![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the range of normal glucose in plasma?
|
4-8mmol/l
|
|
|
Which hormones are involved in levels of adequate nutrition?
|
Insulin
Glucagon |
|
|
Which hormones are involved during levels of stress/exercise
|
Cortisol
Adrenaline (GH) |
|
|
Which hormones are involved during levels of starvation?
|
Cortisol
GH |
|
|
What are the actions of insulin?
|
Promotes uptake of glucose by cells
Promotes glycolysis Promotes formation of glycogen Inhibits glycogenolysis Inhibits gluconeogenesis (OVERALL counteracts increase in plasma glucose/amino acids) |
|
|
How does insulin promote the uptake of glucose into cells?
|
Upregulation of GluT4 transporter protein
|
|
|
On which types of cell is the GluT4 transporter protein found?
|
Adipose tissue
Skeletal and cardiac muscle |
|
|
What happens to GluT4 protein when insulin is present and absent?
|
Insulin absent - usually sequestered - kept in cells
Insulin present - brought to plasma membrane and glucose enters cell by facilitated diffusion down a concentration gradient |
|
|
How does insulin affect the levels of TAGs?
|
Promotes the synthesis and storage of TAGs and inhibits the breakdown of them
Promotes uptake of fatty acids by adipose and formation of glycerol from glucose |
|
|
How does insulin affect the levels of proteins?
|
Promotes protein synthesis and amino acid uptake while inhibiting protein degradation
|
|
|
Does insulin promote catabolism or anabolism?
|
ANABOLISM
|
|
|
Why do insulin levels decrease during the postabsorptive phase?
|
To prevent hypoglycaemia
|
|
|
Why is it important to feed diabetics insulin when they are feeding?
|
Absorptive phase - insulin should be high otherwise hyperglycaemia (high sugar level in blood)
|
|
|
Alpha cells in the pancreas make:
Beta cells make: |
Glucagon
Insulin |
|
|
What effects does glucagon have?
|
Opposite of insulin - liver and adipose tissue
Increases glycogenolysis Increases gluconeogenesis Increases lipolysis Decreases glycogen synthesis |
|
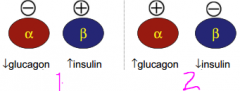
What happens to glucose plasma levels in each circumstance?
|
1. Decrease plasma glucose levels
2. Increase plasma glucose levels |
|
|
What is the insulin:glucagon ratio after a) a high carb meal and b) postabsorptive state?
|
a) High
b) Low |
|
|
What is the insulin:glucagon ratio like in ruminants?
|
Fairly low and fairly constant
|
|
|
Which precursors do ruminants use during feeding and during postabsorptive state?
|
Propionate, amino acids
Amino acids, glycerol |
|
|
How do high protein meals affect insulin and glucagon?
|
Stimulate release of both, preventing hypoglycaemia
|
|
|
What happens to plasma glucose levels during physical activity?
|
They stay constant because:
Physical activity stimulates Sympathetic nervous system which stimulates Glucagon increase, insulin decreases Keeps glucose in plasma |
|
|
How does muscle take up glucose during exercise?
|
Insulin-independently
|
|
|
What effect does adrenaline have on blood glucose levels during exercise?
|
Increases glucagon, decreases insulin
Increases glucose release to plasma, increase lipolysis Catabolic |
|
|
What effect do glucocorticoids have on metabolism?
|
Increase amino acids in blood
Increase lipolysis Increase blood glucose Catabolic |
|
|
What effect does GH have on metabolism?
|
Anabolic on protein (and breakdown)
Breakdown of fats Promotes insulin secretion but gluconeogenesis and uptake of glucose by tissues |

