![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the best street orientation in cool climates? |
Major streets should be oriented perpendicular to winter winds and street networks should use a discontinuous organization with many T-intersections to slow and block wind flow.
|
|
|
What do the lines indicate on a sunpath diagram?
|
Lines radiating from the center indicate azimuth.
Concentric lines indicate altitude. |
|
|
What is a Wind Rose?
|
A wind rose is used to characterize the direction, speed, and frequency of wind in a particular location by month and year.
Speed is measured in knots. |
|
|
What is a Wind Square? |
It gives more time-specific information than a Wind Rose.
It represents patterns of wind direction and speed by TIME of DAY and MONTH of YEAR for a specific location. |
|
|
Where is wind data determined? |
Wind data is typically taken at locat airports.
In relation to our location, we can comprehend this data by: 1. Wind tunnel simulation 2. Estimate wind direction and speed by using the following principles that govern air movement: A. Friction causes air velocity to be slower near the ground and faster away from the ground. B. Inertia causes air to continue moving the same direction when it meets an obstruction. C. Air flow from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. C.1. Air heated by solar radiation causes a reduction in its pressure (add Forest, Meadow, Forest sketch from Sun/Wind Notes, pp2) |
|
|
What are the Microclimate Phenomena on building sites?
|
1. Venturi effect: occurs when wind accelerates after its been constricted, such as between two buildings.
2. Window shadow: are low pressure eddy zones downwind from a building. 2a. Wind velocity increases: 2a.1. when the roof pitch increases. 2a.2. when building gets taller. 2a.3. when building gets longer. 2a.4. High pressure is on the windward side. 2a.5 Low pressure is on the leeward side. 3. Near bodies of water, breezes blow off water towards land during the day. This flow reverses at night. (Add sketch from Sun/Wind, pp3) |
|
|
How do you determine the best building location on site?
|
Base building citing on sun, wind, and shade and which of these is desirable for local climate region.
|
|
|
What do you analyze for a building site's microclimate?
|
1. Determine shadow patterns.
2. Determine wind flow 3. Convert shadow and wind data into a grid cell system (for example 6-9am, noon, 3pm) 4. Overlay the sun and wind conditions at each hour. 5. Assign numerical values to the combinations of conditions in each cell. 6. Overlay the hourly combination layers for each season; adding the three values of each cell. 7. The higher numbers will indicate the more favorable microclimate for each season. |
|
|
Daylighting.
What are typical sky conditions? |
1. Overcast: the sky is three times brighter at the ZENITH then at the horizon. Here, illumination evenly distributed and makes for a minimum design condition.
2. Clear sky: sky is three brighter at the HORIZON than the zenith. Illumination varies depending on POSITION OF THE SUN, SEASON, AND WATER VAPOR QUANTITY in the atmosphere. 3. Partly cloudy day: the most common condition |
|
|
Sunlight reflection: |
Sunlight reflected from the ground represents 10%-15% of the total illumination reaching a vertical window.
It can account for more than 50% when the window is shaded from direct radiation. |
|
|
Direct sunlight:
|
Is so powerful that it often causes unwanted glare and heat gain.
|
|
|
What is Daylight Factor (DF%)?
|
It is the percentage of exterior illumination available inside a building.
A. Based on window size, placement, sky obstructions, glazing transmission, and interior reflectances. B. It is determined by: required interior illum. / available exterior illum X 100% C. Window sizes can be determined once you know DF%. |
|
|
How many components does Daylight available to a building usually consider? |
Two:
A. Sky components (SC) B. External reflected component (ERC) that based on light bounced from ground and other surfaces outside the building. |
|
|
What four things does the Bioclimatic Chart presume? |
1. A 0.8 clo level (typical for winter clothing)
2. A 1.3 met activity level (slow walking/office work) 3. If temperature/humidity combination is above the shading line, shading is presumed. 4. If temperature/humidity combination is below wind line, then still air (wind blocked) is presumed. |
|
|
Three factors cause a building to change its internal microclimate, list them. |
1. Thermal lag of its material. (The time elapsing between the cause of a thermal phenomenon and the appearance of its effect. A material's thermal mass in terms of time. A material with high thermal mass (high heat capacity and low conductivity) will have a high thermal lag)
2. The controlled infiltration rate (the unintentional or accidental introduction of outside air into a building. volumetric flow rate of outside air into a building, typically in cubic feet per minute (CFMs)) 3. Latent heat (Two of the more common forms of latent heat (or enthalpies or energies) encountered are latent heat of fusion (melting) and latent heat of vaporization (boiling). These names describe the direction of energy flow when changing from one phase to the next: solid → liquid → gas. In both cases, the change is endothermic, (system absorbs energy on going from solid to liquid to gas. The change is exothermic (the process releases energy) for the opposite direction.) |
|
|
INTERIOR HEAT GAIN |
1. Age, sex, activity.
2. Most passive systems cannot remove moisture from the air. 3. Sensible heat gain: Occupant density of bldg. X rate of heat gain per person = total sensible heat gain from people. |
|
|
What factors determine the amount of heat generated by lights?
|
1. Illumination level of fixtures.
2. Efficiency of the light sources. |
|
|
What factors determine the amount of heat generated by equipment and applicances?
|
1. The type of equipment. |
|
|
What happens to the electrical energy that goes into equipment, such as motors?
|
The energy ends up as waste heat in the space.
|
|
|
What are some ways to reduce heat gain from hot water systems?
|
1. By insulating the hot water storage.
2. By using tankless, on-demand hot water heaters. (define) 3. By insulating hot water pipes. |
|
|
What is thermal resistance (R)?
|
1. It is the rate of heat flow through building material.
2. R-Value is °K m2/W 3. The ratio of the temperature difference across an insulator and the heat flux (heat flow per unit area, Qa) through it or R = Delta T / Qa. The bigger the number, the better the insulation's effectiveness. R-value is the reciprocal of U-value. 4. The number of hours needed for 1 Btu to flow through 1 s.f. of skin, given a temperature difference of 1 degree F. |
|
|
How does Earth Sheltering reduce heat loss/gain? |
1. By increasing the resistance of the envelope.
2. By reducing the temperature difference between inside and outside. |
|
|
What is Balance Point Temperature (Tb)?
|
It is the outdoor temparature at which a building changes from a need for cooling to a need for heating, or vice versa.
|
|
|
Why are cities windier than their surrounding countryside when regional wind climates are calm?
|
1. Because the Urban Heat Island Effect causes centripetal wind patterns moving from areas of low density to areas of high density.
2. Because cities produce and store more heat during the day and retain it longer, the city/county temperature differential increases. 3. As the warmer, polluted city air rises, it draws in cooler air from the surrounding areas or city perimeter. |
|
|
What two phenomena can be used to flush heat and pollution out of cities?
|
1. Surround the city perimeter with a band of undeveloped (preferrably vegetated) land.
2. Design the city with wide corridors to provide a pathway for the air to move from less dense areas to more dense areas. 2a. A system of linear greenways or boulevards with one or more centers can be implemented. 2b. Minimum 328 ft (100m) 2c. 40%-60% of the urban area to be cooled 2d. Include open spaces of 1300 ft x 1300 ft (400m x 400m) as a minimum. |
|
|
WIND:
Why is it better to locate undeveloped, vegetated areas on higher slopes? |
Because they can provide a cool air source to displace rising air in lower elevation developed areas. In addition, provide unobstructed dowhill corridodrs towards the high density areas.
|
|
|
CLIMATES:
What are the basis of design for building heights in hot arid climates? |
The street width proportions should be 4:1 or greater. These are used so buildings can shade each other and adjacent streets.
1. This creates an "urban canyon" which is a space formed by street and building walls. 1a. A North-South axis canyon is most beneficial. |
|
|
What are the four disadvantage of narrow streets in hot, arid climates?
|
1. They are associated with higher pollution concentrations.
2. More noise (sound vibrations increased). 3. Have lower wind speeds. 4. Radiant night sky cooling is less effective in these areas. |
|
|
What are some characteristicsof sites located near oceans and large lakes? |
1. They have less climate variation between day and night than inland sites.
2. They have less climate variation between summer and winter than inland sites. |
|
|
Regarding windward and leeward slopes, what is the diffence between a mountain verses a hill?
|
Mountains create wet windward slopes while hills create wet leeward slopes.
|
|
|
MICROCLIMATE: |
Cold region: low on a south-facing slope.
Temperate region: middle to upper part of the slope. Hot-arid: bottom of the slope on east orientation. Hot-humid: top of the slope on east orientation. |
|
|
What is solar envelope?
|
It defines the maximum buildable volume for a given site that will not shade adjacent sites.
|
|
|
What is Downwash Vortex Effect?
|
Turbulent wind spiral in an area of low pressure at the ground adjacent to a tall building. It occurs on the windward side.
|
|
|
What is the Corner Effect?
|
An increase in wind velocity created by wind moving aroud a building.
This effect worsens as building height increases and/or widens. |
|
|
Whais the Wake Effect?
|
Spiralling, erratic, upward wind flow creating turbulence on the leeward side.
|
|
|
WIND:
What is the Gap Effect? |
Zones of higher velocity in a passageway and the open space downwind under a tall slab building.
|
|
|
What is Comfort Parametr (Y)?
|
An indicator of comfort in relation to wind.
|
|
|
As it pertains to wind protection, what's the difference between tall and short buildings and narrow and wide streets?
|
For regular organization of buildings in an urban pattern, tall buildings on narrow streets yield the most wind protection, while shorter buildings on wider streets promote more air movement.
|
|
|
What the best major street orientation in cool climates?
|
Major streets should be oriented perpendicular to the winter winds and street networks should use a discontinuous organization with many T-intersections to slow and block wind flow.
|
|
|
What is the benefit of gradual height transitions of building groups sloped in the direction of prevailing winds?
|
It minimizes wind movement in the streets.
|
|
|
What is the benefit of increasing tree cover on a site?
|
A 25% increase in tree cover may result in a 17-57% savings in cooling energy due to the combined effect of shading and evapotranspiration.
|
|
|
What is evapotranspiration?
|
A term used to describe the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration from the Earth's land surface to atmosphere. Evaporation accounts for the movement of water to the air from sources such as the soil, canopy interception, and waterbodies. Transpiration accounts for the movement of water within a plant and the subsequent loss of water as vapor through stomata in its leaves. Evapotranspiration is an important part of the water cycle.
|
|
|
What is evapotranspiration? |

The combined processes of evaporation, sublimation, and transpiration of the water from the earth's surface into the atmosphere.
|
|
|
What is Migration?
|
It is the moving from one place to another to maintain thermal comfort.
Design should incorporate different zones that are comfortable under different climatic conditions. |
|
|
What is the advantage of clustered rooms? |
They reduce skin area which reduces heat gain and loss. |
|
|
Natural Ventilation: |
IBC states a minimum ventilation of 4% of the floor area. |
|
|
Define Azimuth. |
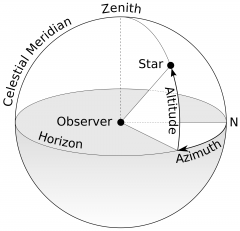
Azimuth is the angular distance along the horizon to the location of the object. |
|
|
Define Altitude. |
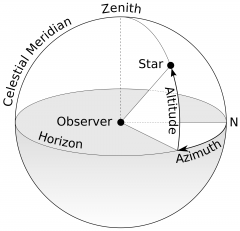
Altitude is the distance an object appears to be above the horizon. |

