![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe the contemporary view of conflict |
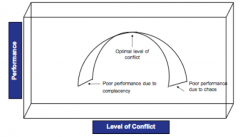
|
|
|
What are the 3 main types of conflict? |
1. Task conflict: Disagreements over the nature of the task 2. Relationship conflict: Focusing on the characteristics of a person or a group rather then the actual task 3. Process conflict: Disagreements over how to go about completing the task, who will be doing what |
|
|
Name 9 causes of conflict |
1. Ambiguity 2. Communication 3. Differences between line/staff 4. Differences in values, beliefs ad goals 5. Participation 6. Resource/task interdependence 7. Rewards 8. Scarce resources 9. Structure |
|
|
What is the difference between interest-based frame and rights based frame? |
Interest based: focuses on the issue and not the person, resolves differences though problem solving discussion Rights/power based: focuses on personal rights, low consideration for other party, resolves differences through threats, generates conflict |
|
|
Describe the 5 conflict resolution styles and the dimensions that the sit on |
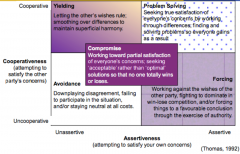
|
|
|
What are 5 strategies for managing conflict? |
1. Standardisation: put in policy and process 2. Planning and scheduling 3. Negotiation or bargaining 4. Superordinate goals 5. Mediation or arbitration |
|
|
What is mediation, inquisition and arbitration and what dimensions do they sit on? |
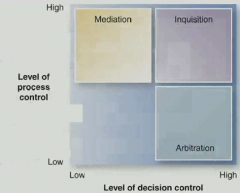
- managers prefer inquisitional but this is usually not the best approach - mediation offers the highest satisfaction with process and outcomes - use arbitration when mediation fails |
|
|
|
The best possible outcome you could achieve from a negotiation |
|
|
What is your resistance point goal? |
The bare minimum you would accept from a negotiation |
|
|
How do you assess the power you have? |
1. consider alternatives - BATNA 2. what skills do you have? |
|
|
What is a BATNA? |
Best alternative to a negotiated agreement determine BATNA before negotiation compare offers to it during the negotiation |
|
|
What are the two general negotiation approaches and how do they differ? - Goal - Motivation - Focus - Info sharing - Duration |
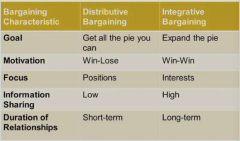
|
|
|
What are the 5 phases of negotiation? |
1. Preparation 2. Contact 3. Explore interests 4. Create options 5. Endgame |
|
|
What is involved in the prep phase of negotiation? |
- planning and goal setting - identify target point/resistance point/ BATNA - develop your power (substantive = improve your BATNA, process = home ground advantage, concessions, agenda) |
|
|
What is involved in the contact phase of negotiation? |
- gathering info - listen - understand - acknowledge - act |
|
|
What is involved in the explore interests phase of negotiation? |
- ask lots of questions - substantive interests = the outcome desired - procedural interests = to be fully heard - psychological and emotional interests = to save face, to have a personal victory |
|
|
What is involved in the options phase of negotiation? |
- make some concessions - suggest more dimensions |
|
|
What is involved in the endgame phase of negotiation? |
- achieve the best possible outcome for your side - power used to trigger agreement - concessions in smaller increments |
|
|
Name 4 common negotiation pitfalls |
1. Myth of the fixed pie 2. Possibility of escalating commitment 3. Negotiators often develop overconfidence in their positions 4. Communication problems |

