![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
148 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
cephal/o |
Head |
|
|
-oma |
Tumor;mass;fluid collection |
|
|
albin/o |
White |
|
|
-osis |
Condition (usually abnormal) |
|
|
trans- |
Across;through |
|
|
carp/o |
Wrist bones |
|
|
-dynia |
Pain |
|
|
ferrum- |
Iron |
|
|
ad- |
Toward |
|
|
contra- |
Against;opposite |
|
|
post- |
After;behind |
|
|
heter/o |
Different |
|
|
-plegia |
Paralysis;palsy |
|
|
necr/o |
Death |
|
|
-brady |
Slow |
|
|
kines- |
Movement |
|
|
brachi/o |
Arm |
|
|
-itis |
Inflammation |
|
|
crypt/o |
Hidden |
|
|
-cide |
Killing |
|
|
bucc/o |
Cheek |
|
|
-edema |
Swelling |
|
|
cyan/o |
Blue |
|
|
rhin/o |
Nose |
|
|
-tripsy |
Crushing |
|
|
lith/o |
Stone |
|
|
-ac, -al, -ic, -ary, -ical, an |
Pertaining to |
|
|
hepat/o |
Liver |
|
|
erythr/o |
Red |
|
|
cardi/o |
Heart |
|
|
ventr/o |
Belly side of body |
|
|
neur/o |
Nerve |
|
|
-poiesis |
Formation |
|
|
jaund/o |
Yellow |
|
|
-emesis |
Vomiting |
|
|
cyte/o |
Cell |
|
|
leuk/o |
White |
|
|
gastr/o |
Stomach |
|
|
-rrhage |
Bursting forth (of blood) |
|
|
caus- |
Burn |
|
|
multi- |
Many |
|
|
morph- |
Shape;form |
|
|
lingu/o |
Tounge |
|
|
melan/o |
Black |
|
|
oste/o |
Bone |
|
|
gingiv/o |
Gum |
|
|
tachy- |
Fast |
|
|
auto- |
Self;own |
|
|
endo- |
In;within |
|
|
neo- |
New |
|
|
pseud/o |
False |
|
|
-pathy |
Disease |
|
|
-centesis |
Surgical puncture to remove fluid |
|
|
enter/o |
Intestines (usually small intestines) |
|
|
-algia |
Pain |
|
|
-ectomy |
Removal;excision;resection |
|
|
myel/o |
Spinal cord/bone marrow |
|
|
cervic/o |
Neck |
|
|
ab- |
Away from |
|
|
hemi- |
Half |
|
|
kerat/o |
Cornea;hard;horny tissue |
|
|
thyr/o |
Thyroid gland |
|
|
infra- |
Below;beneath |
|
|
esthes- |
Feeling (nervous sensation) |
|
|
poli/o |
Grey matter |
|
|
myx/o |
Mucus |
|
|
Diffusion |
Movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration |
|
|
Facilitated diffusion |
Diffusion assisted by specialized proteins who are basically the body guards who decide what enters and what doesn't. |
|
|
Osmosis |
Net movement of water over a semi permeable membrane. Water will always go where there is more solute. If there is an equal amount of solute in and outside the cell, the cell remains isotonic. If there is more solute in a cell than outside, water will go into the cell to try and dilute it causing the cell to basically explode. This is called hypotonic. When there is more solute outside the cell than inside the cell, the water from the cell moves out to dilute the solvent, causing the cell to implode. This is called hypertonic. |
|
|
Filtration |
Movement of solvents and disolved substances across membranes by gravity/pressure. Similar to the way a strainer works. |
|
|
Dialysis |
The separation of large molecules from small by diffusion across a semi permeable membrane. |
|
|
Active transport |
Across plasma membrane usually involving proteins from low concentration to high concentration. |
|
|
arthr/o |
Joint |
|
|
Phagocytosis |
Cell eating. The act of eating. |
|
|
Pinocytosis |
Cell drinking. The act of drinking. |
|
|
-sepsis |
Infection |
|
|
Characteristics of living matter |
Eat, excrete, have sex (procreate) |
|
|
Metabolism |
meta- : to change |
|
|
Anabolism |
ana-: building up |
|
|
Catabolism |
cata-: to throw/breakdown |
|
|
Anatomy |
The study of body structure and it's parts |
|
|
Physiology |
Study of of the normal functions of an organism. |
|
|
Pathology |
The study of disease and it's causes |
|
|
Emryology |
The study of origin and development |
|
|
Histology |
The study of tissue and it's components |
|
|
Biology |
The study of all life forms |
|
|
Cell/Plasma membrane |
Semi-permeable membrane that separates the organelles from the external environment. Made up of a phospho-lipid bi-layer and contains proteins. |
|
|
Cytoplasm. |
Surrounds the organelles located between the plasma membrane and the nucleus. Provides shape for the cell and is where chemical reactions occur. |
|
|
Nucleus |
Control center of the cell. Contains heredity, controls cell structure and controls many cellular activities. |
|
|
Nucleoli |
Made up of protein, DNA, RNA. Only active during cell division. |
|
|
Ribosome's |
Contains RNA and makes protein. Can be free or attatched to the endoplasmic reticulum. |
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum |
Makes fat, carbohydrates and protein. Mechanical support and distribution of cytoplasm and provides surface area for chemical reactions. |
|
|
Golgi Apparatus |
Looks like a pile of stacked dishes. Processes, sorts, packages and delivers protein to different parts of the cell. |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Power house of the cell. Provides surface area for cellular respiration, are self replicating. They respond to increased energy requirements. |
|
|
Lysosomes |
Have digestive enzymes which perform phagocytic actions of eating anything that might be harmful to the cell. They are formed by Golgi apparatus. Responsible for cell digestion and destruction. |
|
|
Flagella |
Whip like organelle that is used to move the cell. Bacterial flagella rotates like screws and eukaryotic flagella whips back and forth. |
|
|
Cilia |
Motile cilum beats in one direction to project the cell. Non-motile cilium can not beat and usually serves as a sensor. |
|
|
Vacuole |
Is the garbage collector. They capture food or unwanted debris or any substance that might be toxic or unwanted from the cell. |
|
|
Chromosome |
Continuous piece of DNA that contains many genes. Is found in the nucleus and has two arms. |
|
|
Chromatin |
Contains DNA and will coil into chromosomes during cell division. |
|
|
DNA |
Deoxyribonucleic Acid. Determines heredity. |
|
|
RNA |
Ribonucleic acid. Contains proteins... |
|
|
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum |
The smooth part of ER creates fats, carbs and protein. |
|
|
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum |
Rough ER creates protein. |
|
|
Mitosis |
Direct copy of each other. PMAT Interphase: in between phases when nothing is occuring Prophase: chromosomes prepare, nucleus dissappears. Chromosomes duplicate right before Metaphase. Metaphase: chromosomes line up in the middle and spindle fibers attach. Anaphase: chromosomes are pulled apart to their poles Telophase: a nuclear membrane is created and pinches apart in the center to create two cells. |
|
|
Meiosis |
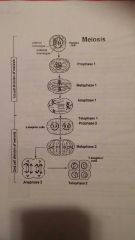
A cycle. Prophase1: chromosomes duplicate and stay close and coil Metaphase1: coiled chromosomes go to center Anaphase1: pull apart from the middle with each chromosome now being different with having exchanged different information Telophase1: two daughter cells are now formed, each with one chromosome of the homologous pair Metaphase2: chromosomes align at the center Anaphase2: they divide each going to a separate pole Telophase2: cells divide by pinching apart. 4 daughter cells are now created |
|
|
Prefix |
Usually appears at the beginning of a word. Will change the meaning of the word. |
|
|
Root |
The basic meaning of the word. Words may contain more than one roof and roots can stand alone. |
|
|
Combining vowel |
A vowel that is used to link a root to a suffix or another root that begins with a consonant. Is used to help with pronunciation. |
|
|
Combining form |
Root with a combining vowel. Usually displayed with a slash between them. |
|
|
Compound words |
Words that contain more than one root. |
|
|
Suffix |
Follows the root word and changes the meaning of the root. |
|
|
Splenomegaly |
Enlargement of the spleen. |
|
|
Optic |
Pertaining to the eye;vision |
|
|
Melena |
Black tarry feces that contain digested blood |
|
|
Hepatitis |
Inflammation of the liver |
|
|
Adipose |
Pertaining to fat cells or tissues |
|
|
Hyaline |
Glassy and translucent;cartilage in between ball joints and hinge joints etc |
|
|
Cardiomyopathy |
Disease of the heart muscle |
|
|
Cardiovascular |
Blood vessels of the heart and it's system. |
|
|
Gastroenteritis |
Inflammation of the stomach and intestines |
|
|
Epithelial Tissue |
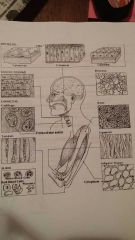
Covering for external & internal body structures. Protects and absorbs important substances back into the body and secretion glands secrete hormones. Necessary body function. Endothelial tissue lines things. Endo=inside Mesothelial tissue covers serious membranous structures. Pleura (products the lungs) Pericardium (sac of fluid surrounding the heart) Peritonitis? TYPES Simple: one layer Stratified: many layered Pseudo stratified: Pseudo/o=false Have one layer but appears to have more Squamous: flat, scale-like appearance Columnar: resemble columns Transitional: found only in the urinary tract, change appearance according to its environment. Have the ability to stretch.
Covering of all body surfaces Line body cavities and hollow organs Is the major tissue in glands Function: protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, diffusion, sensory reception Simple=1 layer Simple cuboidal epithelium found in glandular tissue and in kidney tubules Simple columnar epithelium lines stomach and intestines Pseudostratified columnar epithelium lines parts of the respitory tract and some tubes in make reproductive tract Transitional epithelium found mostly in the bladder Glandular epithelium produces and secretes substances
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Functions: -binds structures together -supports body and organs -stores fat -transports substances -helps repair tissue damage Types: Loose/areolar: connects skin, organs and coverings Adipose: fat that ortects and supports organs and stores minerals and vitamins Dense fibrous: in ligaments and tendons Elastic: in arteries and some glands, sphincters, etc Cartilage: such as hyaline. Found at end of long bone during joint movement Osseous: bone Blood |
|
|
Muscle tissue |
Made of cells that shorten or contract in order to have movement. Produce heat. -are long and slender -arranged in bundles or layers that are surrounded by connective tissue Types: Skeletal: striped and attached to skeleton. If you can move it, it is skeletal muscle. Voluntary control. Cylindrical Smooth: has a single centrally located nucleus. Lacks situations. Involuntary control. Eg) iris Cardiac: the heart. Branching fibers. One nucleus per cell. Striations. Involuntary control.
|
|
|
Nervous tissue |
found in brain, spinal cord, nerves. Controls body activities such as: muscle contraction, awareness of the environment (feeling), emtions and memory. The cells (neurons) communicate by using electrical nerve impulses. Neuron has 3 parts: Dendrites- conducts impulse toward the body of a nerve cell Cell body- directs the impulses and has does general functions Axon- conducts impulses away from the cell body
Nervous tissue also has cells that don't transmit impulses. They support activities of the neurons. Glial cells: bind and insulate neurons |
|
|
Cranial vault |
Contains brain, sinuses etc. Protected by the skull. |
|
|
Thoracic cavity |
Contains lungs, heart, blood vessels, trachea etc. |
|
|
Cranial |
Toward the head |
|
|
Caudal |
Toward the tail |
|
|
Rostral |
Within the head toward the muzzle |
|
|
Medial |
Toward the midline |
|
|
Lateral |
Outward toward the side |
|
|
Dorsal |
Toward the back |
|
|
Ventral |
Toward the belly |
|
|
Proximal |
Near to the point of attachment |
|
|
Distal |
Further from the point of attachment |
|
|
Palmer |
Caudal surface of the forelimb below the carpus. The surface of the front paw. |
|
|
Planter |
Caudal surface of the hind limb below the tarsus. Surface of back paw. |
|
|
Internal |
Inside |
|
|
External |
Outside |
|
|
Dorsal plane |
Separates the back and the belly. Like a sandwich. |
|
|
Median plane |
Separates the body into right and left equal sides |
|
|
Sagittal plane |
Separates the body into right and left unequal sides |
|
|
Transverse plane |
Separates the the head half of the body from the rear half of the body. |
|
|
Recumbent |
Lying down |
|
|
Ventrally/sternally recumbent |
Lying down on the belly or breastbone. Also called prone. |
|
|
Dorsally recumbent |
Lying down on the back. Also called supine. |
|
|
Latterally recumbent |
Lying in the side. Right/left |

