![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
146 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Drugs that can cause pancreatitis
|
1. Furosemide, Thiazides
2. Sulfasalazine, 5-ASA 3. Azathioprine 4. Valproic acid 5. Didanosine, pentamidine (AIDS) 6. Metronidazole, tetracycline |
|
|
GI symptoms + pruritic papules/vesicles over extensor surfaces
|
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Associated with celiac! +anti-endomysial antibodies Risk of GI lymphomas |
|
|
Workup in newly diagnosed HIV patients (13)
|
1. H&P
2. Routine chem, hematology 3. 2 x plasma HIV RNA levels 4. CD4 count 5. VDRL for syphilis 6. Anti-toxoplasma antibody 7. PPD 8. MMSE 9. Pneumococcal vaccine (unless CD4 < 200) 10. Hep A, B serology 11. Hep A, B vaccine if negative 12. HIV counseling 13. Info, assistance for possible ppl infected by subject |
|
|
Triad of pericarditis
|
1. Pleuritic chest pain
2. Diffuse ST elevation on EKG (+/- PR depression) 3. Friction rub |
|
|
Signs of right-sided MI
|
1. Hypotension
2. Increased CVP 3. Clear lung fields 4. ST elevation in V4R --> Need to get right-sided EKG in anyone with inferior STEMI |
|
|
Dizziness + palpitations
Hx of illness with fever, myalgia Flat erythematous expanding rash |
Lyme carditis with associated AV block
|
|
|
Late complications following STEMI
|
1. VSD
2. Cardiogenic shock 3. Ventricular wall rupture 4. Mitral regurgitation 5. Thrombus (LV) |
|
|
Common acute life threatening reactions of HIV therapy
1. Didanosine 2. Abacavir 3. NRTIs 4. NNRTIs 5. Nevirapine |
1. Didanosine - Pancreatitis
2. Abacavir - hypersensitivity 3. NRTI - lactic acidosis 4. NNRTIs - steven's-johnson 5. Nevirapine - liver failure |
|
|
Common side effect of protease inhibitors
|
Precipitation in urine = crystals, urinary obstruction
--> monitor UA, Cr |
|
|
Diseases associated with vitiligo (hypopigmentation, well-circumscribed)
|
Autoimmune stuff
1. Pernicious anemia 2. Graves 3. Type I DM 4. Primary adrenal insufficiency 5. Hypopituitarism 6. Alopecia ariata |
|
|
Light's criteria for exudative fluid
|
1. Fluid/Serum protein > 0.5
2. Fluid/Serum LDH > 0.6 3. Pleural LDH > 2/3 normal serum LDH (90) = Pleural LDH > 60 |
|
|
Hallmark of ischemic hepatopathy
|
Huge jump in AST/ALT without accompanying jump in bili, alk phos
|
|
|
What do nitrites and leuk esterase on UA indicate?
|
Nitrites = enterobacteriaceae (convert urinary nitrates to nitrites)
Leuk esterase = pyuria |
|
|
Pickwickian syndrome (obesity hyperventilation syndrome)
|
1. Obesity
2. Hypoxia during sleep 3. Hypercapnia during day resulting from hypoventilation Distant heart sounds Low EKG voltage Crappy CXR quality Polycythemia 2/2 hypoventilation Respiratory acidosis |
|
|
Associated conditions with temporal arteritis
|
Polymyalgia rheumatica
Jaw claudication Aortic aneurysm Blindness |
|
|
3 main side effects of ACE inhibitors
|
Cough
Hyperkalemia Angioedema!! |
|
|
Otitis externa most common organisms
|
Pseudomonas!!
Rarely, S Aureus, aspergillus |
|
|
Side effects of EPO
|
HTN - 30%
HA - 15% Flu-like symptoms - 5% Red cell aplasia - rare |
|
|
Gout, Pseudogout
|
Gout
• Negatively birefringent • Tophi Pseudogout • Positively birefringent • Chondrocalcinosis |
|
|
1. Muddy brown casts
2. RBC casts 3. WBC casts 4. Fatty casts 5. Broad/waxy casts |
1. Muddy brown casts - ATN
2. RBC casts - glomerulonephritis 3. WBC casts - interstitial nephritis, pyelonephritis 4. Fatty casts - nephrotic syndrome 5. Broad/waxy casts - chronic renal failure |
|
|
Aspirin sensitivity syndrome
|
PSEUDO-allergic reaction
Persistent nasal blockage Episodes of bronchoconstriction Aspirin induces prostaglandin/leukotriene misbalance in some people Tx with avoiding NSAIDs, leukotriene receptor blockers |
|
|
Renal vein thrombosis is most commonly associated with which nephrotic syndrome?
|
Membranous glomerulonephritis
Also most common associated with carcinoma |
|
|
Prutitis with hot baths
- Dx? - Associated with which condition? |
Polycythema vera - release of histamine from increased number of circulating basophils
• Associated with gout! |
|
|
Causes of pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
6Hs, 6Ts |
H:
1. Hypovolemia 2. Hypoxia 3. H+ (acidosis) 4. Hypothermia 5. Hypoglycemia 6. Hypo/hyper kalemia T: 1. Tamponade 2. Tension PTX 3. Thrombosis (MI, PE) 4. Trauma 5. Toxins 6. Tablets (drugs) |
|
|
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) triad and pentad
|
1. Hemolytic anemia (indirect bilirubinemia)
2. Thrombocytopenia 3. Renal failure |
|
|
Osteomyelitis
- Most common bacterial cause? - Frequent cause with nail puncture (often through footwear)? |
1. Staph aureus
2. Pseudomonas! |
|
|
What two therapies shown to decrease mortality in COPD?
|
Home O2
Smoking cessation |
|
|
How does hereditary spherocytosis cause abdominal pain?
|
Chronic hemolysis --> pigmented (calcium bilirubinate) gallstones
|
|
|
Rank effectiveness of non-pharmacologic treatments on blood pressure
|
1. Weight loss to BMI < 25
2. DASH diet 3. Decrease dietary sodium 4. Exercise 5. Decrease alcohol intake |
|
|
Risk factors for pancreatic cancer
|
1. FH
2. Chronic pancreatitis <b>3. Smoking!!!!! </b> 4. DM 5. Obesity 6. High fat diet |
|
|
What happens to BP if you have HTN crisis from pheochromocytoma and you treat with propranolol?
|
BP will rapidly increase due to alpha activity!!!
Must give alpha + beta blockade! |
|
|
Thiazide effects on electrolytes and lipids and glucose
|
Hyponatremia
Hypokalemia HYPERcalcemia Decreased glucose tolerance (hyperglycemia) Increased TGs, LDL |
|
|
Causes of pulsus paradoxus
|
Cardiac tamponade
Tension pneumothorax Severe asthma |
|
|
Drugs causing agranulocytosis
|
PTU
Methimazole Procainamide Macrolides (-mycins) Chloramphenicol Clozapine Carbamazepine |
|
|
Pneumonia in ____, think:
• Alcoholics • Immigrants • Nursing home • HIV + • Organ transplant, renal failure, chronic lung disease |
• Alcoholics = Klebsiella
• Immigrants = TB • Nursing home = strep pneumo, pseudomonas • HIV + = PCP, TB, but common agent still more common • Organ transplant, renal failure, chronic lung disease = legionella |
|
|
Antipseudomonal antibiotics
|
1. Zosyn (piperacillin/tazobactam), ticarcillin, carbenicillin
2. Ceftazidime, cefepime 3. Imipenem/cilastatin 4. Aztreonam 5. Ciprofloxacin 6. Gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin |
|
|
What defines a complicated effusion and what do they require that uncomplicated ones dont?
|
1. Light's criteria for exudate
2. pH < 7.2 3. Glucose < 60 4. Positive gram stain/culture Requires chest tube drainage or VAS decortication |
|
|
FSGS is associated with:
|
1. AA
2. Obesity 3. Heroin 4. HIV |
|
|
1st line chemotherapy anti-emetic
|
Ondansetron (5HT3 antagonist)
|
|
|
Causes of bacterial endocarditis:
1. Pre-existing valvular disease 2. IV drug abuse 3. Colon cancer 4. Prosthetic valve |
1. Pre-existing valvular disease
• Viridans strep 2. IV drug abuse • S aureus • GNRs • Enterococcus 3. Colon cancer • Strep bovis 4. Prosthetic valve • Staph epidermidis |
|
|
Formula for corrected Ca level in patients with liver problems
|
Corrected Ca = 0.8(Δalbumin) + serum Ca level
|
|
|
Diagnosis not to miss with acute UC flare
diagnostic criteria |
Toxic megacolon
1. Colonic distension + 2. 3/4: • T > 38 • HR > 120 • WBC > 10.5K • Anemia + 3. 1/4: • Volume depletion • AMS • Electrolyte disturbances • Hypotension |
|
|
First-line DMARD for RA
(Second-line agents?) |
Methotrexate
Alternate 1st line (less effective) Hydroxychloroquine Sulfasalazine Etanercept Infliximab Adalimumab (Humira) Azathioprine |
|
|
Glomerular hematuria post URI in adult
1. < 5d after infx, normal serum complement 2. 10-21 days after infx, low serum complement |
IgA nephropathy
Post-infectious glomerulonephropathy |
|
|
Watershed areas of the colon and blood supply (2)
|
1. Splenic flexure - SMA terminal branches
2. Recto-sigmoid junction - IMA terminal branches |
|
|
3 mechanisms by which cancer can cause hypercalcemia
|
1. PTHrP
2. Osteolytic lesions 3. (ectopic?) Conversion of 25-vitD to 1,25-vitD |
|
|
Endocarditis HACEK organisms + treatment
|
Haemophilus
Actinobacillus Cardiobacterium Eikenella Kingella Ceftriaxone |
|
|
Tumor lysis syndrome electrolyte changes:
- K - PO4 - Ca - Uric acid |
- K increases
- PO4 increases Both are intracellular and released into serum - Ca decreases Binds to increased PO4 and intracellular products - Uric acid increases, result of degradation of cell proteins |
|
|
Causes of elevated BUN/Cr ratio
|
1. Prerenal disease
2. GI bleeding (urea from bacterial digestion of Hgb) 3. Steroids |
|
|
Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase (LAP)
|
Elevated in leukemoid reaction (infection)
Decreased in CML |
|
|
SLE diagnostic criteria
|
Need 4 of 11
1. Mucocutaneous (each counts as one) • Butterfly rash • Photosensitivity • Oral/nasopharyngeal ulcers • Discoid rash 2. Arthritis 3. Pleuritis, pericarditis 4. Hematologic (hemolytic anemia with ↑ retics and ↓ WBC, plts) 5. Renal disease - proteinuria, casts 6. CNS - seizures, psychosis 7. Immunologic - false (+) VDRL, ant-ds DNA, anti-Sm Ab 8. ANA (+) |
|
|
What Ab are seen in drug-induced lupus?
Common drugs? |
Anti-histone (100% of the time)
Chlorpromazine Hydralazine Isoniazid Procainamide Methyldopa |
|
|
Antibodies for scleroderma
1. General 2. Limited form 3. Diffuse form |
1. ANA (+ in >98%)
2. Anti-centromere (limited form) - 60-70% 3. Anti-topoisomerase I = anti-scl-70 - 30% OR anti-RNApol ab - 20-30% |
|
|
Sjogren's syndrome is associated with which cancer?
|
NHL
|
|
|
RA diagnostic criteria (5)
|
1. Inflammatory arthritis of 3 or more joints
2. Symptoms > 6 weeks 3. ↑ CRP and ESR 4. RF +, anti-citrullinated peptide Ab + 5. Radiographic changes (erosions, periarticular decalcification) |
|
|
Features of dermatomyositis
|
Gottron's papules
Heliotrope rash Shawl sign Perivascular/perimysial fibrosis |
|
|
Vaccines contraindicated in HIV patients
|
Live vaccines:
MMR (OK if CD4 > 200) Oral polio Yellow fever BCG Typhoid Varicella |
|
|
Approach to metabolic alkalosis
|
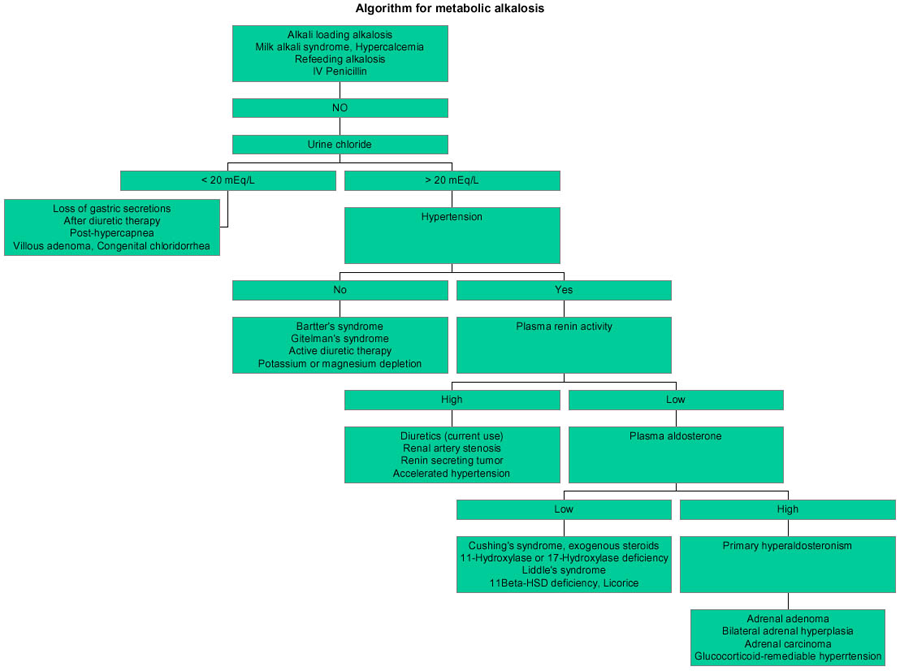
1. Chloride sensitive
• Urine Cl < 20 • Signs of volume depletion --> kidneys hold on to NaCl, mineralocorticoid effect causes ↑ K secretion - Diuretics - Loss of gastric secretions (e.g. vomiting) 2. Chloride resistant • Urine Cl > 20 - Barterr's, Gitelman's - Diuretics - RAA problem - Hyperadrenalism (cushings, aldo) |
|
|
What is the Somogyi effect?
|
Nocturnal hypoglycemia (often caused by high evening doses of insulin) that result in morning HYPERglycemia 2/2 response of increased hormone secretion (epi, NE, glucagon)
|
|
|
Contraindications to nitrates in the setting of MI
|
1. Aortic stenosis (may lead to 4)
2. PDE inhibitor use 3. RV infarction (decreases preload, exacerbates "RHF" symptoms) 4. Hypotension |
|
|
Sacroiliitis
|
Think ankylosing spondylitis
|
|
|
Centrilobular vs panlobular emphysema
|
Centrilobular - smokers
Panlobular - A1AT deficiency |
|
|
Hepatolenticular degeneration
|
= Wilson's disease
|
|
|
Causes of
Monoarthritis Polyarthritis Migratory arthritis |
1. Mono
• Septic • Gout, pseudogout • Trauma • Hemarthrosis 2. Poly - Infectious • GC • Meningococcal • Lyme • Rheumatic fever • Bacterial endocarditis • Parvovirus B19 • Rubella - Inflammatory • RA, JRA • SLE • ReA, psoriatic arthritis • Sarcoid 3. Migratory • Rheumatic fever • GC • Early Lyme |
|
|
MPGN pathology
|
Dense C3 deposits caused by IgG anti-C3 convertase
|
|
|
Cause and Treatment of mucormycosis
|
Rhizopus
Amphotericin B |
|
|
Why does pernicious anemia lead to increased risk of gastric cancer?
|
Chronic atrophic gastritis as a result of pernicious anemia leads to increased risk
|
|
|
Fever
Rash Lymphadenopathy Arthritis |
Rubella!
|
|
|
Effect of quitting smoking on COPD prognosis
|
Quitting smoking changes rate of deterioration to approach that of nonsmoker
|
|
|
Guidelines for O2 therapy for COPD (4)
|
1. PaO2 ≤ 55
2. SpO2 ≤ 88% 3. Hct ≥ 55% 4. Cor pulmonale |
|
|
Ventilation vs. oxygenation
- How to decrease PCO2 vs PO2 |
↓ PCO2:
• ↑ RR or tidal volume ↓ PO2: • ↓ FiO2 or PEEP |
|
|
Modified Wells' criteria (7)
|
3 pts
1. Symptoms/signs of DVT 2. Alternative dx less likely than PE 1.5 pts 3. HR > 100 4. Immobilization/surgery in prev 4 weeks 5. Previous DVT/PE 1 pt 6. Hemoptysis 7. Malignancy |
|
|
Patients with carcinoid syndrome are at risk of which vitamin/mineral deficiency? Mechanism?
|
Niacin
Tumor produces serotonin, uses up tryptophan which is also used in niacin synthesis |
|
|
Test for cystine stones
|
Urinary cyanide nitroprusside test
|
|
|
Fever, malaise, headache, myalgias, nausea, vomiting
No rash Tick bite 1. Dx 2. Lab findings? 3. Tx |
Ehrlichiosis
"spotless Rocky Mountain spotted fever" Leukopenia +/- thrombocytopenia Elevated LFTs Doxycycline |
|
|
Hemochromatosis vs Sarcoidosis vs Amyloidosis
|
All 3 are restrictive cardiomyopathies
Hemochromatosis • Bronze skin • Pancreatic dysfunction (DM) • Hepatomegaly • <b>Increased risk of listeria infections</b> Sarcoidosis • AAs • b/l hilar adenopathy, erythema nodosum Amyloidosis • Proteinuria (kidney deposits) • Easy bruising (liver deposits) |
|
|
Fomepizole
|
alcohol dehydrogenase inhibitor
Used in alcohol or ethylene glycol poisoning |
|
|
CMV retinitis
- Presentation - Treatment HSV retinitis |
CMV:
- Yellow/white patches of retinal opacification with retinal hemorrhages - Ganciclovir vs foscarnet *HIV patients with CD4 < 50 HSV: - Pale peripheral lesions with necrosis of retina - Keratitis, conjunctivitis, rapid vision loss |
|
|
1. Gilbert
2. Crigler-Najjar type I and II 3. Dubin-Johnson 4. Rotor |
1. Gilbert
• ↓ UDP-glucoronyltransferase = ↓ bilirubin uptake • ↑ indirect bilirubin (unconjugated) • No hemolysis • Jaundice provoked by triggers (stress, fasting, illness) 2. Crigler-Najjar type I and II • Type I - absent UDP-glucuronyltransferase = die early in life • Type II - less severe, responds to phenobarb (↑ liver enzyme synthesis) 3. Dubin-Johnson • Defective excretion = direct (conjugated) bilirubinemia • BLACK LIVER 4. Rotor • Dubin-Johnson without black liver and milder symptoms |
|
|
CHA<sub>2</sub>DS<sub>2</sub>-VASc
|
CHF
HTN Age (> 75 = 2, > 65 = 1) DM Stroke = 2 Vascular dz = 1 Sex female = 1 |
|
|
Causes of ESR > 100
|
1. PMR
2. Endocarditis 3. Paraproteinemia 4. Miliary TB 5. Osteomyelitis |
|
|
Symptoms of hypercalcemia vs hypocalcemia
|
1. HYPERcalcemia
- Groans = constipation - Moans = fatigue, lethargy, depression - Bones = bone pain - Stones = kidney stones - can't pick up the Phone = weakness, loss of coordination 2. HYPOcalcemia: CATS go numb - Convulsions - Arrhythmias - Tetany (Trousseau - main d'accoucheur, Chvostek - cheek) - Spasms, seizures, stridor - Numbness in fingers |
|
|
Pt presents with severe flank pain. KUB negative but small stone in ureter on U/S. Urine pH 4.5, no bacteria, etc.
Dx, Tx |
Differential for no stones on KUB:
1. Radiolucent (uric acid) stones 2. Small calcium stones 3. Non-stone obstruction (clot, tumor) --> Uric acid stone Tx: alkalinization with potassium citrate (Urocit-K) |
|
|
Bacillary angiomatosis
1. Who does it affect? 2. What bacteriae? 3. Symptoms 4. Tx |
Affects immunocompromised pts
Bartonella henselae or quintana Fever, wt loss, malaise, abdominal pain Skin + visceral lesions - large pedunculated exophytic papule, angioma-like Tx: erythromycin |
|
|
Alcohol as risk factor for gout - mechanism?
|
Ethanol metabolized to lactate and competes with urate for renal excretion = urate accumulation
|
|
|
DDx solid liver lesion
|
1. Hemangioma
2. Focal nodular hyperplasia • Non-malignant, not vascular • Bx: sinusoids, Kupffer cells 3. Hepatic adenoma • OCPs 4. Metastatic cancer 5. HCC • Hep B/C, Cirrhosis • AFP |
|
|
What is contraction alkalosis?
|
Volume-depleted state = ↑ renin/ATII/aldo
Angiotensin: • ↑ Na/H exchange in proximal tubule = ↑ HCO3 reabsorption Aldosterone • ↑ H+ secretion at distal tubule + increased HCO3 generation as a result • Hypokalemia |
|
|
Most common cause of mitral regurgitation
|
MVP
|
|
|
Approach to acetaminophen toxicity
|
< 4 hours: activated charcoal
4 hours: plasma acetaminophen level - Decide to administer N-acetylcysteine based on result |
|
|
Indications for hemodialysis
|
AEIOU
Acidosis (refractory metabolic) Electrolytes Intoxication Overload (refractory to diuretics) Uremic pericarditis |
|
|
Management of sciatica-type acute back pain
|
1. No neurologic deficit - NSAIDs and early mobilization
2. MRI, CT if neurologic deficit, perianal loss of sensation, etc. to rule out cauda equina syndrome • Also if 4-6 weeks of conservative therapy doesn't help |
|
|
Most common thyroid nodule
Cancer? |
Colloid nodule
Papillary |
|
|
Triad of disseminated gonococcal infection
|
1. Polyarthralgias
2. Tenosynovitis 3. Vesicopustular skin lesions |
|
|
ARDS criteria
|
1. Acute onset of respiratory distress in the setting of predisposing condition (e.g. sepsis, PNA, ...)
2. PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 200 3. b/l infiltrates on CXR 4. Normal PCWP |
|
|
Best test for chronic pancreatitis
|
Stool elastase
Diagnoses malabsorption 2/2 pancreatic exocrine failure |
|
|
Hyperglycemia extremes and AMS in DM I vs II
|
1. DM-I = DKA
2. DM-II = nonketotic hyperosmolar syndrome • Type II DM has enough insulin to prevent ketosis but not hyperglycemia |
|
|
Most common cause of death in dialysis patients
|
CV disease
|
|
|
Hydrogen breath test used for diagnosis of:
|
Bacterial overgrowth
Lactose intolerance |
|
|
GERD, ↓ LES sphincter tone, absent peristaltic waves in lower 2/3 of esophagus
|
Scleroderma
|
|
|
Anatomic causes of HOCM (2)
|
1. Septal hypertrophy
2. Systolic anterior motion (SAM) of mitral valve |
|
|
DC cardioversion vs pharmacotherapy for Afib
|
DC cardioversion more successful in pts who are hemodynamically unstable
|
|
|
First-line treatments for uncomplicated cystitis (2)
Complicated cystitis (1) |
Bactrim
Nitrofurantoin (Macrobid) Fluoroquinolone |
|
|
Chronic headaches and painless hematuria
|
Renal papillary necrosis 2/2 analgesic overuse (nephropathy)
• Chronic tubulointerstitial damage |
|
|
Pneumocystis pneumonia
1. CD4 count 2. Triad of sx 3. CXR 4. Misc (2) 5. Tx |
1. CD4 count
• < 200 2. Triad of sx • Fever • SOB • Dry cough (nonproductive) 3. CXR • Bilateral insterstitial infiltrates 4. Misc (2) • Hypoxia out of proportion to CXR • ↑ serum LDH 5. Tx • Bactrim • Steroids if PaO2 < 70 or A-a gradient > 35 |
|
|
Which hyperthyroid disease is most likely to result in hypothyroidism s/p radioactive iodine ablation? Why?
|
Graves' disease
Entire thyroid gland is hyperfunctional, so it is all more likely to absorb iodine |
|
|
Dietary recommendations for patients with renal stones (4)
|
1. ↓ protein and oxalate
2. ↓ sodium 3. ↑ fluid intake 4. ↑ calcium!!! |
|
|
Target cells
|
Think thalassemia
|
|
|
Thalassemia vs Fe-deficiency anemia
|
Fe-deficiency:
• ↑ RDW • Abnormal iron studies • Responds to Fe • Normal electrophoresis Thalassemia: • Hct > 30% <b>• Target cells</b> • Normal iron studies • Does not respond to Fe • Electrophoresis normal (α) vs elevated HbA2 (β) |
|
|
How does lactulose work to reduce ammonia?
What should be done for non-responders? |
Bacteria action on lactulose acidifies colonic contents
= ammonia --> ammonium (non-absorbable) Ornithine-aspartate infusion PO sodium benzoate Neomycin |
|
|
Calcineurin inhibitors toxicities (7)
Cyclosporin vs. Tacrolimus |
1. Nephrotoxicity
2. Neurotoxicity 3. HTN 4. Glucose intolerance 5. Infection 6. CA - SCC skin, lymphoproliferative 7. GI symptoms Cyclosporin also has gingival hyperplasia and hirsutism |
|
|
Azathioprine toxicities (3)
|
1. Dose-related diarrhea
2. Leukopenia 3. Hepatoxicity |
|
|
Mycophenolate toxicity
|
bone Marrow suppression
|
|
|
Describe the rash of secondary syphilis.
|
Starts on trunk, extends to periphery, including palms and soles.
Non-pruritic maculopapular rash |
|
|
What causes increased tactile fremitus?
|
Consolidation (PNA)
|
|
|
SAAG calculation and abnormal?
|
Serum albumin - ascites albumin
≥ 1.1 highly accurate in transudative process |
|
|
Concentric hypertrophy
Eccentric hypertrophy Dilated ventricles |
Concentric hypertrophy - chronic pressure overload
- Sarcomeres added in parallel Eccentric hypertrophy - chronic volume overload - Sarcomeres added in series Dilated ventricles - dilated cardiomyopathy (infx, toxins, metabolic...) - ALCOHOL! |
|
|
Corrected equation for anion gap for albumin
|
Corrected AG = calc AG + 2.5 (4-alb)
= AG + 10 - 2.5 (albumin) |
|
|
Signs pointing to legionella pneumonia
|
le<b>GI</b>o<b>Na</b>lLa
1. GI symptoms 2. Hyponatremia 3. Abnormal LFTs CMV also has lung + intestinal involvement |
|
|
Most frequent cause of traveler's diarrhea?
|
ETEC
|
|
|
Hashimoto's - at risk for developing ____
|
Thyroid lymphoma (60x risk!!)
|
|
|
Advanced sleep phase vs delayed sleep phase
|
Advanced = fall asleep early (7pm), can't stay up socially
Delayed = fall asleep late (2am), tired in AM |
|
|
SIRS criteria
|
≥ 2 meets criteria
1. T > 38<sup>o</sup> C (=100.4 F) or T < 36<sup>o</sup> C (= 96.8 F) 2. HR > 90 3. RR > 20 or PaCO2 < 32 mm Hg 4. WBC > 12,000 OR WBC < 4,000 OR > 10% bands |
|
|
Interpret Weber and Rinne tests
|
1. If Rinne is abnormal = conduction deficit
• If Weber localizes to same side as Rinne = exclusively conduction • If Weber localizes to opposite side = mixed 2. If Rinne is normal = sensorineural hearing loss • Weber localizes to <b>contralateral</b> side |
|
|
What common dietary thing will increase INR in patients on coumadin?
|
Vitamin E!
|
|
|
Fever phases in different types of malaria
|
1. P vivax, P. ovale = q 48 hrs
2. P malariae = q 72 hrs 3. P falciparum - No periodicity - Cold phase, hot phase, sweating and loss of fever |
|
|
De Quervain tenosynovitis
Tendons affected? |
Mothers who hold their infants with thumb outstretched (abducted)
Abductor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis brevis |
|
|
Hypercalcemia due to immobilization
|
Increased osteoclastic bone resorption
Tx with bisphosphonates |
|
|
Conn syndrome
|
Hypertension
HyperNa HypoK Metabolic ALKALOSIS |
|
|
What is the hallmark of ventricular aneurysm on EKG?
|
Persistent ST elevation (~1mo out post-MI)
|
|
|
Criteria to diagnose diabetes
|
1. 2 x fasting plasma glucose > 126
2. Random glucose > 200 with symptoms of DM 3. OGTT > 200 |
|
|
Elevated ACTH and elevated cortisol, suppression with high dose dexamethasone but not low dose
|
Suggests pituitary microadenoma producing Cushings
Ectopic ACTH would not suppress |
|
|
Most common extra-articular complication of ankylosing spondylitis?
|
Anterior uveitis
|
|
|
Risk of radioactive iodine treatment
|
Kills the thyroid cells = release of thyroid hormone, may precipitate Afib in pts with CV disease, elderly
Do PTU/methimazole first to deplete thyroid stores |
|
|
Characteristics of erisypelas and causative organism
|
Well-demarcated, raised, erythematous, edematous, tender skin lesion with raised borders
Febrile Caused by Group A strep (S. pyogenes) |
|
|
TCA overdose symptoms and treatment
|
Anticholinergic:
• Dilated pupils • Hypoactive bowel sounds • Hypotension • CNS depression • Hyperthermia • Prolonged QRS Sodium bicarbonate - improves BP and prevents arrhythmia by increasing extracellular Na concentrations |
|
|
Smudge cells, lymphocytosis, elderly
|
CLL
|
|
|
Causes of high-output heart failure
|
AVF (congenital vs acquired)
Thyrotoxicosis Pagets Thiamine deficiency |
|
|
Screening guidelines for AAA
|
All men 65-75 who have ever smoked
Abdominal U/S |
|
|
Most common association with DIC
|
Gram negative sepsis (e.g. 2/2 pyelo)
|
|
|
When does odds ratio (in case control studies) approach relative risk?
|
When prevalence is LOW
|
|
|
Increase marker cutoff effect on Sp, Sn
Increase Sp or increase Sn effect PPV, NPV |
Increase marker = increase Sp, decrease Sn
Increase Sp = Increase PPV (r/i) Increase Sn = Increase NPV (r/o) |
|
|
Treatment for dermatitis herpetiformis
|
Dapsone
|
|
|
Causes of erythema nodosum
|
Recent strep infection
Sarcoidosis TB Histoplasmosis IBD |
|
|
MCP, PIP, DIP for RA vs OA
|
RA: MCP, PIP
OA: PIP, DIP |
|
|
Osmolal gap formula
|
2Na + glucose/18 + BUN/2.8
|
|
|
One of leading causes of death on polymyositis/dermatomyositis
|
pHTN from interstitial lung disease
|

