![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
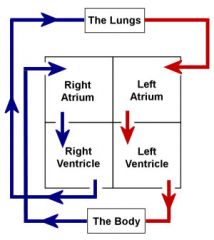
Heart’s Blood Flow
|
|
|
|
Ventricles |
Two lower chambers of the heart that pump blood out of the heart. The walls of the chambers, and particularly the walls of the left ventricle, are far more heavily muscled than the walls of the atria. |
|
|
Right Ventricle |
Receives blood from the right atrium, opens into the pulmonary artery, which transports blood to the lung. |
|
|
Left Ventricle |
Hardest working chamber in the heart, receives blood from the left atrium, opens into the aorta disseminating oxygen-rich blood to the tissues through the circulatory system. |
|
|
Atria |
Upper chamber of the heart that receives blood into the heart and drives it into a ventricle. |
|
|
Right Atrium |
Receives from the veins blood low in oxygen and high in carbon dioxide; this blood is transferred to the right ventricle and is pumped to the lungs. |
|
|
Left Atrium |
Receives from the lungs blood high in oxygen and low in carbon dioxide; this blood flows into the left ventricle and is pumped through the arteries to the tissues. |
|
|
Pulmonary Vein |
Vessel through which oxygenated blood is returned to the heart from the lungs. |
|
|
Lungs |
Right lung has 3 lobes, left lung has 2. |
|
|
Diaphragm |
Dome-shaped, muscular and membranous structure that separates the thoracic (chest) and abdominal cavities. It is the principal muscle of respiration. Flattens (contracts) during inspiration. Also important in expulsive actions—e.g., coughing, sneezing, vomiting, crying, and expelling feces, urine, and, in parturition, a fetus. |
|
|
Peristalsis |
A series of wave-like muscle contractions thatmoves food to different processing stations in the digestive tract. The processof peristalsis begins in the esophagus when a bolus of foodis swallowed. |
|
|
Small Intestine flow of nutrients |
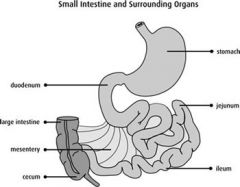
Duodenum → Jejunum → Ileum |
|
|
Large Intestine flow of nutrients |
Cecum → Ascending Colon (right side of body) →Transverse Colon → (Left Splenic Flexure) → Descending Colon (left side of body) → (Sigmoid Flexure) → Sigmoid Colon → Rectum |
|
|
Peritonitis |
Inflammation of the membrane lining the abdominal cavity and covering the abdominal organs. |
|
|
Hemodialysis |
Removal of waste products from the blood. |
|
|
Adrenal Gland |
Also called suprarenal gland; located on the superior surface of the kidney; consists of two parts: an inner medulla, which produces epinephrine and norepinephrine (adrenaline and noradrenaline), and an outer cortex, which produces steroid hormones. |
|
|
Trochanter |
A broad, flat process on the femur, at the upper end of its lateral surface (greater trochanter), or a short conical process on the posterior border of the base of its neck (lesser trochanter). |
|
|
Medulla Oblongata |
Lowest part of the brain and the lowest portion of the brain stem, connected by the pons to the mid brain and is continuous posteriorly with the spinal cord, controls blood pressure, heart rate and respiration. |
|
|
Meningioma |
Tumor of the meninges. |
|
|
Meninges (singular meninx) |
Three membranous envelopes (pia mater, arachnoid, and dura mater) that surround the brain and spinal cord. |
|
|
Neurolysis |
Destruction of a nerve or nervous tissue. |
|
|
Lacrimal Sac (Dacrocyst) |
The upper dilated end of the nasolacrimal duct, and is lodged in a deep groove formed by the lacrimal bone and frontal process of the maxilla. Receives tears from the lacrimal ducts and carries to the nasal cavity. |
|
|
Dacryocystectomy |
Excision of the lacrimal sac. |
|
|
Gonioscopy |
Examination of the anterior chamber of the eye. |
|
|
Polysomnography |
A diagnostic tool in sleep medicine. |
|
|
Thyrotoxicosis |
Also called Hyperthyroidism, a condition where the thyroid is overactive. Most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves disease. |
|
|
Psoriasis |
A chronic condition characterized by red, dry, elevated lesions, covered by silvery scales. |
|
|
Stratum Germinativum |
Deepest layer of epidermis, lies on top of the dermis and has access to a rich supply of blood. |
|
|
Superficial Fascia |
The thin layer of loose fatty connective tissue underlying the dermis and anchoring the skin to the underlying musculature,protecting underlying structures, preventing loss of body heat, included in thehypodermis. |
|
|
Primigravida |
Describes a woman in her first pregnancy. |
|
|
Vernix Caseosa |
A white cheese-like substance covering the lanugo (downy hair covering the body) of a fetus. |
|
|
Colostrum |
A form of milk produced the first few days after giving birth. |
|
|
Cowper’s Gland |
Also called Bulbourethral gland. Either of two pea-shaped glands in the male, located beneath the prostate gland at the beginning of the internal portion of the penis; they add fluids to semen during the process of ejaculation to lubricate the urethra. |
|
|
Bartholin's Gland |
Found on either side of the introitus, part of the external female genitalia |
|
|
Tympanic Membrane |
Also called eardrum, separates the external ear from the middle ear, receives sound vibrations from the outer air and transmits them to the auditory ossicles, which are tiny bones in the tympanic (middle ear) cavity. |
|
|
Rinne Test |
Test measuring hearing using bone conduction and air conduction. |
|
|
Body Cavities |
Cranial, Spinal, Thoracic, Abdominal, Pelvic |
|
|
Membranes |
Mucous, Serous, Synovial, Meninges, Cutaneous |
|
|
Urinary System |
Main function - Production of urine for excretion of metabolic wastes, along with fluid and electrolyte balance. |
|
|
Musculoskeletal System |
System of muscles, joints, tendons, andligaments providing movement, form, strength, and protection. |
|
|
Lymphatic System |
Comprised of lymph vessels and lymph nodes.Collects excess fluid from the interstitial spaces and returns it to the heart,operating through a series of one-way valves without a pump. |
|
|
Nervous System |
Network of nerve fibers traversing the human body, composed of central(brain and spinal cord) and peripheral portions. Regulates body functions andprovides an internal method of communication between the brain and other organs, and between the organism and its environment. |

