![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ageusia
|
losss of taste
|
|
|
onychomycosis
|
a fungal infectin of the nails usually caused by tinea species and occasionally
thickening, scaling and discoloration of the nailbed. |
|
|
rhinitis
|
inflammation of the nasal mucous membranes
resulting in runny nose, nasal congestion and or postnasal drainage |
|
|
coryza
|
catarrh
an acute inflammation of the nasal mucosa accompanied by profuse nasal discharge |
|
|
acute rhinitis
|
acute nasal congestion with increased mucus secretion. It is the usual manifestation of the common cold
|
|
|
ehinorrhagia
|
epistaxis
|
|
|
salpingitis
|
inflammation of a fallopian tube
usually because of an STD |
|
|
odyno-
|
pain
|
|
|
rhinorrhea
|
thin watery discharge from the nose
|
|
|
pyuria
|
pus in urine
|
|
|
salpingo
|
tube
|
|
|
dyspareunia
|
pain in the labia, vagina or pelvis during or after sexual intercourse
b/c of infect in the reproductive tract, inadequate vaginal lubrication uterine myomata, endometriosis vaginal foreign body psychosomatic isorder atrophy |
|
|
gustatory rhinorrhea
|
a flow of thin watery material from the nsoe while one is eating
|
|
|
odynophagia
|
pain with swallowing
|
|
|
anosmia
|
loss of smell
|
|
|
parotitis
|
inflammation of the parotid gland
|
|
|
swimmer's ear
|
otitis externa
|
|
|
cholesteatoma
|
epidermal inclusion cyst formation in the middle ear and mastoid cavity
|
|
|
adnexa
|
accessory parts of a structure
namely to the uterus ovaries uterine (fallopian) tube |
|
|
odynophagia
|
pain upon swallowing
|
|
|
trismus
|
spasm of the masticatory musles and difficulty opening the mouth
|
|
|
quinsy
|
peritonsillar abscess formation
peritonsillitis may lead to quinsy |
|
|
supple
|
flexible
|
|
|
exudate
|
any fluid released from the body with a high concentration of protein, cells, or solid debris
|
|
|
Exudates may be classified as?
|
fibrinous
hemorrhagic diphtheritic purulent serous |
|
|
coryza
|
acute rhinitis
|
|
|
empyema
|
collection of pus in a body cavity esp the pleural space
it is usually caused by the local spread of infection from pneumonia or lung abscess |
|
|
transudate
|
Transudate is extravascular fluid with low protein content and a low specific gravity (< 1.012). Transudates are caused by disturbances of hydrostatic or colloid osmotic pressure, not by inflammation. They have a low protein content in comparison to exudates. Medical distinction between transudates and exudates is through the measurement of the specific gravity of extracted fluid. Specific gravity is used to measure the protein content of the fluid. The higher the specific gravity, the greater the likelihood of capillary permeability changes in relation to body cavities. For example, the specific gravity of the transudate is usually less than 1.012
|
|
|
hematochezia
|

passage of bright red blood
|
|
|
epididymis
|

where sperm is stored
|
|
|
melena
|

Black tarry stool
Bleeding originating from the lower GI tract melena usually occurs if the source of bleeding is above the ligament of Treitz |
|
|
dysarthrosis
|
joint malformation or deformity
|
|
|
suppurative
|
Purulent or suppurative exudate consists of plasma with both active and dead neutrophils, fibrinogen, and necrotic parenchymal cells. This kind of exudate is consistent with more severe infections, and is commonly referred to as pus.
|
|
|
Catarrhal exudate
|
Catarrhal exudate is seen in the nose and throat and is characterized by a high content of mucus.
|
|
|
testicular torsion
|
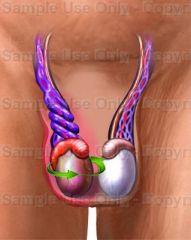
is the twisting of the spermatic cord, which cuts
off the blood supply to the testicle and surrounding structures within the scrotum. |
|
|
dysarthria
|
is a motor speech disorder resulting from neurological injury, characterized by poor articulation
|
|
|
proptosis
|
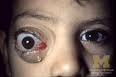
is a condition resulting in forward displacement and entrapment of the eye from behind by the eyelids. The condition is also known as eye dislocation and eye luxation
|
|
|
aphasia
|
a disorder of the content of speech
|
|
|
hyphema
|
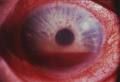
is blood in the front area of the eye
|
|
|
chalazion
|
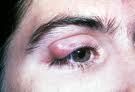
chronic granulomatous inflammation of the meibomian gland
cha-LAY-zee-yon). A chalazion is very different from a stye and is not an infection. It is instead a firm, round, smooth, painless bump usually some distance from the edge of the lid. A chalazion is a local tissue reaction to oily glandular secretions that were unable to reach the lid surface because the duct was blocked by debris. |
|
|
blepharitis
|
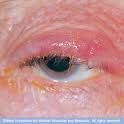
inflammation of the eyelids, causes itching and crusing of the lash line and is usually bilateral
|
|
|
hordeolum
|
stye
Styes are usually caused by staphylococcal bacteria, which often live right on the skin surface. Part of NF. When the conditions are just right the bacteria feast on dead cells and other debris, resulting in the tender pimple |
|
|
ephiphora
|
excessive production of tears
|
|
|
dacryocystitis
|
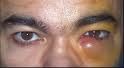
dacryocystitis is an infection of the nasolacrimal sac, frequently caused by nasolacrimal duct obstruction. It causes pain, redness, and swelling over the inner aspect of the lower eyelid and epiphora.
|
|
|
What is a chalazion caused by?
|
A chalazion is caused by blockage of tiny ducts in the eyelid glands that normally transport an oily substance. This oily material (sebum) is the layer of the tear film that reduces tear evaporation. Trapped or misplaced oil stimulates the immune system to clean up the mess. Chalazia develop over weeks to months.
|
|
|
What does photophobia usually indicate?
|
Light bothers eyes
Ocular inflammation or irritation |
|
|
Uveitis definition?
another name? |
Uveitis is swelling and irritation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye. The uvea provides most of the blood supply to the retina.
Iritis |
|
|
chemosis
|
swelling of the conjunctiva
fluid can accumulate beneath the lossely attached bulbar conjunctive, causeing it to balloon away from the globe usually with bacterial conjunctivitis |
|
|
p 61
|
dains
|
|
|
entropion
|
lid turned inward
uni or bilateral? |
|
|
apraxia
|
loss of ability to perform a learned motor task, usually the result of a lesion in the dominant inferior parietal lobe. Hemispatial neglect results from a lesion in the right parietal lobe.
|
|
|
dysarthria
|
speech articulation disturbance. Pt can write a sentence, but can't easily speak it.
|
|
|
agnosia
|
inability to recognize a sensory stimulus despite intact sensory function. Lesions responsible usually in the occipitiotemporal lobe.
|
|
|
photospia
|
seeing sparks or stars or wavy bright lights
|
|
|
Festinating gait
|
(Parkinsonian Gait)
Presentation Pt moves with short, jerky steps; hurried; has difficulty starting, but also has difficulty stopping after starting. This is due to muscle hypertonicity |

