![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are homologous chromosomes? |
same length carry genes that control the same inherited traits one from the mother, one from the father |
|
|
why are gametes produced |
to maintain the same number of chromosomes from gen to gen |
|
|
how many chromosomes do human body cells have |
46 total 23 from each parent |
|
|
how many chromosomes do human gametes contain |
23 |
|
|
cells with 'n' chromosomes |
haploid cell |
|
|
cell with '2n' chromosomes |
diploid cell |
|
|
what does meiosis produce |
gametes- when the gametes come together in fertilization, the number of chromosomes is restored |
|
|
phases(in order) |
interphase I prophase I metaphase I anaphase I telophase I prophase II metaphase II anaphase II telophase II cytokinesis |
|
|
interphase |
chromosomes replicate chromatin condenses |
|
|
prophase I |
pairing of same chromosomes spindles form nuclear membrane breaks down crossing over to exchange genetic info |
|
|
metaphase I |
chromosomes attach to spindle fibers homologous chromosomes line up in middle |
|
|
anaphase I |
homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell |
|
|
telophase I |
spindles break down chromosomes uncoil and form two nuclei cell divides |
|
|
prophase II |
spindle apparatus forms chromosomes condense |
|
|
metaphase II |
a haploid number of chromosomes line up at the equator |
|
|
anaphase II |
the sister chromatids are pulled at the centromere by spindle fibers and move towards opposite ends of the cell |
|
|
telophase II |
chromosomes reach poles nuclear membrane and nuclei reform |
|
|
cytokinesis |
results in four haploid cells, each with n number of chromosomes |
|
|
what are the results of meiosis |
four non identical haploid cells genetic variation |
|
|
variation |
depending on how chromosomes line up at equator, four gametes with four different chromosome combos can result also produced when gametes randomly combine during fertilization and during crossing over |
|
|
what is meiosis |
sexual reproduction in animals |
|
|
how many cromatids does a chromosome have |
two |
|
|
what is crossing over |
when chromosomal segments are exchanged between similar chromosomes (gene recombination) |
|
|
what part of the chromosome attaches to the spindle fibers |
the centromere |
|
|
how many sets of divisions does meiosis have |
two sets of divisions
|
|
|
what are gametes |
sex cells |
|
|
mitosis vs meiosis |
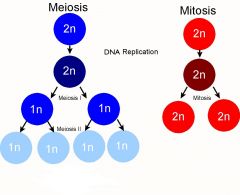
|

