![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Centromere
|
Region containing specific DNA sequences where the chromatic is attached most closely to its sister chromatid
|
|
|
Cebtriole
|
A structure in the centrosome of an animal cell composed of a cylinder of microtubules triplets arranges in a 9+0 pattern
|
|
|
Centrosome
|
A subcellular region containing material that functions throughout the cell cycle to organize the cell's microtubules
|
|
|
Kinetochore
|
A structure of proteins associated with specific sections of chromosomal DNA at each centrpmere
|
|
|
Chromatin
|
The entire complex of DNA and proteins that is the building material of chromosomes
|
|
|
Sister chromatids
|
Joined copies of the original chromosome.
|
|
|
Chromosome
|
Contain packaged DNA molecules
|
|
|
Locus
|
A gene's specific location along the length of a chromosome.
|
|
|
Homologous Chromosomes
|
2 chromosomes containing a pair that have the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern.
|
|
|
Tetrad
|
A group or set of four chromosomes
|
|
|
Somatic Cell
|
Body Cell
|
|
|
Gamete
|
Sperm and Eggs
|
|
|
Gonad
|
Ovaries or Testes
|
|
|
Fertilization
|
Fusion of 2 gametes together, returning chromosome number to 46
|
|
|
Sex Chromosomes
|
X or Y chromosomes
|
|
|
Autosomes
|
All chromosomes other than X and Y
|
|
|
Haploid
|
Cell with a single set of chromosomes. Has a haploid number -n
|
|
|
Diploid
|
A cell with 2 chromosomal sets. Represented by 2n, or the diploid number.
|
|
|
Synapsis
|
When paired homologs become physically connected to each other along their lengths by a zipper like protein structure
|
|
|
Crossing Over
|
A genetic rearrangement between non-sister chromatids involving the exchange of corresponding segments of DNA molecules
|
|
|
Chiasmata
|
The x shaped region on the homologous pair where crossing over has occurred
|
|
|
G1
|
1st gap: Synthesizes proteins and produces organelles
|
|
|
S phase
|
DNA synthesis, synthesizes proteins and produces organelles
|
|
|
G2
|
Synthesizes proteins and produces organelles
|
|
|
Density Dependent Inhibition
|
A phenomenon in which crowded cells stop dividing.
|
|
|
Restriction Point
|
In G1, it will tell the cell to continue with division or stop and go into G0 phase
|
|
|
G0 Phase
|
A nondividing state
|
|
|
Prophase of Mitosis
|
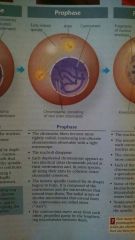
|
|
|
Prometaphase of Mitosis
|

|
|
|
Metaphase of Mitosis
|
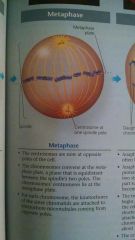
|
|
|
Anaphase of Mitosis
|
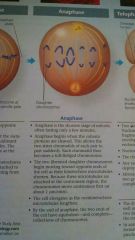
|
|
|
Interphase of Meiosis
|
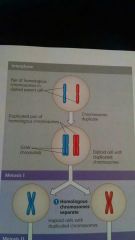
|
|
|
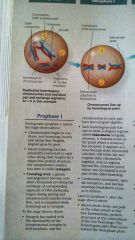
Prophase 1 of Meiosis
|
|
|
|
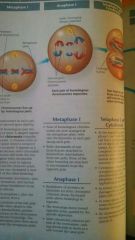
Anaphase 1 of Meiosis
|
|
|
|
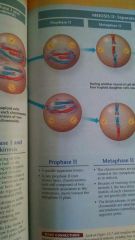
Prophase 2 of Meiosis
|
|
|
|
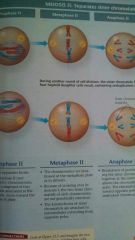
Metaphase 2 of Meiosis
|
|
|
|
Anaphase 2 of Meiosis
|
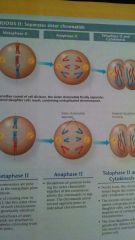
|
|
|
Differences
|

|
|
|
Karyotype
|
The human chromosomes paired and lined up in order
|
|
|
Cyclin
|
A protein that gets its name from its cyclically fluctuating concentration in the cell
|
|
|
MPF
|
Maturation promoting factor, it triggers the cell's passage past the G2 checkpoint into M phase
|

