceous and sweat glands) plus cerumen, the waxy substance produced by the cerumenous glands and sebaceous glands.
|
|
|
What is the function of cerumen?
|
It moistens and protects the external auditory canal and tympanic membrane.
|
|
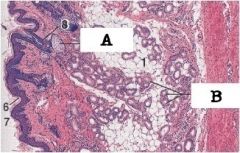
What type of glands are A and B? What part of the ear is this?
|
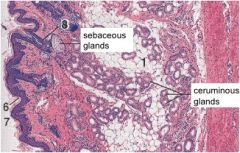
This is the external ear, you can see A - sebaceous glands - and B - sweat glands.
The sebaceous glands are holocrine. The sweat glands are either apocrine or merocrine. |
|
|
What are the components of the middle ear?
|
The tympanic membrane, tympanic cavity, and auditory ossicles.
|
|
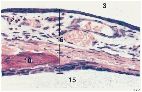
If 3 is the external auditory canal and 15 is the tympanic cavity, what 16? What is 10?
What are the epithelia? |
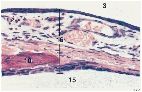
16 is the tympanic membrane.
10 is the malleus. The epithelium on the external auditory canal is stratified squamous epithelium, continuous with the external ear canal. The inner epithelium is simple squamous to cuboidal epithelium continuous with lining of tympanic cavity. |
|
|
What embryonic structures do the outer epithelium, middle layer, and inner epithelium of the tympanic membrane arise from?
|
The outer epithelium arises from the ectoderm, the middle layer from the mesoderm and inner epithelium from the endoderm.
|
|
|
What does the auditory tube connect?
What is its function? What is its epithelium? |
It connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx.
It equalizes air pressure between the two and is lined by ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium. |
|
|
What structures are in the tympanic cavity?
What else is the tympanic cavity known as? What is it filled with? |
Auditory ossicles, vestibular and cochlear windows.
The tympanic cavity is the middle ear. It is filled with air. |
|
|
What are the auditory ossicles? What are they connected to?
What is their main function? |
The tympanic membrane is connected to the malleus, which articulates with the incus, that articulates with the stapes, which is connected to the vestibular window.
The ossicle's function is to change the high amplitude, low power air vibrations to low amplitude, high power vibrations to be transmitted into the inner ear. |
|
|
What are the muscles of the ear?
What is their function? |
The stapedius muscle and tensor tympani muscle.
The stapedius muscle is attached to the stapes and in situations of loud noise, tightens the stapes to not strike the oval window are hard. The tensor tympani muscle attaches to the malleus and acts to tense the tympanic membrane when there are loud noises. |
|
|
What are the nerves of the middle and inner ear?
Which is effected by middle ear infections? |
The chorda tympani nerve of CN VII innervates the middle ear. Effected by middle ear infections.
The vestibular nerve and cochlear nerve are branches of CN VIII and innervate the inner ear. |
|
|
What are the functions of the inner ear?
|
Vestibular and hearing functions.
|
|
|
didn't do any of page 8
|
didn't do any of page 8
|
|
|
What parts of the bony labyrinth are involved in vestibular function and hearing?
What lines the inside of the bony labyrinth? |
The vestibule and semicircular canals are involved in vestibular function. The vestibule and cochlea are involved in hearing.
The bony labyrinth is lined with endosteum. |
|
|
actually stopped at the membranous labryinth of slide 8
|
actually stopped at the membranous labryinth of slide 8
|

