![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the pathophys of cardiomyopathy?
|
either systolic dysfunction - due to an abnormality of ventricular emptying, secondary to impaired contractility - dilated cardiomyopathy
or diastolic dysfunction - due to an abnormality of diastolic relaxation - hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
|
|
what's the difference between cardiomyopathy and HF
|
cardiomyopathy is a Dx based on a test (or pathology) whereas HF is a clinical Dx
|
|
|
What are the consequences of increased LA pressure?
What are the symptoms? |
hydrostatic forces push fluid into the pulmonary interstitium, fluid fills the alveoli
SOBOE orthopnea PND this is LSHF |
|
|
What are the consequences of increased RA pressure?
What are the symptoms? |
hydrostatic forces push fluid into peripheral interstitium (overwhelm the lymphatics ability to remove excess fluid)
edema ascities weight gain elevated JVP |
|
|
what are the classifications of cardiomyopathies?
|
1. Dilated cardiomyopathy
2. Hypertrophy cardiomyopathy 3. Restrcitive cardiomyopathy 4. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia 5. Unclassified cardiomyopathies |
|
|
Causes of DCM?
|
viruses
gene mutations EtOH thyroid disease Toxic medications pregoness most often idiopathic |
|
|
findings of DCM?
|
whole heart dilation
impaired systolic function functional atrioventricular regurgitation is common prone to arryhthmias |
|
|
Physical exam findings of DCM
|
decreased CO:
tachy decreased BP pulsus alternans pulmonary venous congestion crackles, pleural effusions precordial exam laterally displaced apex S3, MR systemic congestion: increased JVP, increased liver size ascities, peripheral edema |
|
|
Dx studies for DCM?
|
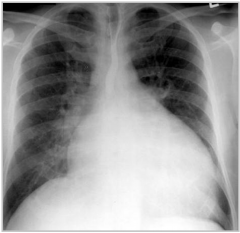
CXR: enlarged cardiac silhouette, vascular redistribution, interstitial edema, pleural effusions
EKG B/W: TSH, ANA, RF, iron, LFTs echo wall motion study cardiac cath |
|
|
treatment and prognosis of DCM?
|
Prognosis 5 year survival 20-60%
treatment (2 categories) - reduce mortality ACEi BB +/- aldosterone anatagonist +/- ICD +/- bi-ventricular pacemaker - improve symptoms diuretics +/- dig +/- nitrate |
|
|
Causes of HOCM
|
most common genetic CV disorder
other causes - severe uncontrolled HTN, AS, athlete's heart, fabry's, metabolic disorders |
|
|
HOCM variants
|
Asymmetric septal hypertrophy without obstruction
Asymmetric septal hypertrophy with obstruction symmetric hypertrophy concentric apical hypertrophy |
|
|
clinical manifestations of HOCM
|
asymptomatic - ECG or echo
symptomatic - dyspnea angina fatigue, pre-syncope, syncope |
|
|
Pathophys of HOCM
|
Diastolic dysfunction due to:
- increased LV cavity stiffness hypertrophy fibrosis - impaired relaxation ischemia - supply demand mismatch abnormal Ca metabolism abnormal LV loading |
|
|
HOCM findings on exam
|
bisferens pulse
S4 murmur of outflow obstruction MR |
|
|
what maneuvers can be done to help differentiate the murmur of HOCM and AS?
How do they work? |
valsava or standing (decrease preload and afterload) making the murmur of HOCM louder and the murmur of AS quieter
squatting (increases preload and afterload) making the murmur of HOCM quieter and the murmur of AS louder |
|
|
management of HOCM
|
investigations:
EKG, ECHO Medical BB CCB LVOT obstruction alcohol spetal ablation myomectomy if high risk for ventricular rhythms - ICD |
|
|
risk factors for SCD
|
family Hx
gene mutations prone to SCD aborted SCD syncope abnormal BP response to exercise non-sustained VT LV septal thickness > 30 mm |
|
|
restrictive cardiomyopathy pathophys
|
non-dilated ventricles with severe impairment of LV filling
diastolic function impaired with normal systolic function results in high LV filling pressures hard to differentiate from constrictive pericarditis |
|
|
major causes of restrictive cardiomyopathy
and what is the great thing about restrictive cardiomyopathy |
amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, fabry's disease
it's rare outside of the tropics |
|
|
clinical manifestations of restrictive cardiomyopathy
|
symptoms of right and left heart failure
- fatigue, dyspnea, peripheral edema |
|
|
management of restrictive cardiomyopathy
|
treat underlying cause
|

