![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
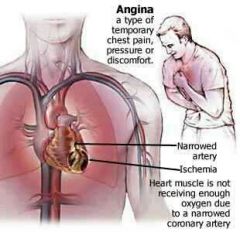
Angina |
Chest pain from myocardial ischemia |
Myocardial ischemicheart disease - heart problems caused by narrowed heart arteries. When arteries are narrowed, less blood and oxygen reaches the heart muscle |
|
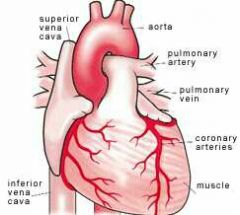
Aorta |
Largest artery in the body |
|
|
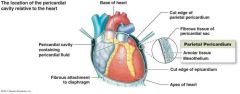
Apex (of the heart) |
Tip of the heart located at the interior aspect of the heart |
|
|
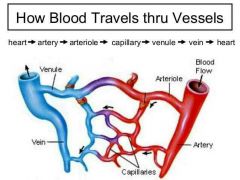
Arteriole |
Small artery |
|
|
|
Artery |
Blood vessel carrying blood away from the heart |
A: away and artery |
|
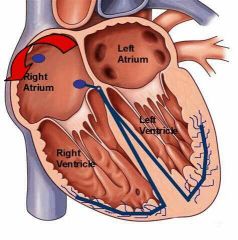
Atrium, Atria |
The upper chambers of the heart |
|
|
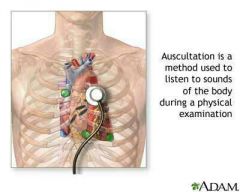
Auscultation |
Listening for sounds in the body structures like blood vessels, the heart, or the lungs, typically using a stethoscope |
|
|
|
Capillary |
Smallest blood vessel; substances can pass into and out of the blood through capillary walls |
|
|
|
Cardiac arrest |
Sudden, unexpected stoppage of heart action, often leading to sudden cardiac death |
|
|
|
Coronary artery |
Blood vessel supplying the heart muscle itself with blood |
|
|
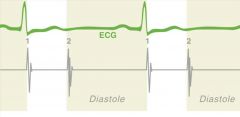
Diastole |
The resting, expanding, and filling phase of the heartbeat |
Gr. Diastole: dilation |
|
|
Electrocardiogram |
Record of the electrical activity of the heart |
|
|
|
Embolus (emboli) |
Clot or other substance that travels and can block a blood vessel |
|
|
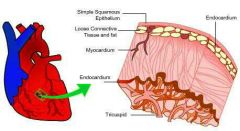
Endocardium |
Inner lining of the heart |
|
|
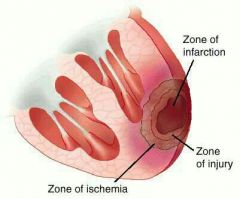
Infarcation |
Area of dead tissue |
|
|
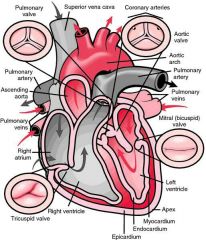
Mitral valve (bicuspid valve) |
Valve between the left atrium and left ventricle |
Bi- two Cuspidus: point, pointy end - refers to teeth Bicuspid: two teeth |
|
|
Murmur |
Abnormal heart sound caused by improper closure of heart valves |
|
|
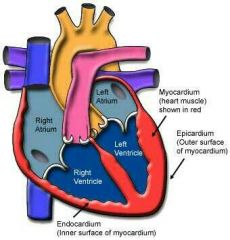
Myocardium |
Muscular middle layer of the heart |
|
|
|
Palpitations |
perceptible forcible pulsation of the heart, usually with an increase in frequency or force, with or without irregularity un rhythm |
Palpitare: to throb, to flutter, to tremble, to quiver |
|
|
Patent |
Open |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Double - layered membrane surrounding the heart |
Peri- around |
|
|
Petechiae |
Small, pinpoint hemorrhages |
|
|
|
Pulmonary artery |
Artery carrying deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs |
|
|
|
Pulmonary vein |
2 pairs of veins carrying oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart |
|
|
|
Pulse |
A heartbeat felt through the walls of the arteries |
|
|
|
Septum (septa) |
Partition or wall between 2 cavities such as between the atria or between the ventricles |
L. saeptum: enclosure, fence, partition |
|
|
Sphygmomanometer |
Instrument to measure blood pressure |
|
|
|
Systole |
Active, contracting, pumping phase of the heartbeat |
|
|
|
Tricuspid valve |
Valve between the right atrium and right ventricle |
Tri- three |
|
|
Valve |
Structure in veins or the heart that can open and close to allow blood to flow in one direction |
|
|
|
Vein |
Vessel that carries blood back to the heart; veins contain valves |
|
|
|
Vena cava |
Largest vein in the body |
|
|
|
Ventricle |
The lower chambers of the heart |
|
|
|
Venule |
A small vein |
|

