![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Chromatin |
Structural component of nucleus, composed of nucleic acid and proteins |
|
|
Chromosome |
Threadless structures w/in nucleus composed of DNA that carries heriditary info encoded in genes |
|
|
Deoxyribonucleic acid |
Molecule that holds genetic info capable of replicating and producing an exact copy whenever a cell divides |
|
|
Diaphram |
Muscular wall that divides the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
Metabolism |
Sum of all physical and chemical changes that take place in a cell or organism |
|
|
Organelle |
Cell structure that provides a specialized function such as nucleus reproduction, ribosome (protein synthesis), golgi apparatus (removal of material from cell wall) and lysosomes (digestion) |
|
|
Histology |
Stuff of tissues |
|
|
Epithelial tissue |
Covers surface of organs, lines cavities and canals, forms tube and ducts, provides secreting portions of glands, and makes up the epidermis of skin |
|
|
Anatomical position |
Is a body posture used to locate anatomical parts or divisions |
|
|
Midsagittal |
Median |
|
|
Coronal |
Frontal |
|
|
Transverse |
Horizontal |
|
|
Dorsal |
Posterior, cranial and spinal cavities |
|
|
Ventral |
Thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities |
|
|
Body cavities |
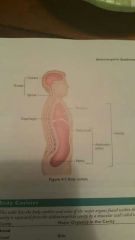
|
|
|
Abdominal pelvic regions |
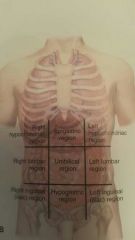
|
|
|
Directional terms |

|
|
|
Idiopathic |
Disease who's cause is unknown |
|
|
Sequelae |
Some diseases, injuries, or treatments cause complications that arise directly from disease, injury or treatment |
|
|
Adhesion |
Abnormal fibrous band that holds or binds together tissues that are normally separated |
|
|
Ascies |
Abnormal accumulation of fluid in abdominal cavity |
|
|
Edema |
Abnormal accumulation of fluid within tissue spaces |
|
|
Ferbilw |
Pertaining to a fever, also called pyretic |
|
|
Gangrene |
Death and decay of soft tissue, usually caused by circulatory obstruction, trauma, or infection |
|
|
Hernia |
Protrusion of any organ through the structure that normally contains it |
|
|
Inflammation |
Body defense against injury, infection, or allergy marked by redness, swelling, heat, pain, and sometimes, loss of function |
|
|
Mycosis |
Any fungal infection in or on the body |
|
|
Perforation |
Hole that completely penatrates a structure |
|
|
Peritonitis |
Inflammation of the peritoneum, the serous membrane that surrounds the abdominal cavity and covers it's organs |
|
|
Rupture |
Sudden breaking or bursting of a structure or organ |
|
|
Sepsis |
Pathological state, usually febrile, resulting from the presences of microorganisms or their products in the bloodstream |
|
|
Suppuration |
Producing or associated with generation of pus |
|
|
Infusion therapy |
Delivery of fluids directly into the bloodstream via a vein for treating various disorders; also called IV therapy |
|
|
Ablation |
Removal of part, pathway, or function by survey, chemical destruction, electrocautery, freezing or radio frequency |
|
|
Anastomosis |
Surgical joining of two ducts, vessels.2or bowel segments to allow flown from on to another |
|
|
Cauterize |
Destruction of tissue by electricity, freezing, heat, or corrosive Chemicals |
|
|
Curettage |
Scraping of of a body cavity with a spoon-shaped instrument called a curette |
|
|
Incision and drainage |
Incision made to allow the free flow or with drawl of fluids from a would or a cavity |
|
|
Laser surgery |
Use of a high intensity laser light beam to remove diseased tissues, stop bleeding blood vessels , or cosmetic purposes |
|
|
Resection |
Removal of part or all of a stucture, organ, or tissue |
|
|
Revision |
Surgical procedure used to replace or compensate for a previously implanted device or a correct an undesirable result of result of effect of previous surgery |
|
|
Inspection |
Sequence of procedures designed to evaluate the health of patient |
|
|
Palpatation |
Gentle application of the hands to a specific structure or body area to determine size , consistency, texture, symmetry, and tenderness of underlying structure |
|
|
Percussion |
Tapping a structure with the hand or fingers to assess consistency and the presence or absence of fluids within the underlying structure |
|
|
Ausculation |
Listening to the heart, bowel, and lungs with or without a stethoscope to assess the presences and quality of sound |
|
|
Endoscopy |
Visual examination of a body cavity or canal using a specialized lighted instrument called an endoscope |
|
|
Blood chemistry analysis |
Laboratory test, usually performed on serum, to evaluate various substances to determine whether they fall within a normal range |
|
|
Complete blood count (CBC) |
Panel of blood tests used as a broad screening test for anemias, infections, and other diseases |
|
|
Organ-disease panels |
Series of blood tests used to evaluate a specific organ (liver panel) or disease (anemia panel) |
|
|
Computed tomography |
Imaging technique in which an x-ray emitter rotates around the area to be scanned and a computer measures the intensity of transmitted x-rays from different angles; formerly called computerized axial tomography |
|
|
Fluoroscopy |
Technique in which x-rays are directed through the body to a floured entry screen that displays internal structures in continuous motion |
|
|
Magnetic resonance imagining (MRI) |
technique that uses radio waves and a strong magnetic field, rather than an x-ray beam, to produce highly detailed, multiple narrow, cross-sectional views of soft tissue |
|
|
Nuclear scan |
Technique in which a radioactive material (radiopharmaceutical) called a tracer is introduced into the body (inhaled, ingested, or injected) and a specialized camera (gamma camera) is used to produce images or organs and structures |
|
|
Positron emission tomography (PET) |
Computed tomography records the position (positive charged particles) emitted from a radiopharmaceutical to produce a cross-sectional image of metabolic activity of body tissues to determine the presence of disease |
|
|
Radiography |
Technique in which x-ray are passed through the body or area and captured on a film to generate an image; also called an x-ray |
|
|
Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) |
Radiological technique that integrates computed technology (CT) and a radioactive material (tracer) injected into the bloodstream to visualize blood flow to tissues and organs |
|
|
Ultrasonography (US) |
High-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) are directed at soft tissue and reflected as "echoes" to produce an image on a monitor of an internal body structure; also called ultrasound, sonography, and echo |
|
|
Biopsy (bx) |
Removal of a representative tissue sample from a body site for microscopic examination, usually to establish a diagnosis |
|
|
Excisional |
Biopsy in which the entire lesion is removed |
|
|
Incisional |
Biopsy in which only a small sample of the lesion is removed |

