![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Another name of Alkaptonuria?
|
Ochronosis
|
|
|
Defect in Alkaptonuria?
|
homogentisic acid oxidase deficiency
(in the degradative pathway of tyrosine and phenylalanine homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase converts homogentisic acid to maleylacetoacetic acid) |
|
|
findings in Alkaptonuria?
|
dark connective tissue
pigmented sclera urine turns black on standing debilitating arghralgias |
|
|
inheritance pattern of alkaptonuria?
|
autosomal recessive, benign disease
|
|
|
deficiency that causes albinism?
|
Tyrosinase (inability to synthesize melanin from tyrosine)
Defective tyrosine transporters |
|
|
Only glycogen storage disease that causes early clinical findings in the heart specifically?
|
Pompe disease.
|
|
|
Only glycogen storage disease caused by a defective lysosomal enzyme?
|
Pompe disease.
|
|
|
What are gangliosides made up of?
|
glycosphingolipid (ceramide + oligosaccharide)
+ sialic acid (one or more) |
|
|
Fabry's disease findings?
|
Peripheral neuropathy of hands/feet
angiokeratomas cardiovascular/renal disease |
|
|
Fabry's disease deficient enzyme?
|
serum trihexosidase (α-galactosidase A)
|
|
|
What substrate accumulates in Fabry's disease?
|
Ceramide trihexoside
|
|
|
Fabry's disease is what kind of disorder?
|
Sphingolipidosis lysosomal storage disorder
|
|
|
Fabry's disease mode of inheritance?
|
X-linked recessive
|
|
|
What type of disorder is Gaucher's disease?
|
glucocerebrosidase lysosomal storage disorder
|
|
|
what is the most common lysosomal storage disease?
|
Gaucher's disease
|
|
|
Gaucher's disease findings?
|
Hepatosplenomegaly
aseptic necrosis of femur bone crises Gaucher's cells (macrophages that look like crumpled tissue paper) X-ray demonstrates an Erlenmeyer-flask appearance of the long bones. |
|
|
What enzyme is deficient in Gaucher's disease?
|
β-glucocerebrosidase
|
|
|
What substrate accumulates in gaucher's disease?
|
Glucocerebroside
|
|
|
Gaucher's disease mode of inheritance?
|
Autosomal recessive
|
|
|
what type of disorder is Niemann-Pick disease?
|
Sphingolipidosis lysosomal storage disease
|
|
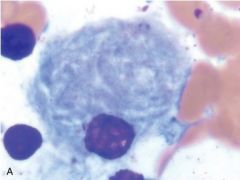
Identify this cell.
|
Gaucher cell
|
|
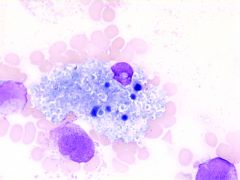
identify this cell.
|
Niemann-Pick histiocyte.
|
|
|
Nieman-Pick findings?
|
Progressive neurodegeneration
hepatosplenomegaly cherry-red spot on macula foam cells |
|
|
Niemann-Pick deficient enzyme?
|
Sphingomyelinase
|
|
|
Niemann-Pick Accumulated substrate?
|
Sphingomyelin
|
|
|
Niemann-Pick mode of inheritance?
|
Autosomal recessive
|
|
|
What type of disorder is Tay-Sachs disease?
|
Sphingolipidosis lysosomal storage disease
|
|
|
Tay-Sachs disease findings?
|
Progressive neurodegeneration
developmental delay cehrry-red spot on macula lysosomes with onion skin no hepatosplenomegaly |
|
|
Deficient enzyme in Sandhoff disease and Tay-Sachs?
|
Hexosaminidase A
|
|
|
Accumulated substrate in Tay-Sachs disease?
|
GM2 ganglioside
|
|
|
mode of inheritance of Tay-Sachs disease?
|
Autosomal recessive
|
|
|
What type of disorder is Krabbe's disease?
|
Sphingolipidosis lysosomal storage disease
|
|
|
Krabbe's disease findings?
|
Peripheral neuropathy
developmental delay optic atrophy globoid cells |
|
|
deficient enzyme in Krabbe's disease?
|
Galactocerebrosidase
|
|
|
Accumulated substrate in Krabbe's disease
|
Galactocerebroside
|
|
|
mode of inheritance of Krabbe's disease?
|
autosomal recessive
|
|
|
What type of disorder is Metachromatic leukodystrophy?
|
Sphingolipidosis lysosomal storage disease
|
|
|
metachromatic leukodystrophy findings?
|
Central and peripheral demyelination with ataxia
dementia |
|
|
deficient enzyme in metachromatic leukodystrophy?
|
Arylsulfatase A
|
|
|
accumulated substrate in Metachromatic leukodystrophy?
|
Cerebroside sulfate
|
|
|
mode of inheritance in metachromatic leukodystrophy?
|
autosomal recessive
|
|
|
What type of disorder is Hurler's syndrome?
|
Mucopolysaccharidosis lysosomal storage disorder
|
|
|
Hurler's syndrome findings?
|
Developmental delay
gargoylism airway obstruction corneal clouding hepatosplenomegaly |
|
|
deficient enzyme in Hurler's syndrome?
|
α-L-iduronidase
|
|
|
accumulated substrate in Hurler's syndrome?
|
Heparan sulfate,
dermatan sulfate |
|
|
mode of inheritance in Hurler's syndrome?
|
autosomal recessive
|
|
|
What type of disorder is Hunter's syndrome?
|
Mucopolysaccharidosis lysosomal storage disease
|
|
|
Hunter's syndrome findings?
|
Mild Hurler's + aggressive behavior
no corneal clouding |
|
|
deficient enzyme in Hunter's syndrome?
|
Iduronate sulfatase
|
|
|
Accumulated substrate in Hunter's syndrome?
|
Heparan sulfate,
dermatan sulfate |
|
|
mode of inheritance of Hunter's syndrome?
|
X-llinked recessive
|
|
|
Findings in von Gierke's disease?
|
Severe fasting hypoglycemia
↑↑ glycogen in liver ↑ blood lactate hepatomegaly |
|
|
deficient enzyme in von Gierke's disease?
|
Glucose-6-phosphatase
|
|
|
von Gierke's disease is what type of disorder?
|
Type I glycogen storage disease.
|
|
|
Pompe's disease is what type of disorder?
|
Type II glycogen storage disease.
|
|
|
Findings in Pompe's disease?
|
Cardiomegaly (can be in neonate)
systemic findings leading to early death |
|
|
What glycogen storage disease is the only one to cause early clinical findings in the heart specifically?
|
Pompe disease, type II
|
|
|
What is seen on muscle biopsy in Pompe's disease?
|
PAS-positive intracellular granules.
|
|
|
Which glycogen storage disease is caused by a defective lysosomal enzyme?
|
Pompe disease.
Lysosomal α-1,4-glucosidase (acid maltase) |
|
|
What type of disorder is Cori's disease?
|
Type III glycogen storage disease
|
|
|
Findings in Cori's disease?
|
milder form of type I
normal blood lactate levels |
|
|
What is the most prominent feature in Pompe's disease?
|
cardiomegaly
|
|
|
Deficient enzyme in Cori's disease?
|
Debranching enzyme
(α-1,6-glucosidase) |
|
|
What type of disorder is McArdle's disease?
|
Type V glycogen storage disorder.
|
|
|
Findings in McArdle's disease?
|
↑ glycogen in muscle
inability to break down glycogen painful cramps, myoglobinuria with exercise |
|
|
Deficient enzyme in McArdle's disease?
|
Skeletal muscle glycogen phosphorylase
(Hers disease is a deficiency of the liver isoform) |
|
|
Deficiency that causes phenylketonuria?
|
Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency
|
|
|
Deficiency that causes histidinemia?
|
I-histidine ammonia-lyase deficiency
|
|
|
Deficiency that causes maple syrup urine disease?
|
Ketoacid decarboxylase deficiency
|
|
|
Deficiency that causes isovaleric acidemia?
|
Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency
|
|
|
juvenile metachromatic leukodystrophy deficiency?
|
sulfatase A deficiency
|

