![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Atoms |
•Smallest unit of matter. Consist of electrons, protons, neutrons. |
|
|
Element |
•A substance that cannot be broken down.(Base) |
|
|
Isotopes |
•Element with the same # of protons but different # of neutrons. (Very reactive) |
|
|
Compound |
•Molecule that contains at least two different kinds of elements. (Glucose) |
|
|
Covalent Bond |
Chemical bond formed by two atoms sharing one or more pairs of electrons. |
|
|
Ionic Bonds |
•An attraction between ions of opposite charge that hold them together to form a stable molecule.(ion, cation, anion) |
|
|
Hydrogen bonds |
•Weak bonds formed by attraction of positively charged hydrogen atom to a negatively charged atom. •Found in DNA |
|
|
Organic |
•When there is a C to C OR C to H bond then it's organic. •Carbon Base |
|
|
Inorganic compound |
•Do not contain C to C bonds or C to H bonds. Typically composed of elements other than carbon. •Carbon base if not it's inorganic. |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
•Organic compounds that include sugars and starches. •H and O in a 2 to 1 ratio. General formula is CH2O |
|
|
Monosaccharide |
•Single sugar molecule(ex. Deoxyribose, glucose, fructose) found in DNA |
|
|
Disaccharide |
•2 monosaccharide connected together through dehydration synthesis.(ex. Maltose, sucrose, lactose) |
|
|
Polysaccharides |
•Polymers of sugars, have storage & structural roles. |
|
|
Starch |
•a storage polysaccharide of plants, consists entirely of glucose monomers. •Is a complex sugar molecule. |
|
|
Cellulose |
•Made the same way as starch. •Polysaccharide is a major component to plant cell walls. |
|
|
Chitin |
•Another structural polysaccharide, is found in the exoskeleton of arthropods and fungi. •No glucose monomer |
|
|
Alpha |
•Starch, all heavy molecules are on one side. |
|
|
Beta |
•Cellulose, heavy molecules alternate. |
|
|
Complex Lipids |
•Can also contain phosphorous, nitrogen, or sulfur. |
|
|
Saturated lipids |
•Do not have C-C double bonds. •Compact, not as much room for enzymes to breakdown. Increase bad cholesterol. (Bad for you) |
|
|
Unsaturated fats |
•Not compact, easier for body to break down. (Good for you) •Have one or more C-C double bonds. |
|
|
Phospholipid |
•Produce cell membrane. •Phospolipid has hydrophilic head & hydrophobic tails. (This creates a barrier) •Barrier called by-layer, will not let things in or out. •Also steroids are hydrophobic & can get pass the by-layer with ease. |
|
|
Monomer |
•Same thing bound together over & over. •Example: Glucose-glucose-glucose-glucose-glucose |
|
|
Dehydration Synthesis |
•Losing water H2O to make something new. •Triglyceride is created by the action of dehydration synthesis. |
|
|
Amino acid groups |
•Hydrophobic amino acid •Alcoholic •Aromatic •Acidic •Basic •Amides •Sulfur •Imino Amino acid=Simpliest form of protein |
|
|
Protein structure- Primary structure |
•The unique sequence in which the amino acids are linked together to form polypeptide. •Form polypeptide |
|
|
Protein structure- Secondary Structure |
•Repetitous twisting or folding of the polypeptide chain which forms alpha helix or beta pleated sheet. •Form alpha helix & beta pleeted sheet |
|
|
Protein structure- Tertiary structure |
5 reasons it folds •Hydrogen Bond occur •Hydrophobic interaction occur •Create Disulfide bond •Create a covalent bond •Create ionic bond |
|
|
Protein structure- Quaternary Structure |
•Two or more individual polypeptides joining to operate as a functional unit. •Formed by same bond types •Separate primary structures, seconday structures & tertiary structures. •Separate peptides entirely •Only thing they share is tertiary structure |
|
|
DNA |
•Thymine, adenine, cytosine, guanine •Double stranded •Everything you are •Deoxyribose is DNA's backbone |
|
|
RNA |
•URACIL, Adenine, guanine, cytokine •Single stranded •Translate •Codes for a single thing •Ribose- RNA's backbone |
|
|
Denature |
•Structure/shapes changes •For a protein to function properly it has to be a specific shape. |
|
|
Protein- Amino acid |
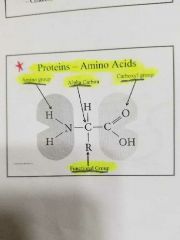
|

