![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Know the metric units of measurement used for microorganisms and their metric equivalents |
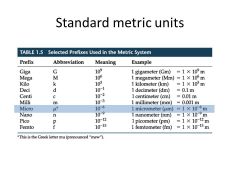
|
|
|
Diagram the path of light through a compound light microscope |
1. Line of Vision (top) 2. Ocular Lens 3. Prism 4. Objective Lens 5. Specimen 6. Condenser Lenses 7. Illuminator (Light comes from here) |
|
|
Study lab exercise on Microscope and look at questions from this LAB! |
do it. |
|
|
Total Magnification |
- objective lens (power) x ocular lens (power) ex. low power (10x) x ocular lens (10x) = 100x Total Magnification |
|
|
Resolution |
ability of lenses to distinguish fine detail and structure. ex. if a microscope has a resolving power of 0.4 um then it can distinguish two parts at least 0.4 um apart - increases with decreasing wave lengths |
|
|
Different Microscopes |
1. Light Microscope 200um-10um 2. Scanning Electron Microscope 10um-1um 3. Transmission Electron Microscope 10um-100um 4. Atomic Force Microscope 0.1 um-10um |
|
|
List steps in preparing a gram stain and describe the appearance of gram-positive and gram negative cells after each step. |
1. Application of Crystal Violet (Primary Stain) Gram + (purple) Gram - (purple) 2. Application of Iodine (Mordant) Gram + (purple) Gram - (purple) 3. Alcohol Wash (Decolorization) Gram + (purple) Gram - (colorless) 4. Application of Safranin (Counter Stain) Gram + (purple) Gram - (Red) |
|
|
Compare gram and contrast Gram Staining and Acid-Fast Staining |
Gram Stain - classifies bacteria into Gram + or Gram - 1. Crystal Violet 2. Iodine 3. Alcohol 4. Safranin Acid-Fast Staining - binds strongly to bacteria with a waxy material in cell walls 1. Carbol Fuchsin (primary stain/mordant) 2. Acid Alcohol (decolorization) 3. Methylene blue (counter stain) |
|
|
Capsule Stain |
used to demonstrate the presence of capsules. because capsules do not accept most stains, the capsules appear as unstained halos around bacterial cells and stand out against a contrasting background. |
|
|
Endospore Stain |
used to detect the presence of endospores in bacteria. When malachite green is applied to a heat-fixed smear of bacterial cells, the stain penetrates the endospores and stains them green When safranin (red) is then applied, it stains the remainder of the cells red or pink. |
|
|
Flagella Stain |
Used to demonstrate the presence of flagella. A mordant is used to build up the diameters of flagella until they become visible microscopically when stained with carbolfuchsin. |

