![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
206 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Stroke -
Types 2 |
Ischemic - 80%
emboli thrombi systemic hypoperfusion hemorrhagic |
|
|
Stroke -
Risk Factors |
Age
male race HTN diabetes obesity smoking hypercholesterolemia AF carotid stenosis coke alcohol IV drug user |
|
|
Stoke -
Aphasia |
Aphasia
|
|
|
Stoke -
neglect |
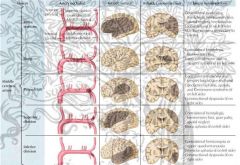
MCA
|
|
|
Stoke -
gaze preference |
MCA
|
|
|
Stoke -
homonymous hemianopsia |
MCA
|
|
|
Stoke -
contralateral hemiparesis - |
MCA
|
|
|
Stoke -
arm/face > leg |
MCA
|
|
|
Stoke -
Amnesia |
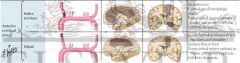
ACA
|
|
|
Stoke -
personality changes |
ACA
|
|
|
foot drop
|
ACA
|
|
|
gait dysfunction
|
ACA
|
|
|
cognitive changes
|
ACA
|
|
|
contralateral hemiparesis -
|
ACA
|
|
|
leg > arm/face
|
ACA
|
|
|
Homonymous hemianopia
|
PCA
|
|
|
memory deficits
|
PCA
|
|
|
dyslexia/alexia
|
PCA
|
|
|
Coma
|
Basilar
|
|
|
CN palsies
|
Basilar
|
|
|
apnea
|
Basilar
|
|
|
visual Sxs
|
Basilar
|
|
|
drop attacks
|
Basilar
|
|
|
dysphagia
|
Basilar
|
|
|
Unilat pure motor or sensory
|
Lacunar
|
|
|
dysarthria -
|
Lacunar
|
|
|
clumsy hand syndrome
|
Lacunar
|
|
|
ataxic hemiparesis
|
Lacunar
|
|
|
Transient neuro deficits
last < 24 hours |
TIA
|
|
|
TIA
most last |
most last < 1 hour
|
|
|
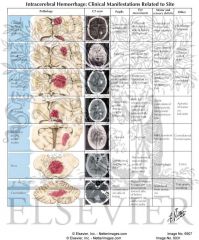
Stoke -
Dx CT without contrast - |
ischemic vs. hemorrhagic
|
|
|
Stoke
Dx |
MRI
EKG echocardiogram |
|
|
Stoke
Dx |
vascular studies -
carotid US MRA |
|
|
Stoke
Dx |
transcranial doppler or MRA
screen for hypercoagulability PE |
|
|
Stoke -
Tx* Vigilance for signs of - |
brain swelling
inc. ICP herniation |
|
|
Stoke -
Tx ischemic stroke if admin within 3 hrs. of onset of Sxs |
* tPA -
|
|
|
Stoke -
Tx ischemic stroke presenting within 48 hours |
* ASA -
|
|
|
Stoke -
Tx * no hypo's |
* no hypotension, hypoxemia,
hypoglycemia |
|
|
Stoke -
Tx for periphery |
* tx aspiration pneumonia,
UTI or DVT |
|
|
Stoke -
Preventive and Long-Term antiagregan |
* ASA, clopidogrel or
dipyridamole/ASA |
|
|
Stoke -
Preventive and Long-Term vascular |
* carotid endarterectomy
|
|
|
Stoke -
Preventive and Long-Term anticoags |
* anticoags
|
|
|
* management of
|
HTN, DM and
hypercholesterolemia |
|
|
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome -
What is it |
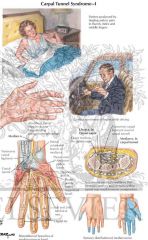
Median n. compression where
passes thru carpal tunnel |
|
|
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome -
Risk factors |
women 30-55
|
|
|
CTS
Risk factors |
repetitive use injury
pregnancy DM |
|
|
CTS Risk factors
|
hypothyroidism
acromegaly RA obesity |
|
|
CTS
pain location and funcionality |
Wrist pain
numbness & tingling of 3 1/2 weak grip dec. thumb opposition |
|
|
CTS when aches
|
thenar atrophy
nocturnal pain & paresthesias |
|
|
CTS Signs ??how worse
|
Sxs may awaken pt. at night
relieved by shaking wrist |
|
|
CTS -
Workup Tinel's sign - |
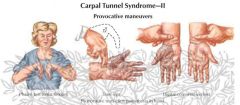
tap
tingle |
|
|
CTS - Phalen's sign -
|
Phalen's sign -
ph-lex (flex) paresthesias |
|
|
CTS to confirm
|
EMG - to confirm
NCV - to confirm eval for risk factors |
|
|
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome -
Tx |
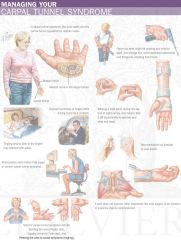
Neutral wrist splint
modify activity create ergonomic work envi |
|
|
CTS Tx medications
|
NSAIDs
corticosteroids - direct injection |
|
|
CTS Tx surgery
|
if Sxs persist -
carpal tunnel release |
|
|
Myasthenia Gravis -
What is it |
Autoimmune
Ab that bind to postsynaptic Ach receptors (nicotinic) block receptors lose receptors |
|
|
MG age
|
young adult women
|
|
|
MG can be associated with -
|
thymoma
thyrotoxicosis |
|
|
Muscle weakness inc. in
periods of activity dec. after rest |
MG
|
|
|
Sx come and go
onset can be sudden fluctuating fatigable ptosis |
MG
|
|
|
MG eye mouth2
|
diplopia (double vision)
dysphagia (swallowing) dysarthria (speech) |
|
|
Sxs worsen throughout day
|
MG
|
|
|
myasthenic crisis -
|
so severe,
resp. failure and aspiration secondary to weakness |
|
|
myasthenic crisis -often secondary to
|
often secondary to infection
(resp. muscles compromised) |
|
|
Myasthenia Gravis -
Hx/PE ocular myasthenia - |
common variant
if doesn't spread in 2-3 yrs, probably won't |
|
|
Myasthenia Gravis -
diagnostic testr |
Edrophonium (tensilon test) -
|
|
|
Myasthenia Gravis -
Dx |
abnormal single-fiber EMG
dec. response to repetitive n. stimulation |
|
|
Myasthenia Gravis - if thymoma
|
chest CT - eval for thymoma
antistriatal ab if thymoma |
|
|
Myasthenia Gravis -
Tx |
* Neostigmine (treat Sx)
|
|
|
* pyridostigmine (treat Sx)
|
* prednisone
|
|
|
* plasmapheresis or IVIG -
temp relief (wks) if severe |
* thymoma resection
|
|
|
Amyotrophic Lat. Sclerosis -
What is it |
Progressive neurodegen. dis
unknown etiology |
|
|
ALS which nerves
|
degeneration of motor neurons
UMN and LMN degenerate => resp. failure and death |
|
|
Amyotrophic Lat. Sclerosis -
Hx/PE |
Slowly progressive weakness
may have fasciculations init UMN and LMN |
|
|
Amyotrophic Lat. Sclerosis -
Dx |
Clinical presentation
EMG and n. conduction studies |
|
|
ALS CT/MRI -
|
cervical spine
check for lesions |
|
|
ALS r/o systemic causes -
|
CBC TSH SPEP UPEP
Ca2+ PTH PFTs |
|
|
ALS urine for heavy metal -
|
(if h/o exposure)
|
|
|
Amyotrophic Lat. Sclerosis -
Tx |
Supportive
pt. education pulmonary specialist |
|
|
ALS medication
|
riluzole
|
|
|
Thiamine (B1) Deficiency -
What are Signs/Sxs |
Wernicke's
|
|
|
Wernicke's
|
inadeq intake or absorption
excessive alcohol interferes with GI absorption and liver storage |
|
|
Wernicke's acute onset -
|
confusion
|
|
|
Wernicke's opthalmoplegia -
|
nystagmus
lat. rectus palsy conjugate gaze palsy abnormal pupils |
|
|
Wernicke's ataxia -
|
vestibular dysfunction
cerebellar dysfunction |
|
|
Wernicke's pts
|
Alcoholics
dialysis hyperemesis starvation |
|
|
Wernicke's pts
|
cancer
AIDS can be triggered by large-dose glucose admin if deficient |
|
|
Wernicke's tx
|
Reversible almost immediately
with thiamine admin |
|
|
Korsakoff's Psychosis -
What is it |
Late complication of
untreated pts. with Wernicke's |
|
|
KP can be triggered by
|
severe or repeated DTs
can be triggered by SAH and thalamic injuries |
|
|
KP ????? memory affected
|
immediate memory affected
confabulation |
|
|
Korsakoff's Psychosis -
Prognosis good |
-
head injury and SAH irreversible - others |
|
|
B12 deficiency -
What are Signs/Sxs |
Subacute combined degen
|
|
|
B12 deficiency -
Pts. |
Pts with pernicious anemia
|
|
|
B12 deficiency -
Tx |
B12 injections or
large oral doses |
|
|
Folate Deficiency -
What are Signs/Sxs |
Irritability
glossitis diarrhea depression neural tube defects |
|
|
Folate Deficiency -
|
glossitis
|
|
|
Folate Deficiency -
Pts |
Alcoholics - alcohol
interferes with absorption Pts. with pernicious anemia |
|
|
Folate Deficiency -
prognosis |
Reversible if corrected early
|
|
|
. Epilepsy -
|
seizure d/o
2+ seizures not related to reversible stressors |
|
|
. was seizure epileptic -
|
Hx
inc. prolactin = epileptic |
|
|
seizure caused by -
. VITAMINS |
vascular
infection trauma autoimmune metabolic idiopathic neoplasm sychiatric (faking it) |
|
|
. anticonvulsant therapy
indicated? |
. anticonvulsant therapy
indicated? 1st seizure not treated when underlying cause unknown |
|
|
Partial Seizures -
What are they |
Arise from focus
limited to one side consciousness usually not lost can progress to generalized simple partial & complex part |
|
|
Partial Seizures -
Simple partial - |
consciousness not impaired
|
|
|
Partial Seizures -motor -
|
Jacksonian march
|
|
|
They are unique in that they travel through the primary motor cortex in succession, affecting the corresponding muscles, often beginning with the fingers. This is felt as a tingling sensation.
|
It then affects the hand and moves on to more proximal areas. Symptoms often associated with a Jacksonian seizure are sudden head and eye movements, tingling, numbness, smacking of the lips, and sudden muscle contractions. Most of the time any one of these actions can be seen as normal movements, without being associated with the seizure occurring
|
|
|
Partial Seizures -
sensory |
- parietal
|
|
|
Partial Seizures -
autonomic |
- BP, HR, PVR
|
|
|
Partial Seizures -psychic -
|
fear, deja vu
|
|
|
Partial Seizures -psychic -
|
fear, deja vu
|
|
|
Partial Seizures postictally -
|
Todd's paralysis is focal weakness in a part of the body after a seizure.
resolves in 1-2 days |
|
|
Partial Seizures Complex partial -
|
consciousness impaired
temporal lobe auditory or visual hallucinat deja vu automatisms |
|
|
Partial Seizures postictal -
|
confusion
amnesia |
|
|
Partial Seizures Workup
|
EEG
|
|
|
Partial Seizures r/o systemic causes -
|
CBC
electrolytes Ca2+ fasting glucose LFTs tox screen RPR renal panel ESR |
|
|
Partial Seizures r/o mass -
|
MRI or CT with contrast
|
|
|
Partial Seizures tx
|
Tx underlying cause
|
|
|
Partial Seizures -
Tx recurrent partial - |
phenytoin
oxcarbazepine tegretol phenobarbital valproic acid |
|
|
Partial Seizures -
Tx kids - |
phenobarbital
|
|
|
Partial Seizures -
Tx |
intractable temporal lobe -
WADA testing |
|
|
Partial Seizures -
Tx |
ant. temporal lobectomy
|
|
|
Generalized Seizures -
What are they |
Begin diffusely throughout
both sides |
|
|
Generalized Seizures - consciousness
|
consciousness always lost
postictal confusion |
|
|
most common types -
|
tonic-clonic (grand mal)
absence (petit mal) |
|
|
Tonic-Clonic Seizures -
|
Start suddenly
with tonic extension of back and extremities rep. symm. clonic movements |
|
|
Tonic-Clonic Seizures -
|
incontinence
tongue biting may look cyanotic consciousness slowly regained |
|
|
Tonic-Clonic Seizures -may complain of -
|
muscle ache
headache |
|
|
Tonic-Clonic Seizures -
Tx |
Tx underlying cause
|
|
|
Tonic-Clonic Seizures -
Tx idiopathic - |
Araklamaci gazeteci - 1st line
lama - adjunctive topiramate - adjunctive |
|
|
Tonic-Clonic Seizures -
Tx symptomatic - |
same therapy as partial sz.
|
|
|
Absence (Petit Mal) Seizures-
What are they |
Begin in childhood
subside before adulthood often familial |
|
|
Absence (Petit Mal) Seizures-
how often |
Brief, often unnoticeable
episodes of impaired consciousness lasts 5-10 seconds have 100's of times/day eye flutters or lips smack |
|
|
amnestic ???
|
amnestic during and
immediately after |
|
|
can be precipitated by
|
hyperventilation
|
|
|
Absence (Petit Mal) Seizures-
Evaluation EEG - |
3 Hz per sec. spike
& wave discharges |
|
|
Absence (Petit Mal) Seizures-
Tx |
eto- 1st line
araklamaci gazeteci zonisamide |
|
|
(West Syndrome) -
|
Infantile Spasms
|
|
|
Infantile Spasms
(West Syndrome) - |
. infantile spasms
(generalized seizures) symmetric tonic |
|
|
Infantile Spasms
(West Syndrome) - |
5-10 at a time while drowsy
or upon awakening . abnorm interictal EEG . arrest of psychomotor dev. |
|
|
Infantile Spasms Tx -
|
ACTH
prednisone clonazepam valproic acid |
|
|
Status Epilepticus -
|
Brain in persist. state of Sz
1 cont. seizure or recurrent w/o regaining cons. > 30 min. med emergency - 20% mortality |
|
|
Status Epilepticus -common causes -
|
anticonv. withdrawal/noncomp
anoxic brain injury alcohol withdrawal metab disturb (hypoNa+) trauma infection |
|
|
Status Epilepticus -usual cause -
|
subtherapeutic or
noncompliance |
|
|
Status Epilepticus -
Evaluation first |
Airway, breathing, circulation
|
|
|
Status Epilepticus -
Evaluation labs - |
electrolytes
anticonvulsants |
|
|
Status Epilepticus -
Evaluation |
get Hx
look for etiology if no prior Hx (tumor, encephalitis, SAH) |
|
|
Evaluation of SE
|
(EEG, CT only when stable)
|
|
|
west syndrome
|
at age of onset
starts at 3-12 months usu male MR |
|
|
Status Epilepticus -
Tx |
Diazepam or lorazepam
|
|
|
Status Epilepticus -
Tx if continues - |
phenytoin or fosphenytoin
|
|
|
Status Epilepticus -
Tx if continues - |
phenobarbital
|
|
|
Status Epilepticus -
Txif continues - |
midazalom or propoful
|
|
|
Headache -
Things to think about (Evaluation) |
Headache new or old
characteristics any associated Sxs any neurological Sxs SAH suspected? |
|
|
Migraine Headache - More commonly affects ????
and those with ???? Hx ????? & ???? abnorm |
More commonly affects women
and those with family Hx vascular & 5HT abnorm |
|
|
Migraine Headache -triggers -
|
menses
OCP chocolate fasting stress bright lights |
|
|
Migraine Headache -
Hx/PE Throbbing > ??? usually lasts < ??? GIS symptoms ????phobia sensitive to ??? |
Throbbing > 2 hrs
usually lasts < 24 hrs n/v photophobia sensitive to noise |
|
|
"classic" migraine -
|
visual aura precedes
unilat |
|
|
"common" migraine -
|
80%
can be b/l, periorbital |
|
|
Migraine Headache -
Dx |
if have focal neuro deficits-
CT or MRI |
|
|
Migraine Headache -
Sxs acute in onset - |
r/o meningitis or SAH
|
|
|
Migraine Headache -
Tx |
Avoid known triggers
aspirin/NSAIDs sumatriptan |
|
|
Migraine triggers
|
aspirin/NSAIDs
sumatriptan |
|
|
Migraine prophylaxis -
|
beta-blockers
TCAs Ca2+ channel blockers valproic acid |
|
|
Cluster Headache -
What is it |
Men
~ 25 y/o - age of onset |
|
|
Cluster Headache -
location duration |
Unilat, periorbital
30 min. - 3 hrs. |
|
|
Cluster Headache -attacks in clusters -
|
same part of head
same time of day same time of year |
|
|
Cluster Headache - precipitators
|
can be precip by alcohol or
vasodilators ipsilat tearing of eye |
|
|
Cluster Headache -
Dx |
HX
|
|
|
Cluster Headache -
Tx Acute therapy with |
high-flow O2
(100% nonrebreather O2) sumatriptan corticosteroids |
|
|
prophylaxis -
|
Ca2+ channel blockers
valproic acid methylsergide |
|
|
prophylaxis important -
|
by the time abortive meds take
effect, has already resolved |
|
|
methylsergine (sansert) - careful??
|
need drug holiday every several months to avoid risk of retroperitoneal fibrosis
|
|
|
MC type diagnosed in adults
chronic |
Tension Headache -
|
|
|
Tension Headache - describe
|
Tight, bandlike pain
occipital and neck |
|
|
Tension Headache - exacerbated by -
|
noise
bright lights stress fatigue |
|
|
Tension Headache - Dx
|
Dx of exclusion
|
|
|
Tension Headache -
Tx |
Avoid exacerbating factors
NSAIDs - 1st line |
|
|
Tension Headache -
prophylaxis - |
Ca2+ channel blockers
alpha blockers TCAs |
|
|
Benign Paroxysmal
|
Peripheral vertigo
otoliths dislodge from usual position migrate over time into semicircular canals abnorm fluid displacement => vertigo |
|
|
Benign Paroxysmal
Positional Vertigo - Hx/PE |
Sudden onset of severe
vertigo and nystagmus vertigo with head movement in direction of affected ear happens turning head in bed 5 sec. - 1 min. n/v Sxs dec. with repetitive tests usu h/o recent trauma |
|
|
Benign Paroxysmal
Positional Vertigo - Dx |
Nylen-Barany Maneuver
(Dix-Hallpike) |
|
|
Benign Paroxysmal
Positional Vertigo - Tx |
Usually subsides spontan.
in wks to months Epley Repositioning Maneuver |
|
|
Meniere's Disease
(Endolymphatic Hydrops) - What is it |
Peripheral vertigo
from buildup of endolymphatic fluid in inner ear |
|
|
Meniere's Disease
|
= V and P change
risk factors - head trauma syphilis |
|
|
Meniere's Disease
(Endolymphatic Hydrops) - Hx/PE |
Sudden attacks of vertigo
lasts up to 24 hours attacks can last hrs to days n/v ear fullness tinnitus hearing loss signif permanent hearing loss can occur over period of yrs |
|
|
Meniere's Disease
(Endolymphatic Hydrops) - Dx |
Audiometry -
low-freq. pure tone hearing loss |
|
|
Meniere's Disease
(Endolymphatic Hydrops) - Tx |
Low-salt diet
acetazolamide |
|
|
Meniere's Disease
(Endolymphatic Hydrops) - Tx acute - |
antihistamines
antiemetics benzos |
|
|
Meniere's Disease
(Endolymphatic Hydrops) - Tx if refractory - |
surgical decompression
|
|
|
Parkinsonism cause antiemetics
|
(metoclopramide),
|
|
|
Parkinsonism cause indole alkaloid antipsychotic and antihypertensive drug
|
reserpine.
|
|
|
Poisoning from 4.................................................... are also causes of Parkinsonism.
|
MPTP, carbon monoxide, cyanide, and
manganese |
|
|
Patients who have
survived an episode of encephalitis can develop |
postencephalitic Parkinsonism.
|
|
|
Parkinsonism + vertical gaze palsy
|
= supranuclear palsy
|
|
|
Parkinsonism + prominent ataxia
|
= olivopontocerebellar atrophy
|
|
|
Parkinsonism + prominent orthostatic hypotension
|
= Shy-Drager syndrome
|
|
|
Severe ................................. can cause a paucity of
spontaneous movement that can mimic Parkinsonism. |
depression
|
|
|
111111111 can be mistaken
for the tremor of Parkinson disease, but the lack of other neurologic symptoms and a positive 22222222 of tremor and its amelioration with 3333333333 distinguish the two entities. |
1 Essential tremor
2family history 33alcohol |
|
|
11111 can present with ataxia and gait disturbances, which can
also be mistaken for Parkinson disease. The presence of 2222 and 333333 with 44444 on a CT scan of the head can help identify this disorder |
1A normal pressure hydrocephalus
2dementia 3urinary incontinence 4dilated ventricles |
|
|
medications available for the medical treatment of Parkinson disease indirecdy
increase the amount of dopamine available |
(COMT inhibitors, selegiline, amantadine),
|
|
|
Direct-acting dopamine agonists such as ----------------can be used alone as initial
therapy or in combination with small doses of levodopa/carbidopa. |
pramipexole or ropinirole
|
|
|
Two other dopamine
agonists are |
bromocriptine and pergolide.
|
|
|
Bromocriptine and pergolide
are 111111 and can cause 222222 |
1ergot derivatives
2cardiac toxicity. |
|
|
Anticholinergics such as benztropine and trihexyphenidyl are used in patientsyounger than 60 years old mosdy to relieve
tremor and rigidity. Avoid with 22222 |
BPH and glaucoma.
|

