![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Group
|
Two or more freely interacting people with shared norms and goals and a common identity
|
|
|
Formal group
|
Formed by the organization
|
|
|
Informal group
|
Formed by friends
|
|
|
Tuckman's Five-Stage Theory of Group Development
|
Forming, storming, norming, performing, adjourning
|
|
|
Forming
|
Group members tend to be uncertain and anxious about their roles, the people in charge and the group’s goals
Mutual trust is low |
|
|
Storming
|
Time of testing
Individuals try to determine how they fit into the power structure Procrastination may occur |
|
|
Norming
|
Questions about authority and power are resolved through unemotional, matter-of-fact group discussion
Group cohesiveness: a “we feeling” binding group members together |
|
|
Performing
|
Actively focused on solving task problems
Climate of open communication, strong cooperation, and lots of helping behavior |
|
|
Adjourning
|
Work is done
Time to move on to other things |
|
|
Roles
|
Expected behaviors for a give position
|
|
|
Task roles
|
Task-oriented group behavior
Keep the group on track |
|
|
Maintenance roles
|
Relationship-building group behavior
Keep the group together |
|
|
Task and Maintenance Roles
|
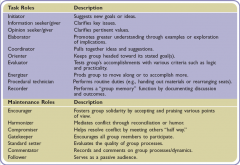
|
|
|
Norms
|
Shared attitudes, opinions, feelings, or actions that guide social behavior
|
|
|
Ostracism
|
Rejection by other group members
If you get ostracized by your team, I’ll have to do something about it |
|
|
How Norms are Developed
|
1. Explicit statements by supervisors or co-workers
2. Critical events in the group’s history 3. Primacy 4. Carryover behaviors from past situations |
|
|
Why norms are enforced
|
Help the group or organization survive
Clarify or simplify behavioral expectations Help individuals avoid embarrassing situations Clarify the group’s or organization’s central values and/or unique identity |
|
|
Team
|
Small group with complementary skills who hold themselves mutually accountable for common purpose, goals, and approach
Task groups that have matured to the performing stage |
|
|
A group becomes a team when...
|
1. Leadership becomes a shared activity
2. Accountability shifts from strictly individual to both individual and collective 3. The group develops its own purpose or mission 4. Problem solving becomes a way of life, not a part-time activity |
|
|
Trust
|
Reciprocal faith in other’ intentions and behavior
|
|
|
How to Build Trust
|
Communication
Support Respect Fairness Predictability Competence |
|
|
Self-managed team
|
Groups of employees granted administrative oversight for their work
|
|
|
Cross-functionalism (self-managed teams)
|
Team made up of technical specialists from different areas
An extremely common form of teaming used today |
|
|
Virtual team
|
Allows group members in different locations using information technology to conduct business
|
|
|
Groupthink
|
Janis' term of coheisve in-group's unwillingness to realistically view alternatives
Syptoms of Groupthink: Invulnerability Inherent morality Rationalization Stereotyped views of opposition Self-censorship Illusion of unanimity Peer pressure Mindguards |
|
|
Social Loafing
|
Decrease in individual effort as group size increases
Reasons for: Equity of effort Loss of personal accountability Motivational loss due to sharing of rewards Coordination loss as more people perform the task |

