![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Know terms |

Without these bad micros would love to grow in their place |
|

|
Symbiosis - a relationship between two organisms (i.e. Normal microbiota and the host) in which at leadt one organism is dependent on the other |
|
|
Microbial antagonism |
Competition between microbes |
|
|
How do normal microbiota protect the host |
-occupying niches that pathogens might occupy -producing acids -producing bacteriocins (protein that is produced by one bacterium and inhibits another ) |
|
|
Probiotics |
Live microbes applied to or ingested into the body, intended to exert a beneficial effect *if host has normal microbiota then taking probiotics won't be beneficial because there isn't enough room or space to fill * taking immunosuppressant drugs or antibiotics may require probiotic because normal microbiota can be flushed out taking medications of this sort. |
|
|
Where can normal microbiota be found on and in the human body? |
Nose and throat (upper respiratory ) Eyes (conjunctivia) Mouth Skin Large intestine Urinary and reproductive systems (lower urethra in both genders and vaginal in females) |
|
|
What is Koch's postulates? |
It is a basis for reasoning used to prove the cause of an infectious disease. |
|
|
Define symptom and sign |
Symptom: a change in body function that is felt by a patient as a result of disease Sign: the change in a body that can be measured or observed as a result of disease |
|
|
Define Syndrome |
a specific group of signs and symptoms that accompany a disease |
|
|
What is the difference between communicable disease, contagious disease non-communicable disease |
Communicable - a disease that is spread from one host to another Contagious - a disease that is easily spread from one host to another Non-communicable - a disease that is not transmitted from one host to another |
|
|
what is the difference between incidence and prevalence |
Incident: fraction of a population that contracted a disease during a specific time
Prevalence : fraction of a population having a specific disease at a given time |
|
|
Malaria is an infectious disease cause by infection with protozoan. In certain tropical regions, malaria is constantly present. We would say that malaria is an ________ disease in these regions. -epidemic -sporadic -pandemic -endemic |
endemic - regularly found among particular people or in a certain area. |
|
|
Which of the following statements about the development of infectious disease is correct? -The period of convalescence is the same time during which the person regains health and fully recovers (back to the pre-disease state) -The period of decline is the time when the infected individual's health rapidly deteriorates -The prodromal period is characterized by very severe symptoms. - During the incubation period, the infected individual exhibits obvious signs of sickness. |
The period of convalescence is the same time during which the person regains health and fully recovers (back to the pre-disease state) |
|
|
WHich of the following is classified as a latent disease? -shingles -infectious mononucleosis -tuberculosis -influenza |
Shingles |
|
|
What is pathology? |
Study of disease |
|
|
What is etiology? |
Study of the cause of the disease |
|
|
What is pathogenesis? |
The development of disease. |
|
|
Infection definition |
Colonization of the body by pathogens. |
|
|
Disease definiton |
Abnormal state at which the body is not functioning normally. |
|
|
(Symbisis) what is mutalism |
A type of Symbisis that both organisms benefit from |
|
|
What is commensalism |
Type of Symbisis where one organism benefits and the other if unaffected. |
|
|
What is parasitism |
When one organism benefits at the expense of the other organism. |
|
|
Opportunistic pathogens |
Normally don't cause disease (e.coli) but may in a different enviroment. |
|
|
Sporadic disease? |
Disease that occurs occasionally in a population (ie H1N1) |
|
|
Endemic vs epidemic |
Endemic is constantly present in a population Epidemic is a disease acquired by many hosts in a given area in a short time |
|
|
Pandemic |
Worldwide epidemic (HIV) |
|
|
Herd immunity |
Immunity in most of a population (ie vaccinating people ) |
|
|
Acute disease |
Symptoms develop rapidly |
|
|
Chronic diease |
Disease develops slowly |
|
|
Subacute disease |
Symptoms between acute and chronic |
|
|
Latent disease |
Disease with a period of no symptoms when the patient is inactive |
|
|
Local infection |
Pathogens are limited to a small area of the body |
|
|
Systemic infection |
An infection throughout the body |
|
|
Focal infection |
Systemic infection that began as a local infection |
|
|
Bacteremia |
Bacteria in the blood |
|
|
Septicemia |
Growth of bacteria in the blood |
|
|
Toxemia |
Toxin in the blood |
|
|
Viremia |
Viruses in the blood |
|
|
Secondary infection |
Opportunistic infection after a primary (predisposing) infection |
|
|
Sublcinical disease |
No noticeable sighs or symptoms (in apparent infection) |
|
|
Primary infection |
Acute infection that causes the initial illness |
|
|
Predisposing factors that make body more susceptible to disease |
*Short urethra in females *Inherited traits such as sicklecell gene *Climate and weather *Fatigue *Age *lifesytle *Chemotherapy
|
|
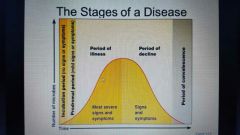
|
Be familiar |
|

|
Be familiar |
|
|
Transmission of disease - contact |
Direct: requires close association between infected and susceptible host Indirect: spread by fomites (door knob, desk etc) Droplet: transmission via airborne droplets |
|
|
Transmission of diseases |
Vehicle : transmission by an inanimate reservoir (food, water) Vectors: antropods, especially fleas, ticks and mosquitoes Mechanical: arthropod carries pathogen on feet (flies) Biological: pathogens Reproduces in vector |
|

|
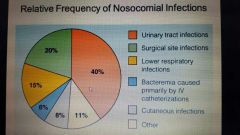
|
|

|
Antibiotic resistance keeps increasing |
|

|

|
|
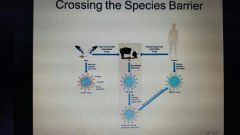
|
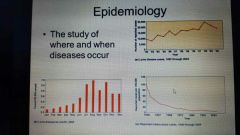
|
|

|

|
|

|

|

